Hibernate アーキテクチャの(非常に)高いレベルからのビュー:
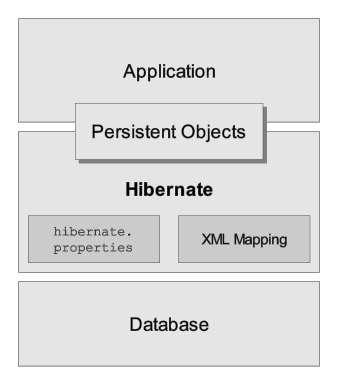
Unfortunately we cannot provide a detailed view of all possible runtime architectures. Hibernate is sufficiently flexible to be used in a number of ways in many, many architectures. We will, however, illustrate 2 specifically since they are extremes.
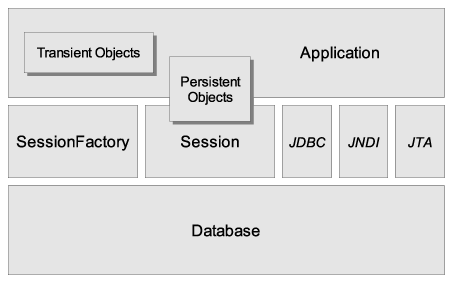
The "minimal" architecture has the application manage its own JDBC connections and provide those connections to Hibernate; additionally the application manages transactions for itself. This approach uses a minimal subset of Hibernate APIs.
The "comprehensive" architecture abstracts the application away from the underlying JDBC/JTA APIs and allows Hibernate to manage the details.
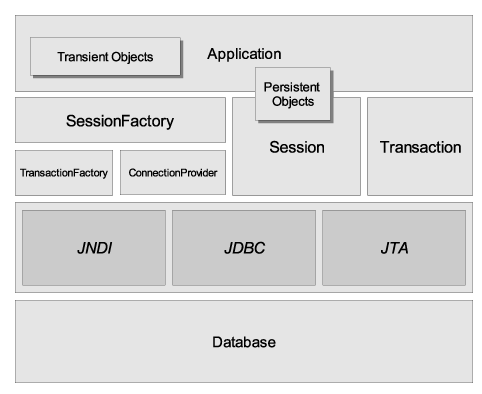
Here are quick discussions about some of the API objects depicted in the preceding diagrams (you will see them again in more detail in later chapters).
- SessionFactory (
org.hibernate.SessionFactory) A thread-safe, immutable cache of compiled mappings for a single database. A factory for
org.hibernate.Sessioninstances. A client oforg.hibernate.connection.ConnectionProvider. Optionally maintains asecond level cacheof data that is reusable between transactions at a process or cluster level.- Session (
org.hibernate.Session) A single-threaded, short-lived object representing a conversation between the application and the persistent store. Wraps a JDBC
java.sql.Connection. Factory fororg.hibernate.Transaction. Maintains afirst level cacheof persistent the application's persistent objects and collections; this cache is used when navigating the object graph or looking up objects by identifier.- Persistent objects と Collections
Short-lived, single threaded objects containing persistent state and business function. These can be ordinary JavaBeans/POJOs. They are associated with exactly one
org.hibernate.Session. Once theorg.hibernate.Sessionis closed, they will be detached and free to use in any application layer (for example, directly as data transfer objects to and from presentation). 11章オブジェクトを扱う discusses transient, persistent and detached object states.- Transient と detached な objects と Collections
Instances of persistent classes that are not currently associated with a
org.hibernate.Session. They may have been instantiated by the application and not yet persisted, or they may have been instantiated by a closedorg.hibernate.Session. 11章オブジェクトを扱う discusses transient, persistent and detached object states.- Transaction (
org.hibernate.Transaction) (Optional) A single-threaded, short-lived object used by the application to specify atomic units of work. It abstracts the application from the underlying JDBC, JTA or CORBA transaction. A
org.hibernate.Sessionmight span severalorg.hibernate.Transactions in some cases. However, transaction demarcation, either using the underlying API ororg.hibernate.Transaction, is never optional.- ConnectionProvider (
org.hibernate.connection.ConnectionProvider) (Optional) A factory for, and pool of, JDBC connections. It abstracts the application from underlying
javax.sql.DataSourceorjava.sql.DriverManager. It is not exposed to application, but it can be extended and/or implemented by the developer.- TransactionFactory (
org.hibernate.TransactionFactory) (Optional) A factory for
org.hibernate.Transactioninstances. It is not exposed to the application, but it can be extended and/or implemented by the developer.- Extension Interfaces
Hibernate は、永続層の振る舞いをカスタマイズするために、多くのオプション拡張インタフェースを用意しています。詳細は API ドキュメントを参照してください。
JMX は Java コンポーネント管理の J2EE 標準です。 JMX 標準サービスを通して、 Hibernate は管理されます。ディストリビューションの中に org.hibernate.jmx.HibernateService という MBean 実装を用意しています。
Another feature available as a JMX service is runtime Hibernate statistics. See 「Hibernate 統計」 for more information.
Hibernate を使ったアプリケーションは、ほとんど、なんらかの形で「コンテキスト上の」セッションが必要になります。「コンテキスト上のセッション」は、特定のコンテキストのスコープのなかで有効なセッションのことです。しかし、通常アプリケーションごとにコンテキストを構成するものの定義は異なります。しかも、異なる複数のコンテキストは、現時点に対して異なるスコープを定義します。バージョン3.0より前の Hibernate では、自作の ThreadLocal ベースの「コンテキスト上のセッション」を利用するか、 HibernateUtil のようなヘルパークラスを利用するか、 proxy/interception ベースの「コンテキスト上のセッション」を提供する (Spring や Pico のような)サードパーティのフレームワークを利用するかのいずれかでした。
Starting with version 3.0.1, Hibernate added the SessionFactory.getCurrentSession() method. Initially, this assumed usage of JTA transactions, where the JTA transaction defined both the scope and context of a current session. Given the maturity of the numerous stand-alone JTA TransactionManager implementations, most, if not all, applications should be using JTA transaction management, whether or not they are deployed into a J2EE container. Based on that, the JTA-based contextual sessions are all you need to use.
しかし、バージョン 3.1 からは、 SessionFactory.getCurrentSession() の後の処理が、プラガブルになりました。これを受けて、現在のセッションを定義するスコープとコンテキストのプラガビリティを可能にするために、新しい拡張インタフェース ( org.hibernate.context.CurrentSessionContext ) と新しい構成パラメータ ( hibernate.current_session_context_class ) が追加されました。
See the Javadocs for the org.hibernate.context.CurrentSessionContext interface for a detailed discussion of its contract. It defines a single method, currentSession(), by which the implementation is responsible for tracking the current contextual session. Out-of-the-box, Hibernate comes with three implementations of this interface:
org.hibernate.context.JTASessionContext-JTAトランザクションによって、現在のセッションが追跡され、スコープを決められます。この処理は、古い JTA だけのアプローチとまったく同じです。詳細は Javadoc を参照してください。org.hibernate.context.ThreadLocalSessionContext- スレッドの実行によって、現在のセッションが追跡されます。詳細は Javadoc を参照してください。org.hibernate.context.ManagedSessionContext- スレッドの実行によって、現在のセッションが追跡されます。しかし、このクラスの static メソッドでSessionインスタンスをバインド/アンバインドする責任はあなたにあります。これは決してSessionをオープン、フラッシュ、クローズしません。
The first two implementations provide a "one session - one database transaction" programming model. This is also known and used as session-per-request. The beginning and end of a Hibernate session is defined by the duration of a database transaction. If you use programmatic transaction demarcation in plain JSE without JTA, you are advised to use the Hibernate Transaction API to hide the underlying transaction system from your code. If you use JTA, you can utilize the JTA interfaces to demarcate transactions. If you execute in an EJB container that supports CMT, transaction boundaries are defined declaratively and you do not need any transaction or session demarcation operations in your code. Refer to 13章Transactions and Concurrency for more information and code examples.
hibernate.current_session_context_class 設定パラメータは、 org.hibernate.context.CurrentSessionContext のどの実装を使うかを指定します。下位互換性のため、このパラメータが設定されず org.hibernate.transaction.TransactionManagerLookup が設定されていた場合、 Hibernate は org.hibernate.context.JTASessionContext を使うことに注意してください。通常このパラメータの値には、3つの実装の中から使用する実装クラスの名前を直接指定します。しかし、"jta"、 "thread"、 "managed"というそれぞれの省略名も用意されています。