Have you ever caught yourself by unintentionally doing things like
annotating Strings with @Min to specify a minimum length (instead of using @Size)
annotating the setter of a JavaBean property (instead of the getter method)
annotating static fields/methods with constraint annotations (which is not supported)?
Then the Hibernate Validator Annotation Processor is the right thing for you. It helps preventing such mistakes by plugging into the build process and raising compilation errors whenever constraint annotations are incorrectly used.
Warning
A first version of the Hibernate Validator Annotation Processor is part of Hibernate Validator since release 4.1. It is currently still under development and should therefore be considered as an experimental feature. Some known issues can be found at the end of this chapter. In case any problems arise when using the processor feel free to ask for help at the forum or create an issue within JIRA.
The Hibernate Validator Annotation Processor is based on the "Pluggable Annotation Processing API" as defined by JSR 269. This API is part of the Java Platform since Java 6. So be sure to use this or a later version.
As of Hibernate Validator 4.1 the Hibernate Validator Annotation Processor checks that:
constraint annotations are allowed for the type of the annotated element
JavaBean getter methods are annotated in case of property validation
only non-static fields or properties are annotated with constraint annotations
only non-primitive fields or properties are annotated with @Valid
only such annotation types are annotated with constraint annotations which are constraint annotations themselves
The behavior of the Hibernate Validator Annotation Processor can be controlled using the processor options listed in tableTable 8.1, “Hibernate Validator Annotation Processor options”:
Table 8.1. Hibernate Validator Annotation Processor options
| Option | Explanation |
|---|---|
diagnosticKind | Controls how constraint problems are reported. Must be the
string representation of one of the values from the enum
javax.tools.Diagnostic.Kind, e.g.
WARNING. A value of
ERROR will cause compilation to halt
whenever the AP detects a constraint problem. Defaults to
ERROR. |
verbose | Controls whether detailed processing information shall be
displayed or not, useful for debugging purposes. Must be either
true orfalse. Defaults to
false. |
This section shows in detail how to integrate the Hibernate Validator Annotation Processor into command line builds (javac, Ant, Maven) as well as IDE-based builds (Eclipse, IntelliJ IDEA, NetBeans).
When compiling on the command line using javac, specify the following JARs using the "processorpath" option:
validation-api-1.0.0.GA.jar
hibernate-validator-annotation-processor-4.1.0.Final.jar
The following listing shows an example. The processor will be detected automatically by the compiler and invoked during compilation.
Example 8.1. Using the annotation processor with javac
javac src/main/java/org/hibernate/validator/ap/demo/Car.java \ -cp /path/to/validation-api-1.0.0.GA.jar \ -processorpath /path/to/validation-api-1.0.0.GA.jar:/path/to/hibernate-validator-annotation-processor-4.1.0.Final.jar
Similar to directly working with javac, the annotation processor can be added as as compiler argument when invoking the javac task for Apache Ant:
Example 8.2. Using the annotation processor with Ant
<javac srcdir="src/main"
destdir="build/classes"
classpath="/path/to/validation-api-1.0.0.GA.jar">
<compilerarg value="-processorpath" />
<compilerarg value="/path/to/validation-api-1.0.0.GA.jar:/path/to/hibernate-validator-annotation-processor-4.1.0.Final.jar"/>
</javac>There are several options for integrating the annotation processor with Apache Maven. Generally it is sufficient to add the Hibernate Validator Annotation Processor as dependency to your project:
Example 8.3. Adding the HV Annotation Processor as dependency
...
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hibernate</groupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-validator-annotation-processor</artifactId>
<version>4.1.0.Final</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
... The processor will then be executed automatically by the compiler. This basically works, but comes with the disadavantage that in some cases messages from the annotation processor are not displayed (see MCOMPILER-66).
Another option is using the Maven Annotation Plugin. At the time of this writing the plugin is not yet available in any of the well-known repositories. Therefore you have to add the project's own repository to your settings.xml or pom.xml:
Example 8.4. Adding the Maven Annotation Plugin repository
...
<pluginRepositories>
<pluginRepository>
<id>maven-annotation-plugin-repo</id>
<url>http://maven-annotation-plugin.googlecode.com/svn/trunk/mavenrepo</url>
</pluginRepository>
</pluginRepositories>
...
Now disable the standard annotation processing performed
by the compiler plugin and configure the annotation plugin by
specifying an execution and adding the Hibernate Validator Annotation
Processor as plugin dependency (that way the AP is not visible on the
project's actual classpath):
Example 8.5. Configuring the Maven Annotation Plugin
...
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<source>1.6</source>
<target>1.6</target>
<compilerArgument>-proc:none</compilerArgument>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.bsc.maven</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-processor-plugin</artifactId>
<version>1.3.4</version>
<executions>
<execution>
<id>process</id>
<goals>
<goal>process</goal>
</goals>
<phase>process-sources</phase>
</execution>
</executions>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hibernate</groupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-validator-annotation-processor</artifactId>
<version>4.1.0.Final</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</plugin>
...
Do the following to use the annotation processor within the Eclipse IDE:
Right-click your project, choose "Properties"
Go to "Java Compiler" and make sure, that "Compiler compliance level" is set to "1.6". Otherwise the processor won't be activated
Go to "Java Compiler - Annotation Processing" and choose "Enable annotation processing"
Go to "Java Compiler - Annotation Processing - Factory Path" and add the following JARs:
validation-api-1.0.0.GA.jar
hibernate-validator-annotation-processor-4.1.0.Final.jar
Confirm the workspace rebuild
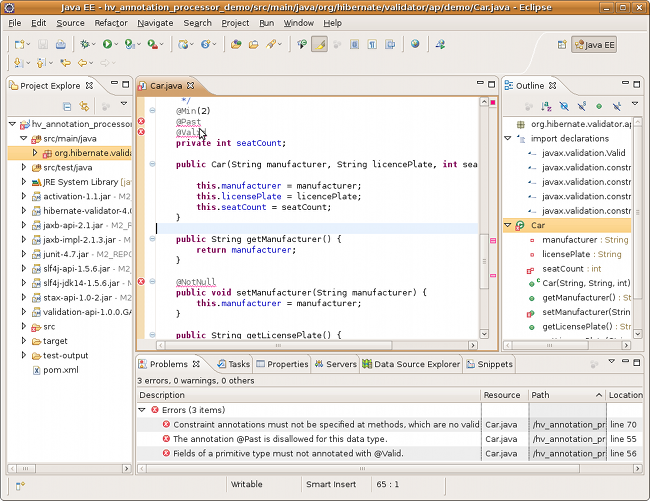
You now should see any annotation problems as regular error markers within the editor and in the "Problem" view:
The following steps must be followed to use the annotation processor within IntelliJ IDEA (version 9 and above):
Go to "File", then "Settings",
Expand the node "Compiler", then "Annotation Processors"
Choose "Enable annotation processing" and enter the following as "Processor path": /path/to/validation-api-1.0.0.GA.jar:/path/to/hibernate-validator-annotation-processor-4.1.0.Final.jar
Add the processor's fully qualified name
org.hibernate.validator.ap.ConstraintValidationProcessorto the "Annotation Processors" listIf applicable add you module to the "Processed Modules" list
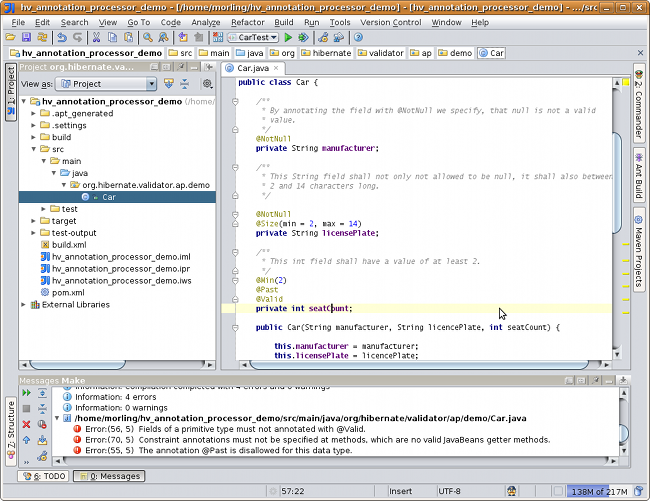
Rebuilding your project then should show any erronous constraint annotations:
Starting with version 6.9, also the NetBeans IDE supports using annotation processors within the IDE build. To do so, do the following:
Right-click your project, choose "Properties"
Go to "Libraries", tab "Processor", and add the following two JARs:
validation-api-1.0.0.GA.jar
hibernate-validator-annotation-processor-4.1.0.Final.jar
Go to "Build - Compiling", select "Enable Annotation Processing" and "Enable Annotation Processing in Editor". Add the annotation processor by specifying its fully qualified name
org.hibernate.validator.ap.ConstraintValidationProcessor
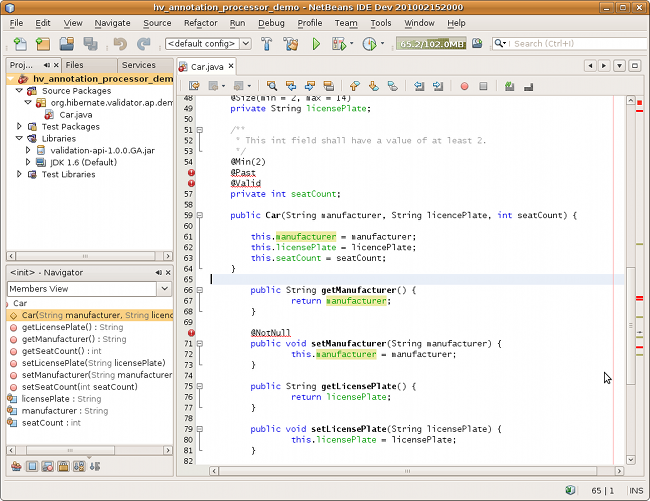
Any constraint annotation problems will then be marked directly within the editor:
The following known issues exist as of May 2010:
HV-308: Additional validators registered for a constraint using XML are not evaluated by the annotation processor.
Sometimes custom constraints can't be properly evaluated when using the processor within Eclipse. Cleaning the project can help in these situations. This seems to be an issue with the Eclipse JSR 269 API implementation, but further investigation is required here.