The basis of a process definition is a graph that is made up of nodes and transitions.
That information is expressed in an xml file called processdefinition.xml.
Each node has a type like e.g. state, decision, fork, join,... Each node has a set of leaving
transitions. A name can be given to the transitions that leave a node in order to make them distinct.
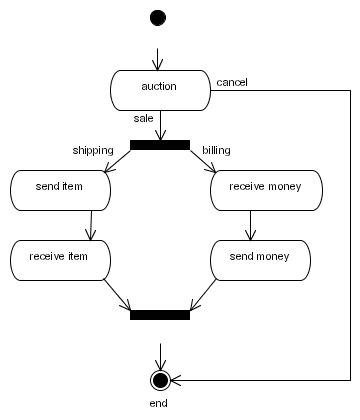
For example: The following diagram shows a process graph of the jBAY auction process.
Below is the process graph of the jBAY auction process represented as xml:
<process-definition>
<start-state>
<transition to="auction" />
</start-state>
<state name="auction">
<transition name="auction ends" to="salefork" />
<transition name="cancel" to="end" />
</state>
<fork name="salefork">
<transition name="shipping" to="send item" />
<transition name="billing" to="receive money" />
</fork>
<state name="send item">
<transition to="receive item" />
</state>
<state name="receive item">
<transition to="salejoin" />
</state>
<state name="receive money">
<transition to="send money" />
</state>
<state name="send money">
<transition to="salejoin" />
</state>
<join name="salejoin">
<transition to="end" />
</join>
<end-state name="end" />
</process-definition>