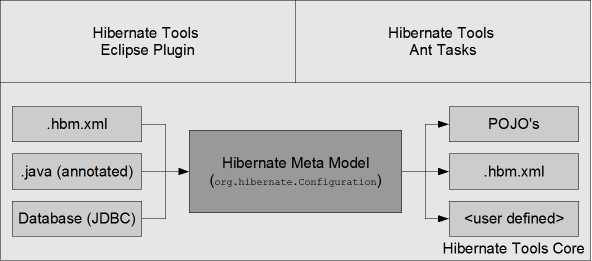
The code generation mechanism in Hibernate Tools™ consists of a few core concepts. This section explains their overall structure, which are the same for the Ant™ and Eclipse™ tools.
The meta model is the model used by Hibernate Core™ to perform its object relational mapping. The model includes information about tables, columns, classes, properties, components, values, collections etc. The API is in the org.hibernate.mapping package and its main entry point is the Configuration class, the same class that is used to build a session factory.
The model represented by the Configuration class can be built in many ways, which are listed below.
A Core configuration uses Hibernate Core™ and supports reading
hbm.xmlfiles, and requires ahibernate.cfg.xmlfile. This is referred to as core™ in Eclipse and<configuration>in Ant.An Annotation configuration uses Hibernate Annotations™ and supports
hbm.xmlfiles and annotated classes, and requires ahibernate.cfg.xmlfile. This is referred to as annotations™ in Eclipse and<annotationconfiguration>in Ant.A JPA configuration uses a Hibernate EntityManager™ and supports
hbm.xmlfiles and annotated classes, and requires that the project has aMETA-INF/persistence.xmlfile in its classpath. This is referred to as JPA™ in Eclipse and<jpaconfiguration>in Ant.A JDBC configuration uses Hibernate Tools reverse engineering and reads its mappings via JDBC metadata + additional reverse engineering files (
reveng.xml). Automatically used in Eclipse when doing reverse engineering from JDBC and referred to as<jdbcconfiguration>in Ant.
In most projects you will normally use only one of the Core, Annotation or JPA configuration and possibly the JDBC configuration if you are using the reverse engineering facilities of Hibernate Tools™.
Note:
No matter which Hibernate Configuration type you are using Hibernate Tools™ supports them.
The following drawing illustrates the core concepts:
The code generation is performed based on the Configuration model no matter which type of configuration has been used to create the meta model, and thus the code generation is independent on the source of the meta model and represented via Exporters.
Code generation is done in so called Exporters. An Exporter is handed a Hibernate Meta Model represented as a Configuration instance and it is then the job of the exporter to generate a set of code artifacts.
The tools provides a default set of Exporter's which can be used in both Ant and the Eclipse UI. Documentation for these Exporters is in Chapter 5, Ant Tools and Chapter 4, Eclipse Plugins.
Users can provide their own custom Exporter's, either through custom classes implementing the Exporter interface or simply be providing custom templates. This is documented at in Section 5.4.7, “Generic Hibernate metamodel exporter (<hbmtemplate>)”.