JBoss.orgCommunity Documentation
Version: 2.1.0.CR1
Copyright © 2007, 2008 JBoss, a division of Red Hat Inc.
April 2008
ESB (Enterprise Service Bus) - an abstraction layer on top of an implementation of an enterprise messaging system that provides the features with which Service Oriented Architectures may be implemented.
If you want to develop applications using ESB technology JBoss ESB also meet your needs. The JBoss Developer Studio provides ESB editor and all necessary wizards for creating ESB file.
In this guide we provide you with the information on ESB Editor which allows you to develop ESB file much faster and with far fewer errors so sparing your time.
You can find a set of benefits and other extra information on:
Since v.1.0.1 Developer Studio supports xml editor for the ESB XML file used in JBoss ESB.
At this point the structured xml editor will prompt you to specify a proper ESB environment.
In this section we will focus more on all concepts that JBDS integrates for working with ESB.
This chapter will provide you with detailed information on how to install JBoss ESB.
To install the JBoss ESB plugins for Eclipse, you need the following:
Get Eclipse 3.3.1 and Web Tools 2.0.1
The quickest way to get a WTP version is to download "Eclipse IDE for Java EE Developers" via www.eclipse.org.
Note:
Remember to choose the download that matches your OS and use Java 5 when you run it.
Get the JBoss ESB build
You can also find the latest development release of JBoss ESB from JBoss ESB Downloads Site
Finally, install the build
Unzip the file(s) directly into your Eclipse plugins/features directory and it will be readily available. It might be necessary to start Eclipse with eclipse -clean to make sure it starts clean and rereads the new list of plugins.
In this chapter we suggest a step-by-step walk-through of creating your own simple file. Let's try to organize a new ESB file.
We will show you how to use the Creation wizard for creating a new ESB file.
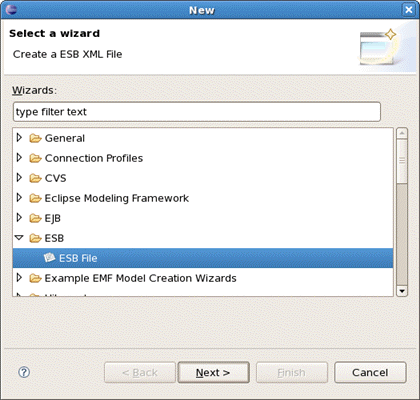
At first you should open any project. Select File >New > Other... in the main menu bar or context menu for selected project and then ESB > ESB File in the New dialog:
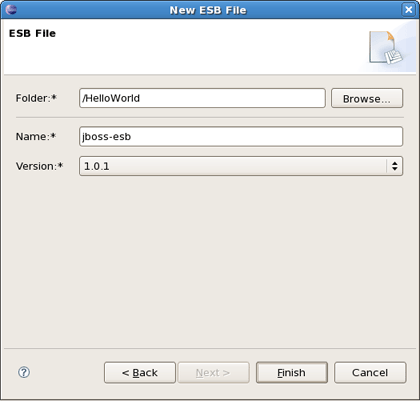
Clicking Next brings us to the wizard page where it's necessary to specify the folder, name and version for the file. We choose, for example, jboss-esb.xml as the name and accept the selected projects folder and default version.
Thus, our file will be created in the selected projects folder by default. If you want to change the folder for your future file click Browse... button to set needed folder or simply type it.
Clicking on Finish results in the file being generated. The wizard creates one xml file.
ESB editor has lots of useful features, they are described in details in this chapter. In addition you get to know ESB Editor uses combined visual and source editing of esb files.
JBoss Developer Studio comes with a powerful and customizable ESB File Editor. You can use the ESB File Editor to develop an application using ESB technology.
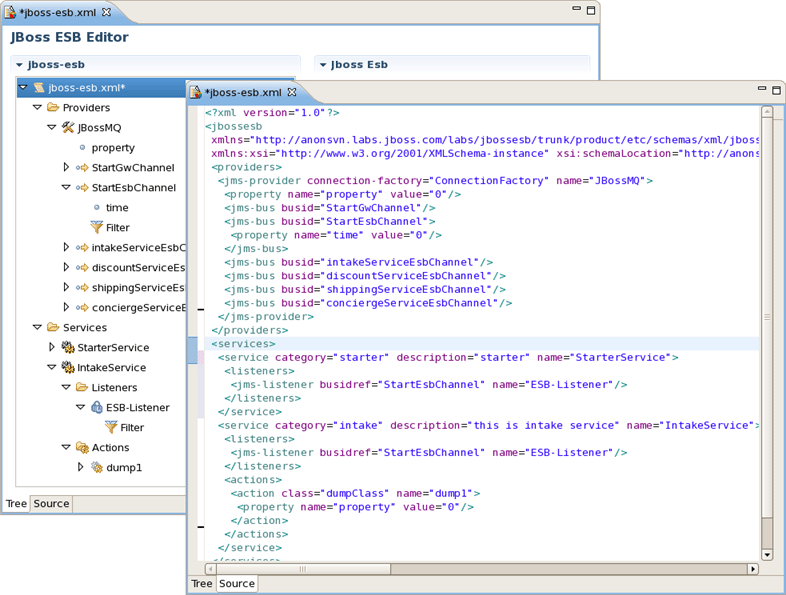
ESB file editor has two tabs: Tree and Source.
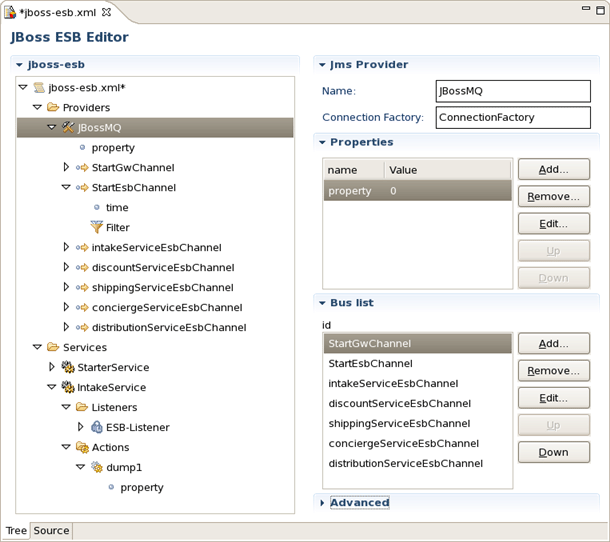
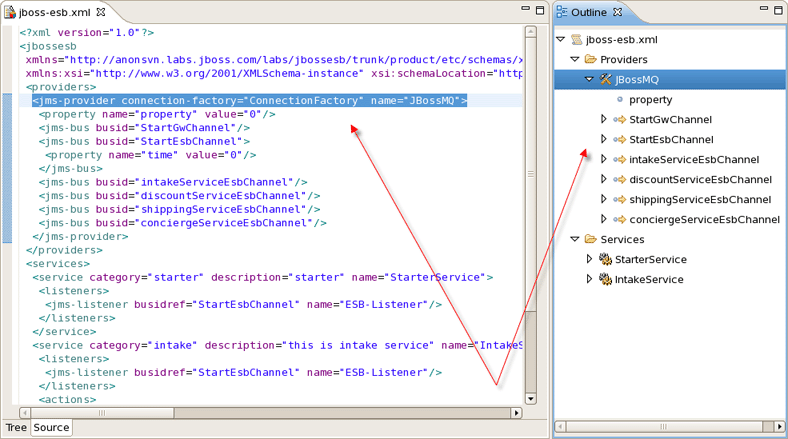
You can switch to Tree. The Tree view for the editor displays all ESB artifacts in a tree format. By selecting any node you can see and edit its properties which will appear in the right-hand area. For example, a Provider:
You can easily switch from Tree to Source by selecting the Source tab at the bottom of the editor and work in Source view.
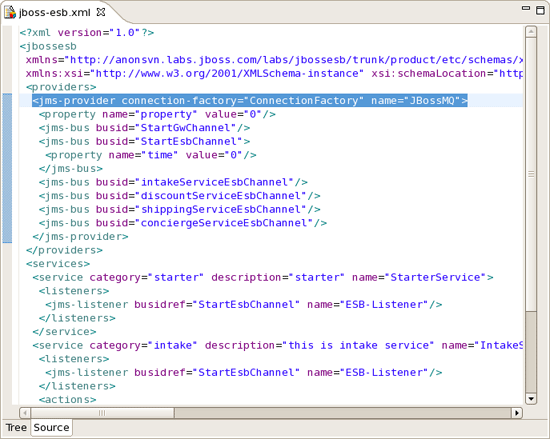
The Source view for the editor displays a text content of the ESB file. It is always synchronized with tree view, so any changes made in one of the views will immediately appear in the other.
No matter what view you select, you get full integration with Outline view. For example, you can work in the Source view with the help of the Outline view. The Outline view shows a tree structure of the ESB file. Simply select any element in the Outline view, and it will jump to the same place in the Source editor, so you can navigate through the source code with Outline view.
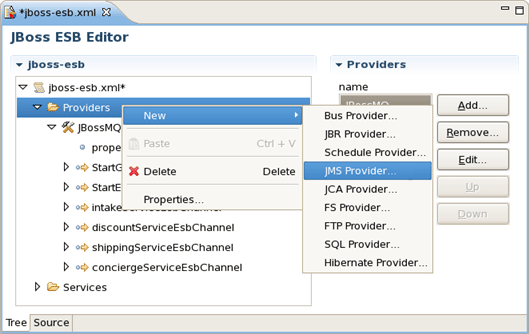
Adding, editing or deleting of some artifacts operations are available right in the Tree view. Right-click any node and select one of the available actions in the context menu. For example, you can easily add a new provider:
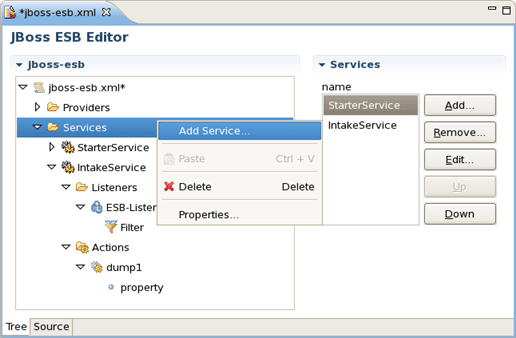
You can easily add a new service too:
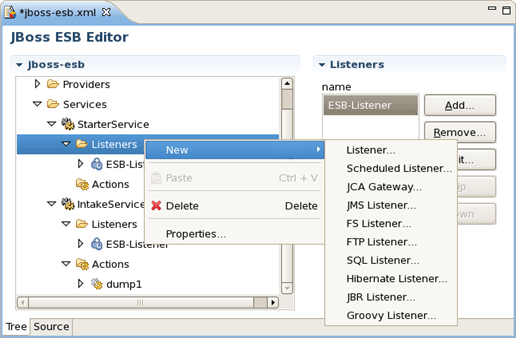
The same way you can create a listener for service and other elements of ESB:
The same actions can be done in the right part of Tree view tab using Add, Edit, Remove buttons.
JBoss Developer Studio has powerful editor features that help you easily make use of content and code assist.
When working in JBoss ESB editor you are constantly provided with feedback and contextual error checking as you type. In the Source viewer, if at any point a tag is incorrect or incomplete, an error will be indicated next to the line and also in the Problems view below.
JBoss Developer Studio fully supports XML files based on schemas as well as DTDs.
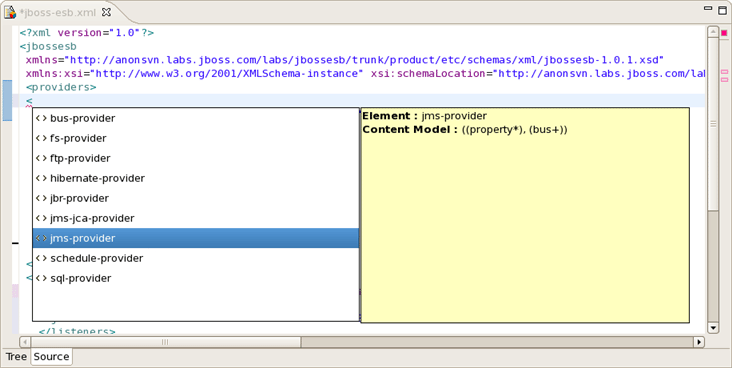
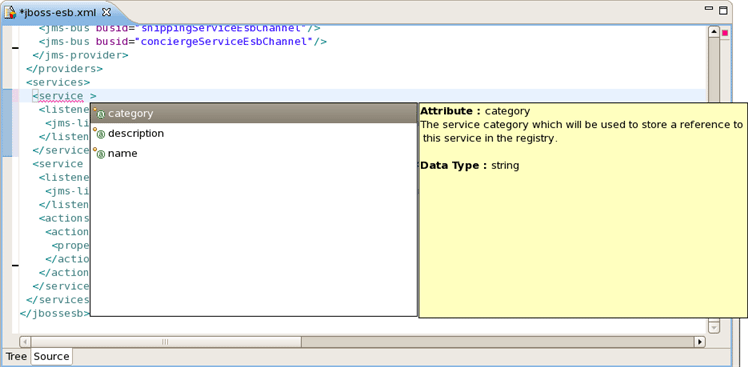
When you work with any ESB XML file Content Assist is available to help you. It provides pop-up tip to help you complete your code statements. It allows you to write your code faster and with more accuracy. Content assist is always available in the Source mode. Simply type Ctrl-Space to see what is available.
Content Assist for ESB XML file:
Content Assist for atributes:
JBoss Developer Studio offers the flexibility to edit ESB file in either source or extra visual modes at the same time.
JBoss Developer Studio provides you two different editors to speed your development: a graphical view (Tree) and source (Source). At the same time, you always have full control over esb source file. Any changes you make in the source view will immediately appear in the tree view. Both views are synchronized, you can edit the file in any view.
The last chapter covers a capabilities on how you can use ESB editor.
In summary, this reference supplies you with all necessary information on the functionality that JBoss ESB Editor provides for work with JBoss ESB.