
Getting Started With JBoss ESB
JBESB-GS-

Legal Notices
The information contained in this documentation is subject to change without notice.
JBoss Inc. makes no warranty of any kind with regard to this material, including, but not limited to, the implied warranties of merchantability and fitness for a particular purpose. JBoss Inc. shall not be liable for errors contained herein or for incidental or consequential damages in connection with the furnishing, performance, or use of this material.
Java™ and J2EE is a U.S. trademark of Sun Microsystems, Inc. Microsoft® and Windows NT® are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation. Oracle® is a registered U.S. trademark and Oracle9™, Oracle9 Server™ Oracle9 Enterprise Edition™ are trademarks of Oracle Corporation. Unix is used here as a generic term covering all versions of the UNIX® operating system. UNIX is a registered trademark in the United States and other countries, licensed exclusively through X/Open Company Limited.
Copyright
JBoss, Home of Professional Open Source Copyright 2006, JBoss Inc., and individual contributors as indicated by the @authors tag. All rights reserved.
See the copyright.txt in the distribution for a full listing of individual contributors. This copyrighted material is made available to anyone wishing to use, modify, copy, or redistribute it subject to the terms and conditions of the GNU General Public License, v. 2.0. This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT A WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
See the GNU General Public License for more details. You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License, v. 2.0 along with this distribution; if not, write to the Free Software Foundation, Inc., 51 Franklin Street, Fifth Floor, Boston, MA 02110-1301, USA.
Software Version
JBoss ESB 4.0 GA
Restricted Rights Legend
Use, duplication, or disclosure is subject to restrictions as set forth in contract subdivision (c)(1)(ii) of the Rights in Technical Data and Computer Software clause 52.227-FAR14.
©
Copyright
Contents
Contents iv
About This Guide 5
What This Guide Contains 5
Audience 5
Prerequisites 5
Organization 5
Documentation Conventions 6
Additional Documentation 7
Contacting Us 7
Getting Started 8
Four Simple Steps to get up and running. 9
The Hello World QuickStart 9
Components of the QuickStart 11
ESB Aware and Unaware Messages 12
QuickStart Sequence of Events 13
TrailBlazer 14
Overview 14
About This Guide
The goal of this document is assist you in getting up and running with test applications on JBossESB as quickly as possible.
This guide is anyone who is responsible for using JBoss ESB 4.0 GA installations and wants to know how to install and use it.
None.
This guide contains the following chapter:
Chapter 1, Installation: This chapter reviews prerequisites (software needed to operate JBossESB), downloading JBossESB, and building JbossESB.
Chapter 2, Trailblazer: A quick summary of the trailblazer example.
|
Convention |
Description |
|
Italic |
In paragraph text, italic identifies the titles of documents that are being referenced. When used in conjunction with the Code text described below, italics identify a variable that should be replaced by the user with an actual value. |
|
Bold |
Emphasizes items of particular importance. |
|
Code |
Text that represents programming code. |
|
Function | Function |
A path to a function or dialog box within an interface. For example, “Select File | Open.” indicates that you should select the Open function from the File menu. |
|
( ) and | |
Parentheses enclose optional items in command syntax. The vertical bar separates syntax items in a list of choices. For example, any of the following three items can be entered in this syntax: persistPolicy (Never | OnTimer | OnUpdate | NoMoreOftenThan) |
|
Note: |
A note highlights important supplemental information. A caution highlights procedures or information that is necessary to avoid damage to equipment, damage to software, loss of data, or invalid test results. |
The following conventions are used in this guide:
Table 1 Formatting Conventions
In addition to this guide, the following guides are available in the JBoss ESB 4.0 GA documentation set:
JBoss ESB 4.0 GA Trailblazer Guide: Provides guidance for using the trailblazer example.
JBoss ESB 4.0 GA Administration Guide: How to manage the ESB.
JBoss ESB 4.0 GA Programmers Guide: How to use JBossESB.
JBoss ESB 4.0 GA Release Notes: Information on the differences between this release and previous releases.
JBoss ESB 4.0 GA Services Guides: Various documents related to the services available with the ESB.
Questions or comments about JBoss ESB 4.0 GA should be directed to our support team.
Chapter 1
Getting Started
After downloading and expanding the JBoss ESB 4.0 Release Candidate distribution, you should have the following file structure.
|-- docs | |-- config | `-- services |-- install | |-- conf | |-- data | |-- deploy | |-- jUDDI-registry | `-- message-store |-- javadocs |-- lib |-- samples | |-- docs | |-- quickstarts | | |-- helloworld | | |-- helloworld_action | | |-- helloworld_embedded_reg | | |-- more_action | | |-- simple_cbr | | `-- simple_transformation | `-- trailblazer | |-- banks | |-- client | |-- docs | |-- esb | |-- loanbroker | `-- template |-- tools | `-- console `-- xml
The quickest way to get started using JBoss ESB is through running one of the quickstarts in the samples/quickstarts folder. This will also perform a basic validation of your system. Before doing this however, be sure to check that your system meets the following minimum requirements:
JDK 5 (v1.5.0_06 recommended)
Ant (v1.6.5 recommended)
JBoss Application Server v4.0.5
There are three ways to run the ESB. You can deploy it to JBossAS, to Tomcat, or run it in standalone mode. In any case you have to copy the 'deployment.properties-example' to 'deployment.properties, and you may have to edit the properties set in this file. This document assumes you have ant (1.6.5 or higher) and java5 installed on your machine, and that you have a fresh copy of jboss 4.0.x. So now go and download the JBossESB 4.0RC1 distribution from http://labs.jboss.com/portal/jbossesb/downloads
Edit your version of the deployment.properties. Open this file and edit the following lines if needed:
# application server root directory
org.jboss.esb.appserver.home=/jboss-4.0.5.GA
# the instance of jboss you are running (default)
org.jboss.esb.appserver.config=default
#the place where the jboss libraries can be found
# Note: You should not need to change this entry unless you altered
# the jbossesb distribution directory structure
org.jboss.esb.dist.lib=../lib
Run 'ant'. This will deploy the esb to your jboss AS instance. It copies the jbossesb.sar and jbossesb-dependencies.sar directories into your deploy directory.
You can deploy custom code (actions) by deploying the jar to the jbossesb.sar directory.
Start your appserver and see:
11:42:24,640 INFO [ConfigurationControllerService] starting message configuration controller with config file jbossesb.xml
11:42:24,671 INFO [ConfigurationController] loading configuration..
11:42:24,843 INFO [ParamFileRepository] Setting parameter repository root dir to [C:\cygwin\home\kstam\apps\jboss-4.0.4.GA\jbossesb\bin\.].
11:42:26,640 INFO [Generator] Serializing ESB Aware Listener 'ConfigTree' configuration to [C:\jboss-4.0.5.GA\server\default\conf\jbossesb-listener.xml].
11:42:26,656 INFO [Generator] Serializing ESB Gateway 'ConfigTree' configuration to [C:\jboss-4.0.5.GA\server\default\conf\jbossesb-gateway.xml].
11:42:26,656 INFO [ConfigurationController] Parameter reload completed.
11:42:26,687 INFO [ConfigurationController] Configuration Controller instance started.
11:42:27,078 INFO [ConnectionFactoryBindingService] Bound ConnectionManager 'jboss.jca:service=ConnectionFactoryBinding,name=JmsXA' to JNDI name 'java:JmsXA'
11:42:27,218 INFO [TomcatDeployer] deploy, ctxPath=/jmx-console, warUrl=.../deploy/jmx-console.war/
11:42:28,109 INFO [Server] JBoss (MX MicroKernel) [4.0.5.GA (build: CVSTag=Branch_4_0 date=200610162339)] Started in 32s:500ms
Edit your version of the deployment.properties. Open this file and edit the following line if needed ######################################################################
# Tomcat
######################################################################
# jbossesb tomcat home directory
org.jboss.esb.tomcat.home=/apache-tomcat-5.5.20
Run 'ant tomcat'. This will deploy the esb to your tomcat instance. It creates a jbossesb.war deploy directory in your tomcat.home/webapps directory.
Follow the steps in the tomcat/README.txt if you do not yet have a juddi database. Note that the JBossAS deploy comes with a preconfigured hsqldb.
You can deploy custom code (actions) by deploying the jar to the tomcat.home/webapps/jbossesb/WEB-INF/lib directory
Start tomcat and see:
12:12:20,875 INFO [ParamFileRepository] Setting parameter repository root dir t
o [C:\apache-tomcat-5.5.20\bin\.].
12:12:21,546 INFO [Generator] Serializing ESB Aware Listener 'ConfigTree' confi
guration to [C:\apache-tomcat-5.5.20\conf\jbossesb-listener.xml].
12:12:21,578 INFO [Generator] Serializing ESB Gateway 'ConfigTree' configuratio
n to [C:\apache-tomcat-5.5.20\conf\jbossesb-gateway.xml].
12:12:21,578 INFO [ConfigurationController] Parameter reload completed.
12:12:21,593 INFO [ConfigurationController] Configuration Controller instance s
tarted.
Jan 30, 2007 12:12:22 PM org.apache.coyote.http11.Http11BaseProtocol start
INFO: Starting Coyote HTTP/1.1 on http-8080
Jan 30, 2007 12:12:22 PM org.apache.jk.common.ChannelSocket init
INFO: JK: ajp13 listening on /0.0.0.0:8009
Jan 30, 2007 12:12:22 PM org.apache.jk.server.JkMain start
INFO: Jk running ID=0 time=0/31 config=null
Jan 30, 2007 12:12:22 PM org.apache.catalina.storeconfig.StoreLoader load
INFO: Find registry server-registry.xml at classpath resource
Jan 30, 2007 12:12:22 PM org.apache.catalina.startup.Catalina start
INFO: Server startup in 2813 ms
Edit your version of the deployment.properties. Open this file and edit the following line if needed
######################################################################
# Standalone launcher
######################################################################
# jbossesb standalone home directory
org.jboss.esb.standalone.home=/jbossesb-4.0.GA
Follow the steps in the launcher/README.txt if you do not yet have a juddi database. Note that the JBossAS deploy comes with a preconfigured hsqldb.
Run 'ant launcher'. This will create a /jbossesb-4.0.GA directory.
You can deploy custom code (actions), by deploying the jar to the /jbossesb-4.0.GA/lib directory
In the /jbossesb-4.0.GA/bin directory start the esb with either the run.sh or run.bat script and see:
Reading config from C:\jbossesb-4.0.GA\bin\..\bin\jbossesb.xml
INFO [ConfigurationController]: loading configuration..
INFO [ParamFileRepository]: Setting parameter repository root dir to [C:\jbosse
sb-4.0.GA\bin\.].
INFO [Generator]: Serializing ESB Aware Listener 'ConfigTree' configuration to
[C:\jbossesb-4.0.GA\bin\..\bin\jbossesb-listener.xml].
INFO [Generator]: Serializing ESB Gateway 'ConfigTree' configuration to [C:\jbo
ssesb-4.0.GA\bin\..\bin\jbossesb-gateway.xml].
INFO [ConfigurationController]: Parameter reload completed.
INFO [ConfigurationController]: Configuration Controller instance started.
INFO [StandAloneBootStrapper]: starting gateway listener with config file - C:\
jbossesb-4.0.GA\bin\..\bin\jbossesb-gateway.xml
INFO [GatewayListenerController]: No value specified for: endTime - Listener wi
ll run until parent container/process terminates.
INFO [StandAloneBootStrapper]: Listeners Ready
INFO [GatewayListenerController]: Reloading parameters ________________________
_____________________________
INFO [GatewayListenerController]: No value specified for: endTime - Listener wi
ll run until parent container/process terminates.
In any case you will see 2 'new' configuration file being generated right next to the jbossesb.xml. They are the :jbossesb-listener.xml and jbossesb-gateway.xml. These represent the configuration as it will be consumed by the esb engine, which where generated from the jbossesb.xml file. There should be no need for you to interact with the generated file. You can add xml fragments in to the jbossesb.xml and when the controller reloads your listeners and gateways come up. So try pasting in xml from the Hello World config sample. Note that if you have a xml editor it should give you auto-complete options to help you creating the configuration xml. As you will do more Quickstarts you will be deploying custom actions (java code) along with your configuration.
This QuickStart allows you get up and running with JBoss ESB, out of the box. It is located in the distribution under samples/quickstarts/helloworld.
To run this QuickStart:
Copy samples/quickstarts/esb-quickstart-service.xml to your JBoss Application Server (/jboss-4.0.5.GA/server/default/deploy). This will bring up all the JMS Queues you need to run the quickstarts. Note that the ESB can interact with any JMS provider, however it does not ship with one. So our examples use JBossMQ, which is the default provider in JbossAS. Note that we have also tested MQSeries and ActiveMQ.
Update the “jbosshome.dir” property setting in samples/quickstarts/quickstarts.properties to reference location of your JBoss Application Server.
Start you JBoss Application Server.
From a command terminal window (“Window1”), change directory into the samples/quickstarts/helloworld directory.
In Window1, type “ant”.
This will start the ESB Message “Listeners”. Wait for “**Listener Ready**” to appear on the terminal window. The ESB is now running!
Open a 2nd command terminal window (“Window2”) and change director to samples/quickstarts/helloworld again.
In Window2, type “ant runtest”.
Switch back to Window1. You should soon see a “Hello World” message appear in the terminal window.
That's it! The QuickStart ran successfully. Your environment is properly configured for JBoss ESB.
The following diagram illustrates the sequence of events that take place in this QuickStart. It touches on a number of the key concepts within JBoss ESB1.
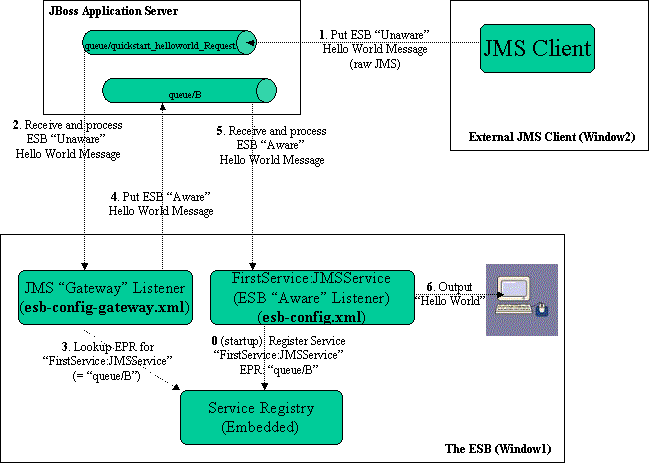
Window1 shows each of the main “ESB” components used in this sample:
Service Registry: This is a JAXR Registry implementation. In this QuickStart, the registry is using an embedded Datastore as the Service repository (Hypersonic). See docs/services/RegistryConfiguration.pdf. For more details on the Registry Service.
JMS Gateway Listener: A “Gateway Listener” is one of the key architectural components within JBoss ESB. This listener type is, as its name would suggest, the gateway to the ESB from endpoints outside the domain of the ESB. In this case, we're using a JMS Gateway.
The ESB Aware Service Listener: The “FirstService:SimpleJMSService” ESB Aware Service Listener listens for “ESB Aware” messages on “queue/B”. This introduces you further to the concept of ESB “Aware” and “Unaware” messages. We will touch on these next.
JBoss ESB has a well defined concept of what a message is. This is defined fully in xml/message.xsd. This construct makes it possible to pass decorated messages payloads between components of the ESB. The message payload is typically stored in the message “Body” (see the Programmers Guide).
This makes a lot of sense from the point of Services in within the ESB domain being able to collaborate effectively. However, it is not practical to expect endpoints outside the domain of a JBoss ESB deployment to be “aware” of these internal ESB constructs. For this reason, JBoss ESB has the concept of ESB Aware and Unaware Messages and Endpoints, with the Gateway acting as the bridge (adapter) between the two worlds.

After starting the ESB in Window1 and before any “Hello World” messages are put on the bus, the “FirstService:SimpleJMSService“ Service is registered with the Registry Service.
The sequence of events in the Hello World QuickStart are as follows:
ESB Unaware JMS Client endpoint puts an ESB Unaware “Hello World” Message (plain String Object) into JMS Queue “queue/quickstart_helloworld_Request”.
The JMS Gateway Listener receives the ESB Unaware message. The Gateways Job is to adapt this message by making it an ESB Aware Message for consumption by an ESB Aware Endpoint.
The JMS Gateway Listener uses the registry to lookup the Endpoint Reference (EPR) for “FirstService:SimpleJMSService” Service. This works out to be JMS Queue “queue/B”.
The JMS Gateway Listener “adapts” the message into an ESB Aware message and places it into JMS Queue “queue/B”.
“FirstService:SimpleJMSService” Service receives the message.
“FirstService:SimpleJMSService” Service extracts the payload from the message and prints it to the console.
Chapter 2
TrailBlazer
JBoss TrailBlazers and Demo Applications are designed to help you get up and running quickly with JBoss products and technologies. We encourage you to Run them, Download them, and enjoy the learning process!
The Loan Broker TrailBlazer example was developed to verify your JBossESB installation and also to exhibit some of the numerous capabilities of JBossESB. This example was based on information from www.eaipatterns.org, along with the example found at JavaZone 2005.
For details of configuring and running the TrailBlazer, see the accompanying “Trailblazer” document.
1 Use the “Zoom” features of you viewer to see the diagram in more detail.
JBESB-GS-