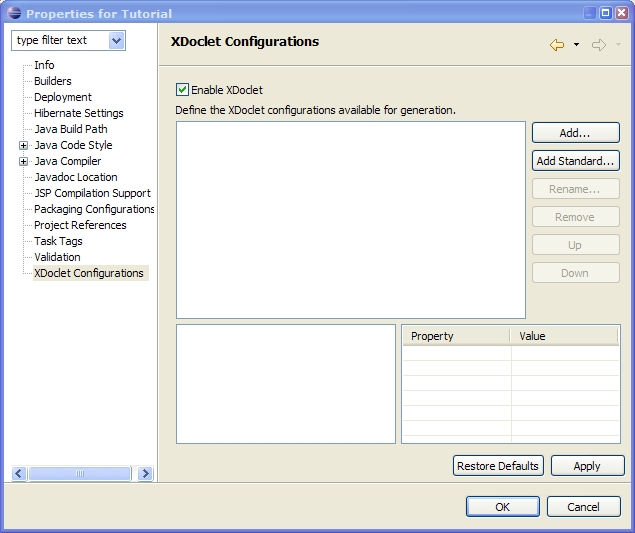
To generate the EJB related classes and descriptors, we need to create some XDoclet configurations. With JBoss Eclipse IDE, you can define several XDoclet generation configurations that will be run against the project.
Procedure 5.1. Enable XDoclet
|  |
Procedure 5.2. XDoclet EJB Configuration Creation
You have created a new generation configuration named EJB. | 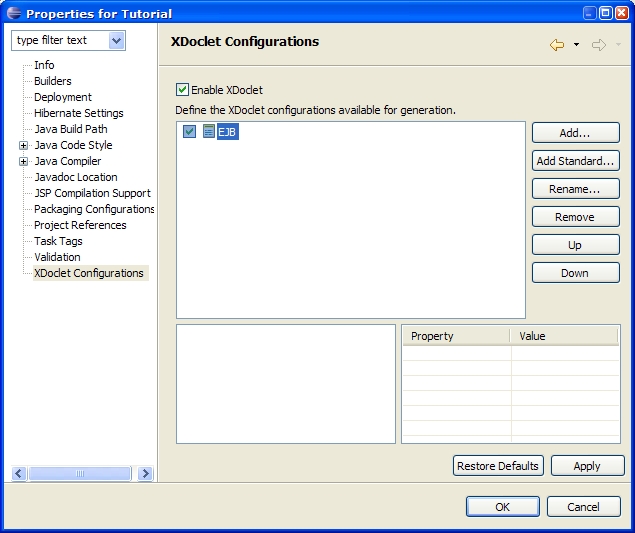 |
Procedure 5.3. Ejbdoclet Configuration
Our configuration now contains an ejbdoclet that will produce files in src folder and for the EJB 2.0 specifications. | 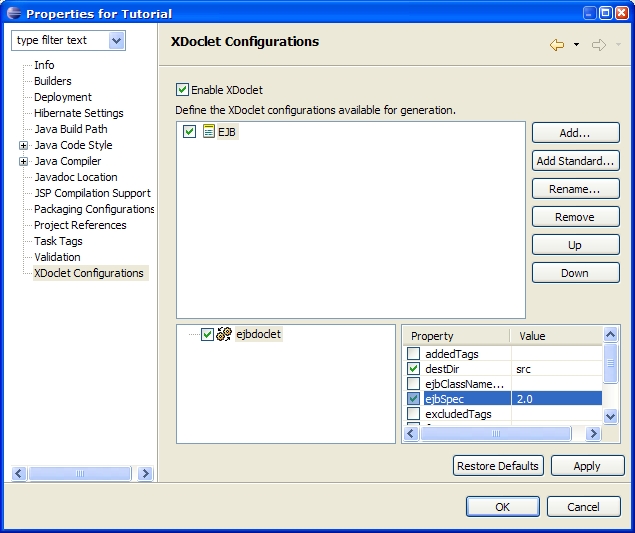 |
Procedure 5.4. Fileset Configuration
Our configuration now contains an ejbdoclet with a fileset that contains the src directory, and all files under it that end in Bean.java. | 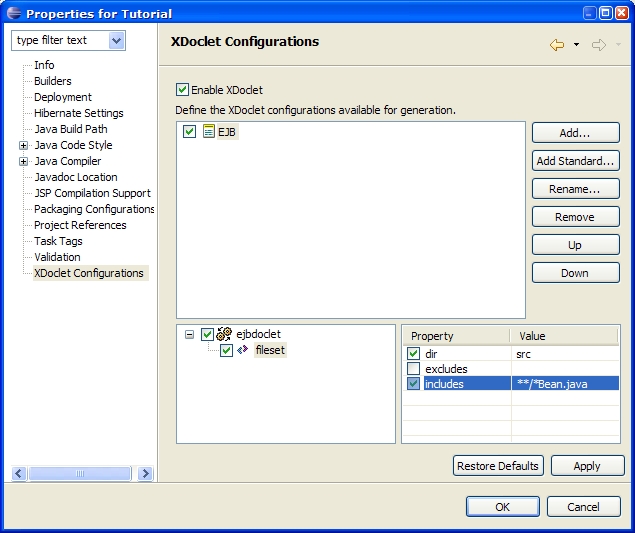 |
Procedure 5.5. Deployment Descriptor Configuration
All of the standard EJB deployment descriptors will now be placed in the src/META-INF directory. | 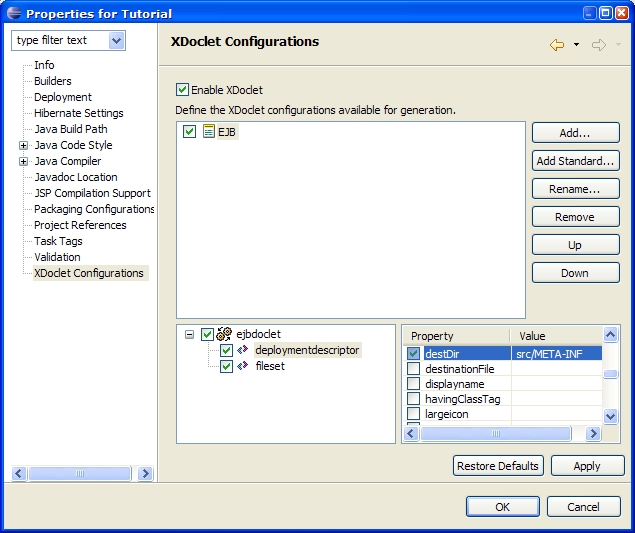 |
Procedure 5.6. JBoss Configuration
All of the JBoss-specific deployment descriptors will now be placed in the src/META-INF directory. | 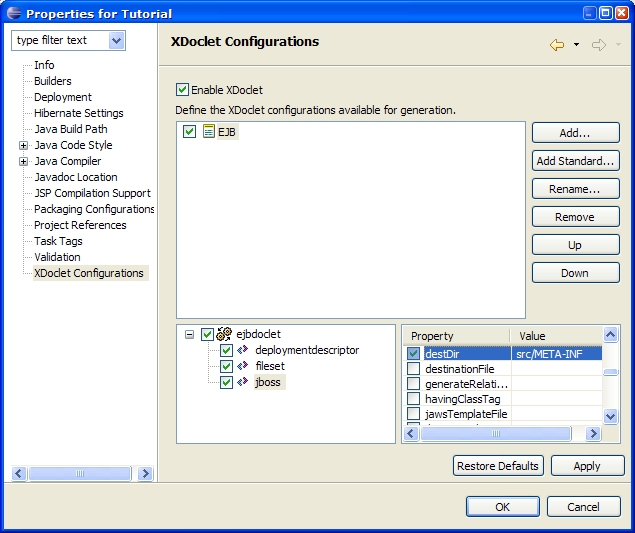 |
Procedure 5.7. Package Substitution Configuration
This will place our generated EJB interfaces in the tutorial.interfaces java package. | 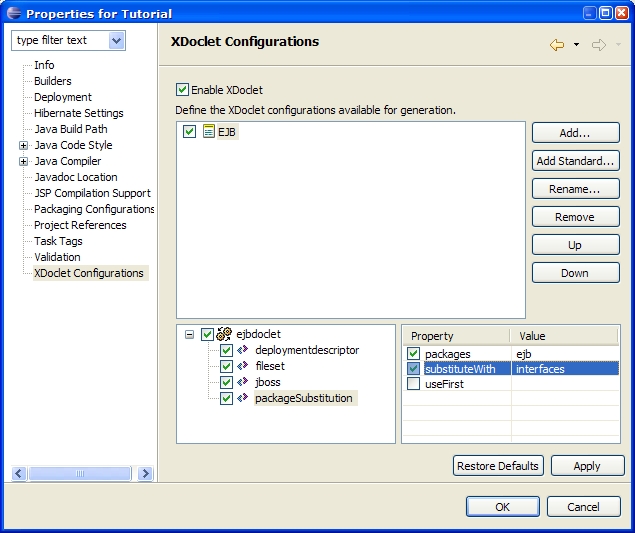 |
Procedure 5.8. Interface Configuration
These subtasks will generate the EJB home and remote interfaces. | 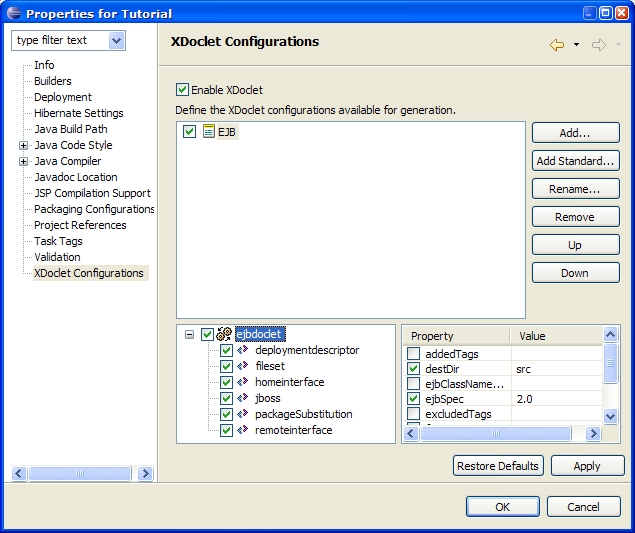 |
Click OK and the XDoclet configuration for the Tutorial will be saved. Once the configuration is saved, right-click on the Tutorial project and select Run XDoclet. The XDoclet generation will display its output in the console. The output should look like this: | 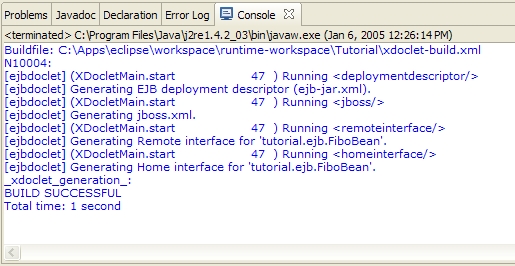 |
After the code generation, select the project and refresh it (you can press F5). You should have a project that looks like this. Note that a tutorial.interfaces package has been created with new classes inside. There is also a META-INF folder with the deployment descriptors (both standard and jboss). | 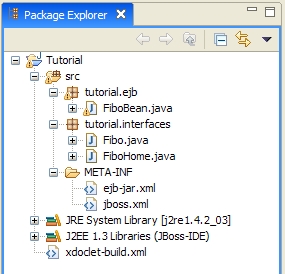 |