This chapter will provide answers to common questions asked by JMX plugin users.
To start using the JMX Tools it is necessary to open MBean Explorer. Select → → , select and click the button.
The MBean Explorer lists all the domains, MBeans, attributes, and operations inside a connection. When you double-click an MBean in the MBean Explorer, it opens a multi-page editor to manage the MBean. The MBean Editor is composed of these pages:
Attributes page, to get/set the attributes of the MBean
Operations page, to invoke operations on the MBean
Notifications page, to receive notifications from the MBean
Info page, which displays general information about the MBean
In this section we will show you how to get connected to a sample Java application and run the sayHello() method remotely from inside of the MBean Explorer.
Save the bundle of JMX API sample classes, jmx_examples.zip, to your working directory.
Unzip the bundle of sample classes.
Compile the example Java classes from within where you unpacked the files directory.
javac com/example/*.java
Start the
Mainapplication, specifying the properties that exposeMainfor remote management:java -Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.port=9999 \ -Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.authenticate=false \ -Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.ssl=false \ com.example.Main
If everything was done correctly you will see the
Waiting for incoming requests...
message on the screen.
Now launch the Eclipse IDE, in Eclipse open the MBean Explorer. Go to → → , select , and then click the button)
Click the icon
 in the MBean Explorer menu bar.
in the MBean Explorer menu bar.
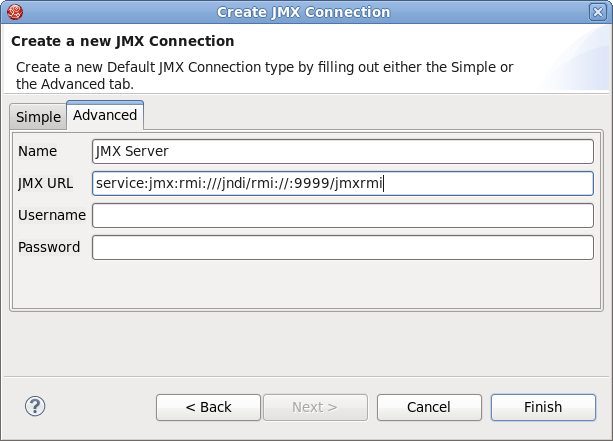
In the Create JMX Connection dialog, click the button and then click the Advanced tab.
In the JMX URL input field enter the following URL:
service:jmx:rmi:///jndi/rmi://:9999/jmxrmi
Click the button to establish the connection with the application.
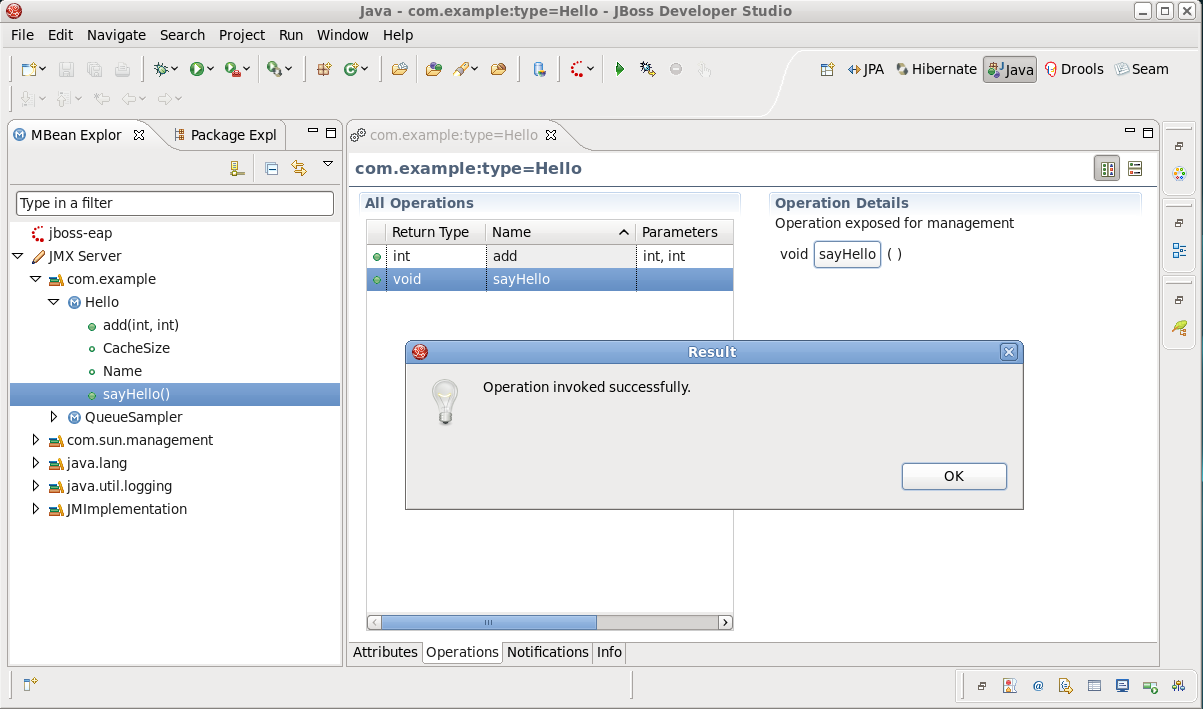
Now expand the connection you have just created, open the com.example package, and click the
sayHello()method.Once the
sayHello()method is selected the MBean Editor is activated.In the MBean Editor go to the Operation Details section and click the
sayHello()button.You will get the "Operation invoked successfully" message.
The final step is to make sure the application worked as expected. Open the terminal where you launched the application in step 3. You should see output similar to the following:
[matthew@localhost jmx_examples]$ java -Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.port=9999 \ > -Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.authenticate=false \ > -Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.ssl=false \ > com.example.Main Waiting for incoming requests... hello, world
It is possible to manage Tomcat using JMX Tools.
Currently, JMX Tooling is able to connect to Tomcat without authentication or with password-based authentication.
Using SSL for authentication is not supported: you need to make sure that the System property com.sun.management.jmxremote.ssl is set to false.
More information to manage Tomcat can be found in the Tomcat management documentation.
Instructions to remotely manage Tomcat are available in Tomcat's monitoring documentation.
Important
If you are running JBos Enterprise Application Platform 6, JBoss Application Server 7 or later, you can connect automatically to a remote server through the Server Behaviour tab in the server settings. For further information on this see the JBoss Server Manager Reference Guide for this release.
The JBoss JMX Tools allow you to easily access and manage a JBoss server remotely. In order to connect to a remote instance of a JBoss server, you need to run the server or make sure the server is launched.
Select → → and select the option.
Switch to the MBean Explorer by selecting → → and selecting the option.
Click the icon
 in the MBean Explorer menu bar.
in the MBean Explorer menu bar.
Select the Advanced tab and set the JMX URL to:
service:jmx:rmi://localhost/jndi/rmi://localhost:1090/jmxconnector
Please note that in this example we are connected to the local host.
This section will outline how to contribute your own Server type with some default behavior.
You might be asking yourself why you would need to extend this framework if JMX is a standard. Perhaps you want a connection to be automatically created after some specific action, or perhaps you want your connection wizard to do more than simply set a host and port. JBoss, for example, requires setting some credentials on the client machine, but uses JBoss classes to do it. This requires that the connection has access to the JBoss JARs.
To create your own JMX Connection type, you must use the org.jboss.tools.jmx.core.MBeanServerConnectionProvider extension point. This point takes one child, a connectionProvider with a class that implements org.jboss.tools.jmx.core.IConnectionProvider.
An IConnectionProvider is responsible for creation and deletion of IConnectionWrapper objects. It must also keep a list of listeners that it is expected to notify when a connection is added or removed from its list.
Each IConnectionWrapper is expected to be able to run arbitrary JMX runnables or getting a "Root" object representing all JMX nodes. There are some utility methods the IConnectionWrapper can make use of.
There are two extension points currently approved for use in the UI
org.jboss.tools.jmx.ui.providerUI- provide an icon, id, displayable name, and wizardPage class for creation of new connectionsorg.jboss.tools.jmx.ui.attribute.controls- allows you to map class types to some Control to present them in the MBean Editor
The MBean Explorer supports several different types of connections. The tooling itself comes only with a default connection type, however other adopters can provide additional connection types that may require additional or non-spec behavior. Connections can be in either the connected state or the disconnected state. Some connection types (such as the default connection type) allow you to control the current state. Other connection types may not.
Similarly, some connection types may be able to be created, and others may not. The default connection type, for example, can be created and deleted at will. The AS Tools connection type, which represents a JBoss server, does not allow you this level of control. A JBoss JMX connection is created when a JBoss server is created in the server's view, and deleted when said server is deleted. The JMX connection for this server is in the connected state only when the server is started.
There are two ways to connect to an application with remote management enabled:
The first step is the same for both methods - to connect to a MBean Server, click the icon ![]() in the MBean Explorer menu bar.
in the MBean Explorer menu bar.
The simple method is to specify the host, port (and optionally user name and password) and click the button.
On the Advanced tab you can set the server name (it will be displayed in MBean Explorer), and a URL to the remote server. For example, to connect to JBoss AS you need to set the JMX URL to
service:jmx:rmi://localhost/jndi/rmi://localhost:1090/jmxconnector
If it is required you can enter user name and password for the server connection.
Note
Only JMX URL based on RMI are supported.