Create new JBoss Tools Documentation Jira issue

JBoss.orgCommunity Documentation
Version: 1.1.0.GA
Copyright © 2009,2010 JBoss by Red Hat
This chapter gives you a short introduction to Smooks, Smooks tools and its installation.
First, have a look at the key features of Smooks tools:
Here, we provide you with a key functionality which is integrated in Smooks tools.
Table 1.1. Key Functionality for Smooks Tools
| Feature | Benefit | Chapter |
|---|---|---|
Smooks Configuration File Wizard | Smooks tools allows to create/edit the Smooks configuration file for Java2Java data transformation. | Smooks Configuration File Wizard |
Smooks Editor | Smooks Editor helps configure the created Smooks configuration file. | Smooks Editor |
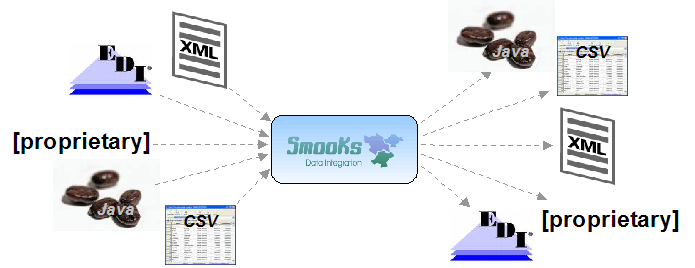
Smooks is a Java Framework/Engine for processing XML and non XML data (CSV, EDI, Java, JSON etc).
Transformation: Perform a wide range of Data Transforms. Supports many different Source and Result types -XML/CSV/EDI/Java/JSON to XML/CSV/EDI/Java/JSON.
Java Binding: Bind into a Java Object Model from any data source (CSV, EDI, XML, Java, JSON etc).
Huge Message Processing: Process huge messages (GBs) - Split, Transform and Route message fragments to JMS, File, Database etc destinations. Route multiple message formats to multiple destinations in a single pass over a message.
Message Enrichment: Enrich a message with data from a Database, or other Datasources.
Combine: Combine the above features in different ways e.g. add Message Enrichment as part of a Splitting and Routing process.
For more informations about Smooks, please visit Smooks official site.
Smooks tools is a set of graphical tools for editing Smooks configuration file based on Eclipse.
The easiest way to use the Smooks Configuration Editor is to create a project (Java project, an ESB project, etc.), right-click on it and select New -> Other to open the New wizard. Drill into Smooks -> Smooks Configuration File and continue through the wizard. We recommend using a minimum Smooks level of 1.1 or 1.2, but if you're using it in a deployed service, it depends on what version your runtime supports. Once the file is created, it will open in the Smooks Configuration Editor.
The Smooks tools was included by the JBoss Tools since 3.0.0 Beta1 version. You can download the JBoss Tools from JBoss download site.
Smooks tools (JBoss Tools) run with the latest Eclipse and other required plug-ins (GEF, EMF, etc.).
You should download the latest IDE for Java EE developers from Eclipse site. It contains many plug-ins ( GEF, EMF, etc. ) required by Smooks dev tools.
The Smooks Configuration depends on having all of the appropriate Smooks runtime jars in the path of the Eclipse Plug-in or Java Project in the Eclipse workspace. The easiest solution is to do the following:
1) Download the Smooks distribution from here: http://www.smooks.org/mediawiki/index.php?title=Downloads . Grab the latest "ALL" distribution (as of today, it is the Smooks v.1.2.2 "ALL" distribution) and it will include binaries, examples, etc.
2) Extract files from the archive somewhere on your machine.
3) In your Eclipse workspace, copy the Smooks jars into a directory of your Eclipse plug-in or Java project named "lib".
4) For your Eclipse Plug-in or Java Project, right-click on the project and select Properties.
5) Select the "Java Build Path" item in the Properties list, select the Libraries tab, and click "Add JARs"
6) In the Jar Selection dialog, select all the jars in the "lib" directory mentioned in step 3 and click OK.
7) Click OK to close the Properties dialog. Now you should see a "Referenced Libraries" node that appeared in your project hierarchy in Eclipse.
Now let's progress to more advanced topics.
This chapter describes the main tasks a user can be faced during Smooks tools usage.
Select the project where you want to create new Smooks Configuration File and right-click on it, select in the menu New > Other, then find Smooks > Smooks Configuration File. Click the Next button.
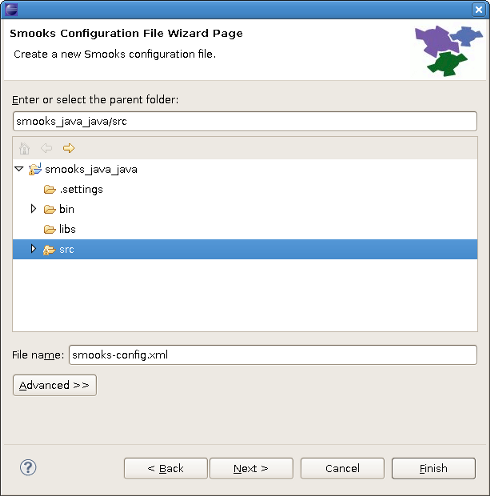
The first wizard page is a file path creation page. Select the src folder to be the files container, and input the name smooks-config.xml. Click Next.
The second wizard page allow you to select Smooks configuration file version. Select the appropriate one and click Finish to complete the wizard.
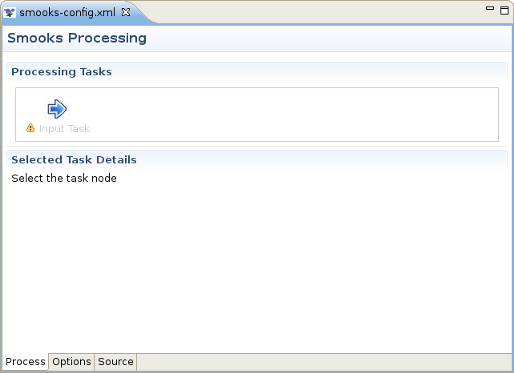
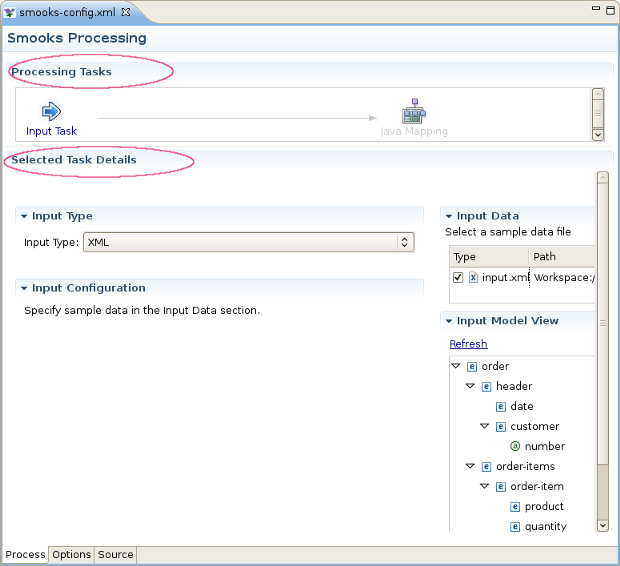
Input task configuring is an obligatory step for your smooks project creation. You can configure it on the Process page of the editor: look for the "Input Task" in the Process Map at the top of the page.
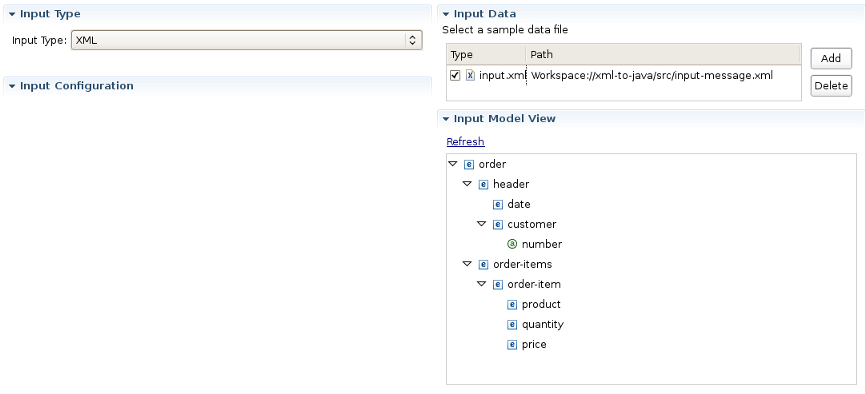
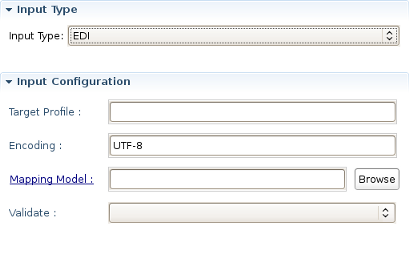
Select it and you will see all the properties to set for the Input reader of your Smooks configuration. "Input type" corresponds to the type of data that you will be working with. For example, to work with incoming CSV (Comma-separated Values) data, you would specify "CSV" in the drop-down list. Each reader type has slightly different configuration details that must be set in the "Input configuration" area. For instance, the CSV reader requires you to specify details such as the encoding, quote character, separator character, and the list of incoming fields. The EDI reader requires the encoding and the path to the Mapping Model describing the incoming data. In the Input data section, you specify some sample data that conforms to your reader configuration.
Once you've specified your reader configuration and sample data, you can see the input model rendered in a tree form in the Input model section. On the picture below you can see the correct configuration of some XML input task.
Though there are many options in Smooks as far as what you can do with input data such as transformation, routing, and persistence, this version of the Smooks Configuration Editor focuses only on these areas: mapping to java and applying templates to create different output formats. If you have a set of Java classes you want to use the incoming data for, you can use the "Java Mapping" task to specify those classes and use drag and drop to map between the input model generated by the reader and elements in the output model. Or if you simply want to transform your output to one or more formats, you can use the "Apply Template" task to map it to a CSV file, XML or XSD file (and other formats in the future).
Note
Now you can't transform your output directly, using only Input and Template tasks. You should use Mapping as an interagent between these tasks.
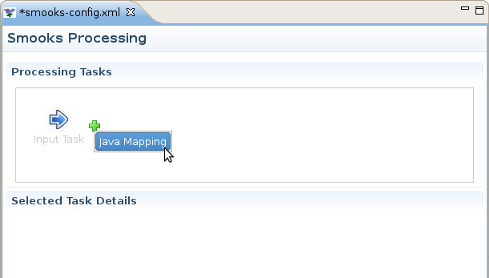
If you decide to do Java Mapping, you need to make sure that your Input reader has been set up and you have some sample data specified. Then you should select Input Task in the Process tab and click the plus (+) sign to the right of the icon. Select Java Mapping from the popup menu and it will appear to the right, connected to Input Task. Then select Java Mapping task.
Another method of adding Java Mapping element to the canvas in the Processing Tasks section is to right click Input Task element and select Java Mapping in the popup menu
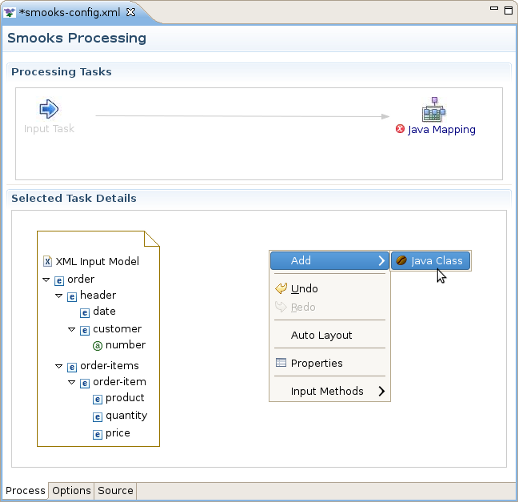
Right-click on the canvas in an empty space and select "Add ->Java Class".
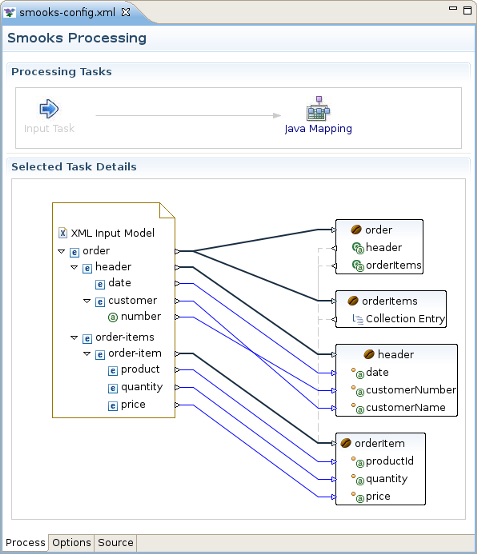
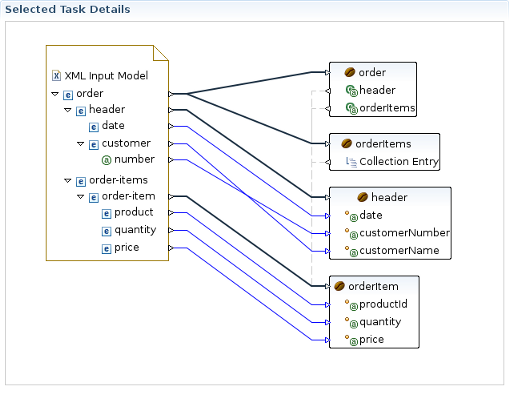
Java Bean Creation wizard appears. Specify a unique identifier for the new class, the class path, whether it's an array or not, and if it is a collection, also specify the collection class. If the Java class is specified, you'll see a list of the properties in the box below. Click Finish when you're done. Now with the input and output models on the canvas, you can click and drag from the various input elements to corresponding output elements. Make sure to connect collection elements to corresponding collection elements. Finally your mapping should look nearly like the one on the picture below.
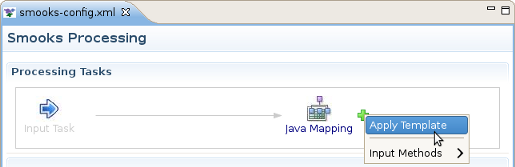
The "Apply Template" task works very similarly to the "Java Mapping" task, where you map between an input model and an output model. Select the Java Mapping task you want to use as the input model in the Process Map pane and click the plus (+) sign to the right of the icon.
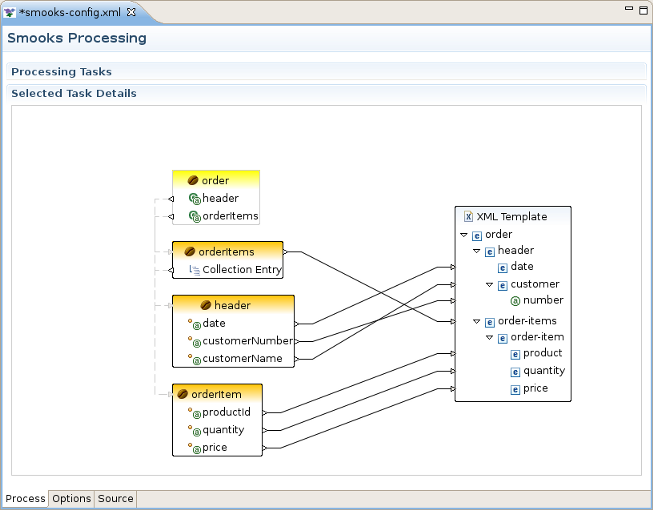
Select "Apply Template" from the popup menu and it will appear to the right, connected to the task you created it from. Then select the "Apply Template" task. Once you've defined your template model, you can click and drag from the various input elements to corresponding output elements in the template. Make sure to connect collection elements to corresponding collection elements
This option is intended to view the results of Smooks transforming procedure. For more detailed information about this option please go here.
This chapter includes detailed reference information about Smooks Tools.
This chapter describes the following tabs of the Smooks Configuration Editor:
The Process tab of the Smooks Configuration Editor helps to configure different types of transformations. By default smooks configuration file is opened in this editor.If you have another default settings for editor opening you should left click smooks configuration file and select:Open With->Smooks Configuration Editor.
The Process tab has two sections:
You can see them on the picture below.
Using the popup menu in the Processing Task section you can select which types of technologies(templating or mapping ones) you will use for transofmation:
The descriptions of the popup menu options are in the following table.
Table 3.1. Process Tab. Processing Task section.
| Option | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
| Add Task | Select one of the following tasks according to the necessary type of Source and Result types of the files:
| |
| Delete | Click this option if you want to delete some task from the section. Note:you can't delete input task because it's required. | |
| Input Methods | Choose one of the following methods:
| System |
The options of this section depends on the selected task in the Processing Task section. Because there are 3 types of tasks there are 3 different sets of its options in the Selected Task Details Section. They will be described one by one.
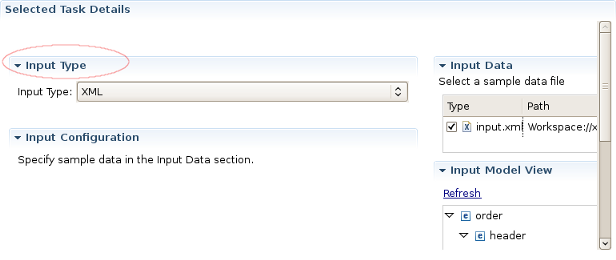
On the picture below you can find an example of Selected Task Details Section view if XML is selected as input type.
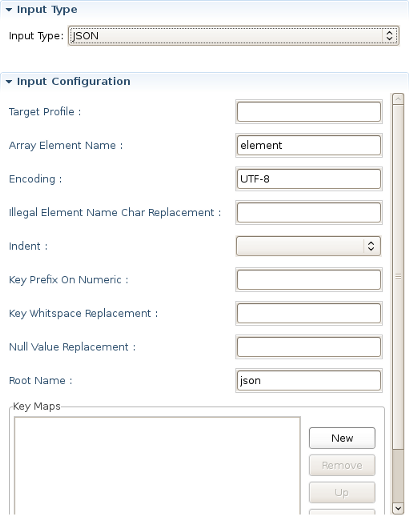
As you can see on the picture above Input Configuration section is empty for XML input file. But this section has special configuration options for CSV,EDI,JSON,Custom input files.
Here are the screens of these configuration options:
CSV:
EDI:
JSON:
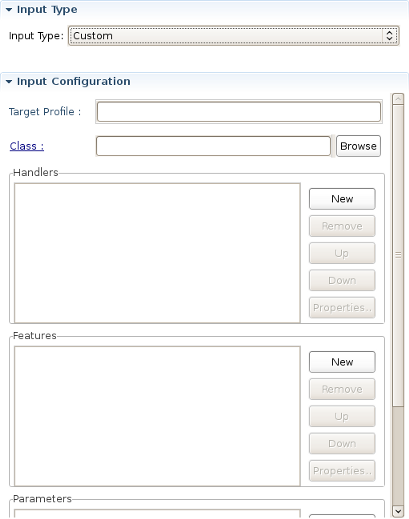
Custom:
All the input task configuration positions can be found in the table below:
Table 3.2. Selected Task Details Section. Options for Input Task.
| Option | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
| Input type | Select your type of input file.
If don't find your type in the list,you should use Custom type:
| XML |
| Input configuration |
|
|
| Input Data | You should select a data file using Add and Delete buttons | |
| Input Model View | Using this view you can see the structure of your input file.If the file has been changed, to see the changes click Refreshlink. |
Selected Task Details section for this task is presented by the graf, that lighten the process of java mapping.
This graphical editor allow you to perform drug/drop operations with the nodes of transform data to map the source data to target data. When you save the changes in the graphical editor the correct Smooks configuration file content will be generated.
Selected Task Details section for this task is presented by the graf, that is similar to the one in the previous section.
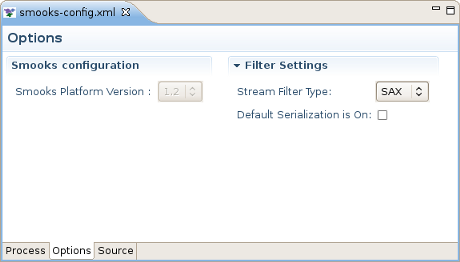
This section describes Options tab of the Smooks Configuration File editor, gives short recommendations how this tab can be used during the project configuring.
In the Smooks Configuration section of Options Tab only one element is availible:Smooks Platform Version
This parameter is not rechangable, and is set according to the vesion of the Smooks libraries that are added to the project.
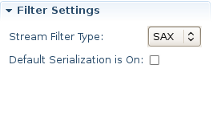
In Filter Settings section you can set the following global options responsible for Smooks filtering configuring:
This behavior can be turned off using this global configuration parameter and can be overriden on a per fragment basis by targetting a Visitor implementation at that fragment that takes ownership of the Result writer (in the case of SAX filtering), or simply modifies the DOM (in the case of DOM filtering). As an example of this, see the FreeMarkerTemplateProcessor.
Table 3.3. Options Tab. Filter Settings section.
| Option | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
| Stream Filter Type | Determines the type of processing model that will be used.
Please refer to
Filtering Process Selection section
of the official Smooks User Guide for more information about these models:
| DOM |
| Default Serialization is On | Defines whether default serialization should be switched on. Default serialization being turned on leads to locating StreamResult/DOMResult to the Result objects provided to the Smooks.filterSource method and to serialization all the events to that Result. | true |
This section provides information about Smooks Source Editor Page.
You can use this editor to edit the Smooks Configuration file directly.
If the Smooks tools can't understand the configuration file or the configuration file is illegal (XML structure isn't right for Smooks Configuration file, etc.), the error is underlined.
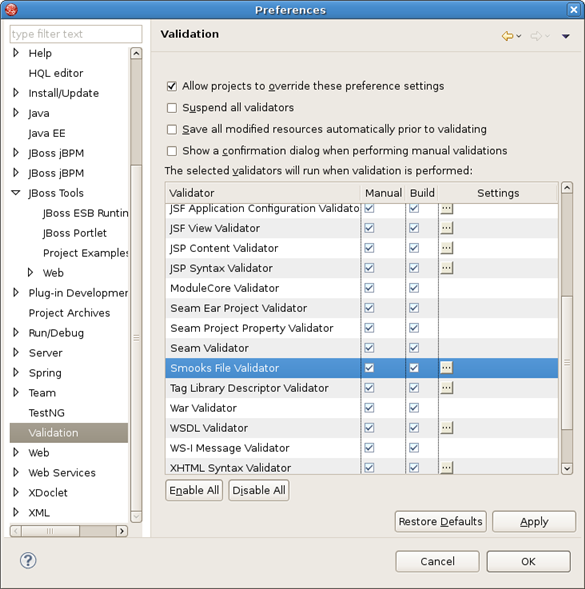
Smooks configuration file validator will validate your Smooks configuration file. Just right-click on the file and then click on the Validate button. The validator can be enabled/disabled in Window -> Preferences -> Validation:
You can set up your Smooks validator to include, exclude groups to validate and specify rules for validation. Just click on the Settings button and use the options provided:
In conclusion, with this document you know all the capabilities of Smooks Tools and could easily start with them. The chapters above walked you through the steps on how to create and configure some XML to JAVA mapping project. If you have questions or suggestions concerned both the documentation and tools behavior, you are welcome to JBoss Tools Users forum. Please, use Jira to report bugs and requests on documentation.
All JBoss Developer Studio/JBoss Tools release documentation you can find at http://docs.jboss.org/tools in the corresponding release directory.
The latest documentation builds are available at http://download.jboss.org/jbosstools/nightly-docs.
For more information about Smooks technology please visit Smooks Technology Home Page