A domain-specific language is a set of custom rules, that is created specifically to solve problems in a particular domain and is not intended to be able to solve problems outside it. A DSL's configuration is stored in plain text.
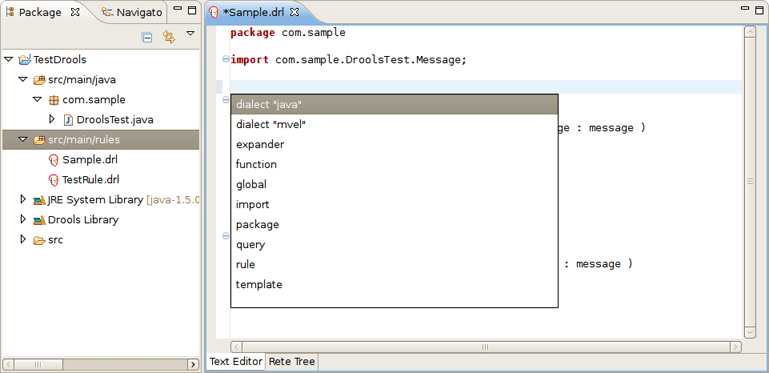
In Drools this configuration is presented by .dsl files that can be created selecting → → → → from the projects context menu.
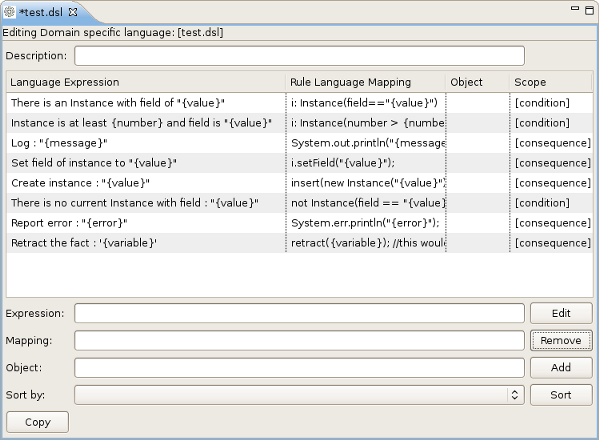
DSL Editor is a default editor for .dsl files:
In the table below all the components of the DSL Editor page are described:
Table 4.1. DSL Editor Components.
| Components | Description |
|---|---|
| Description | User's comments on a certain language message mapping |
| Table of language message mappings | The table is divided into 4 rows:
|
| Expression | Shows the language expression of the selected table line (language message mapping). |
| Mapping | Shows the rule of language mapping for the selected table line (language message mapping). |
| Object | Shows the object for the selected table line (language message mapping) |
| Sort By | Using this option you can change the sorting order of the language message mappings. To do this select from the drop down list the method of sorting you want and click the button. |
| Buttons |
|
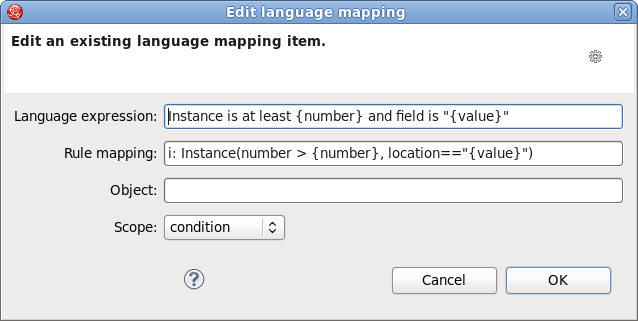
This wizard can be opened by double clicking some line in the table of language message mappings or by clicking the button.
On the picture below you can see all the options the Edit Language Mapping Wizard will allow you to change.
Their names as well as the meaning of the options are correspond to the rows of the table (see the Table of language message mappings row in Table 4.1, “DSL Editor Components.”).
To change the mapping a user should edit the appropriate options and finally click the button.
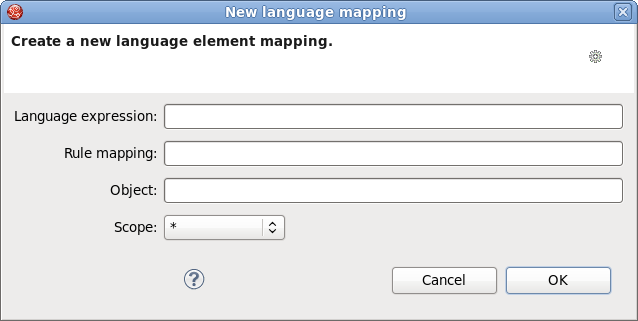
This wizard is equal to the wizard described in Section 4.1.1, “Edit language mapping Wizard”. It can be opened by clicking the button.
The only difference is that instead of editing the information you should enter new one.
Drools tools also provides the ability to define the order in which rules should be executed. The Ruleflow file allows you to specify the order in which rule sets should be evaluated using a flow chart. This allows you to define which rule sets should be evaluated in sequence or in parallel as well as specify the conditions under which rule sets should be evaluated.
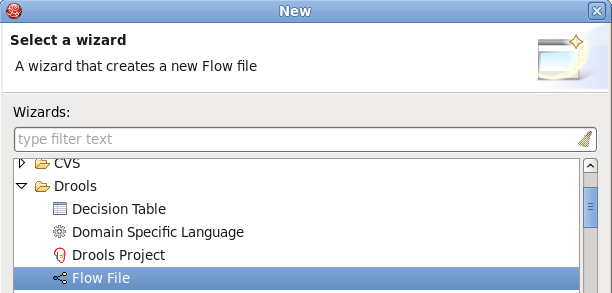
Ruleflows can be set only by using the graphical flow editor which is part of the Drools plugin for Eclipse. Once you have set up a Drools project,you can start adding ruleflows. Add a ruleflow file(.rf) by clicking on the project and selecting → → → :
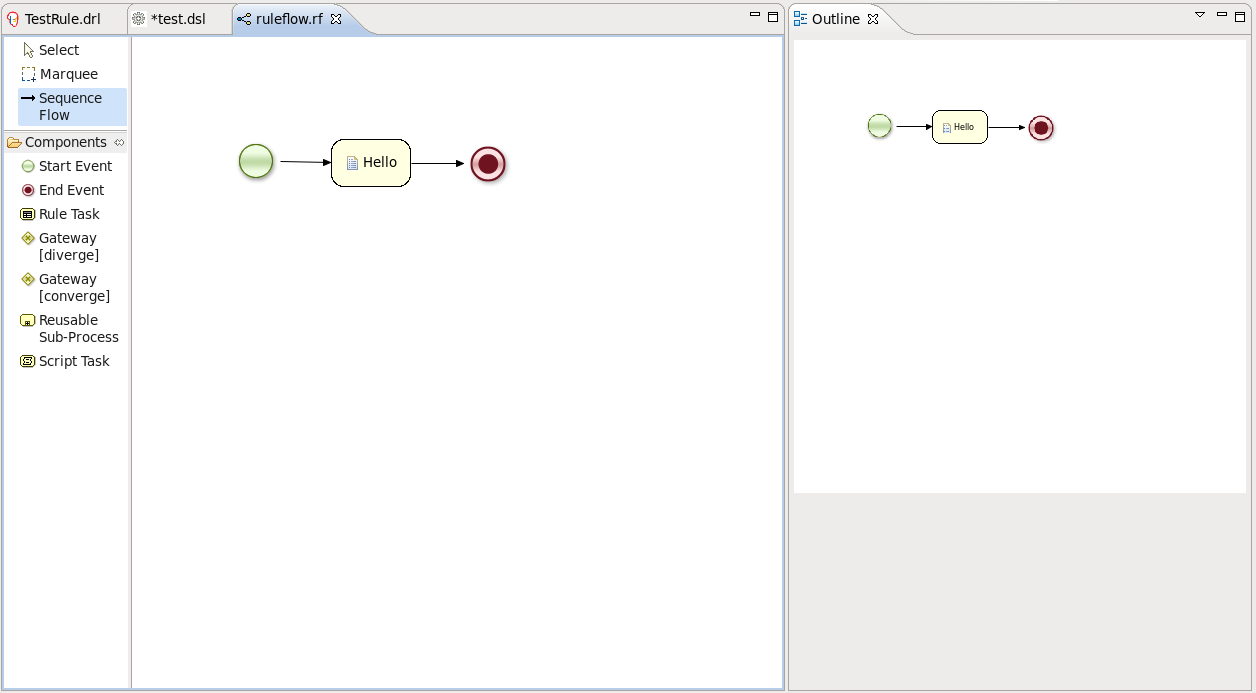
By default these ruleflow files (.rf) are opened in the graphical Flow editor. You can see this in the picture below.
The Flow editor consists of a palette, a canvas and an outline view. To add new elements to the canvas, select the element you would like to create in the palette and then add it to the canvas by clicking on the preferred location.
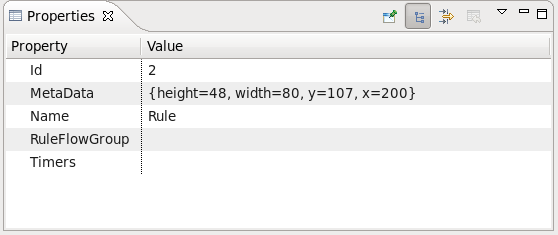
Clicking on the Select option in the palette and then on the element in your ruleflow allows you to view and set the properties of that element in the Properties view.
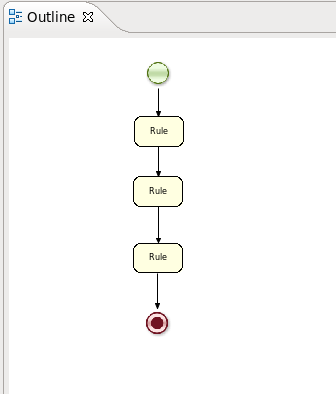
The Outline view is useful for big complex schemata where not all nodes are seen at one time. So using your Outline view you can easily navigate between parts of a schema.
Flow editor supports three types of control elements. They are:
Table 4.2. Flow Palette Components.Part 1
| Component Picture | Component Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
| Select | Select a node on the canvas |
|
| Marquee | Is used for selecting a group of elements |
|
| Sequence Flow | Use this element to join two elements on the canvas |
Currently, ruleflow supports seven types of nodes. In the table below you can find information about them:
Table 4.3. Flow Palette Components.Part 2.
| Component Picture | Component Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
| Start Event | The start of the ruleflow. A ruleflow should have exactly one start node. The Start Event can not have incoming connections and should have one outgoing connection. Whenever the ruleflow process is started, the execution is started here and is automatically proceeded to the first node linked to this Start Event |
|
| End Event | A ruleflow file can have one or more End Events. The End Event node should have one incoming connection and can not have outgoing connections. When an end node is reached in the ruleflow, the ruleflow is terminated (including other remaining active nodes when parallelism is used). |
|
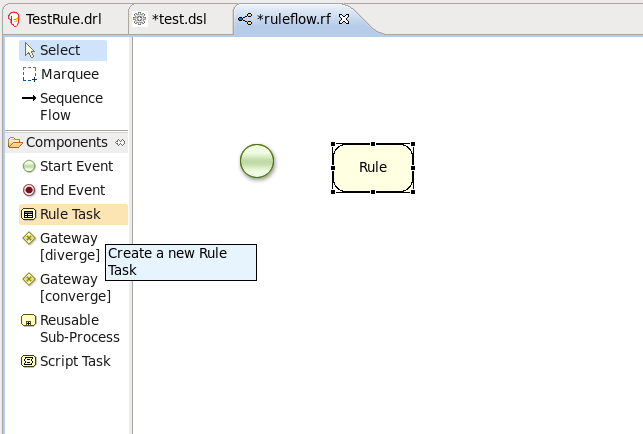
| Rule Task | Represents a set of rules. A Rule Task node should have one incoming connection and one outgoing connection. The RuleFlowGroup property which is used to specify the name of the ruleflow-group that represents the set of rules of this Rule Task node. When a Rule Task node is reached in the ruleflow, the engine will start executing rules that are a part of the corresponding ruleflow-group. Execution automatically continues to the next node when there are no more active rules in this ruleflow-group. |
|
| Gateway[diverge] | Allows you to create branches in your ruleflow. A Gateway[diverge] node should have one incoming connection and two or more outgoing connections. |
|
| Gateway[converge] | Allows you to synchronize multiple branches. A Gateway[converge] node should have two or more incoming connections and one outgoing connection. |
|
| Reusable Sup-Process | Represents the invocation of another ruleflow from this ruleflow. A subflow node should have one incoming connection and one outgoing connection. It contains the property processId which specifies the id of the process that should be executed. When a Reusable Sup-Process node is reached in the ruleflow, the engine will start the process with the given id. The subflow node will only continue if that subflow process has terminated its execution. Note that the subflow process is started as an independent process, which means that the subflow process will not be terminated if this process reaches an end node. |
|
| Script Task | Represents an action that should be executed in this ruleflow. An Script Task node should have one incoming connection and one outgoing connection. It contains the property "action" which specifies the action that should be executed. When a Script Task node is reached in the ruleflow, it will execute the action and continue with the next node. An action should be specified as a piece of (valid) MVEL code. |
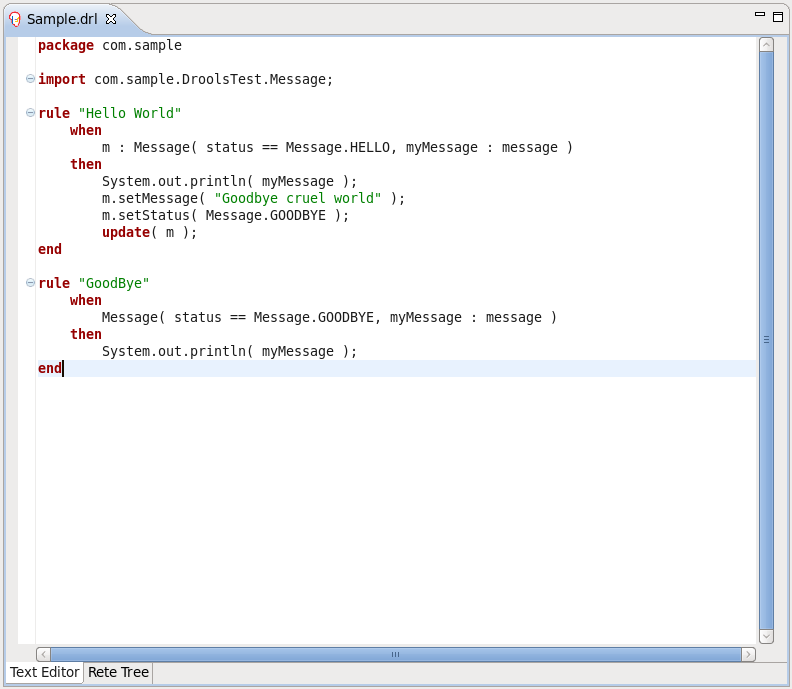
The Rule editor works on files that have a .drl (or .rule in the case of spreading rules across multiple rule files) extension.
The editor follows the pattern of a normal text editor in eclipse, with all the normal features of a text editor:
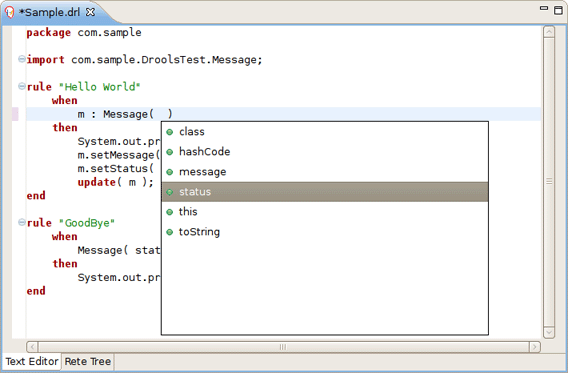
While working in the Rule editor you can get a content assistance the usual way by pressing Ctrl+Space.
Content Assist shows all possible keywords for the current cursor position.
Content Assist inside of the Message suggests all available fields.
Code folding is also available in the Rule editor. To hide and show sections of the file use the icons with minus and plus on the left vertical line of the editor.
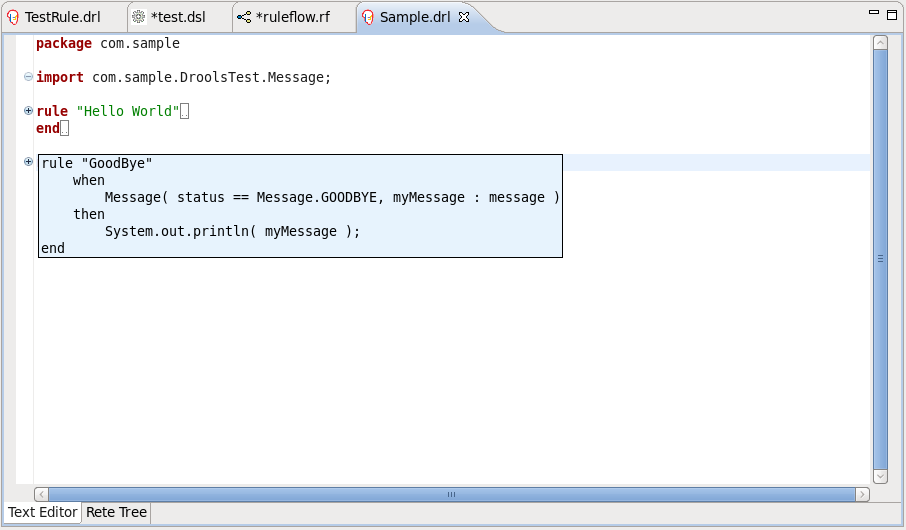
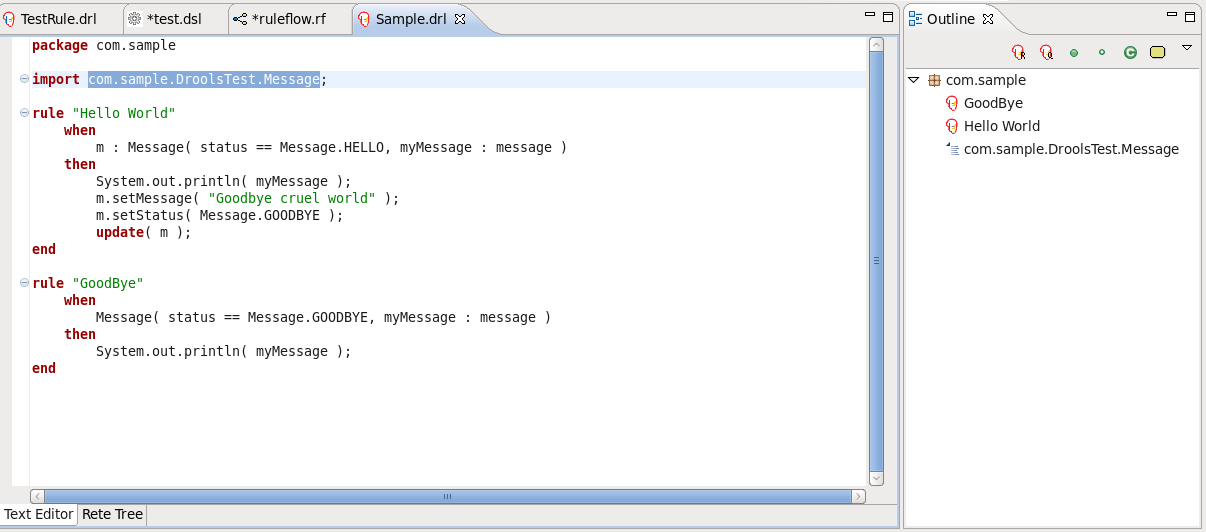
The Rule editor works in synchronization with the Outline view which shows the structure of the rules, imports in the file and also globals and functions if the file has them.
The view is updated on save. It provides a quick way of navigating around rules by names in a file which may have hundreds of rules. The items are sorted alphabetically by default.
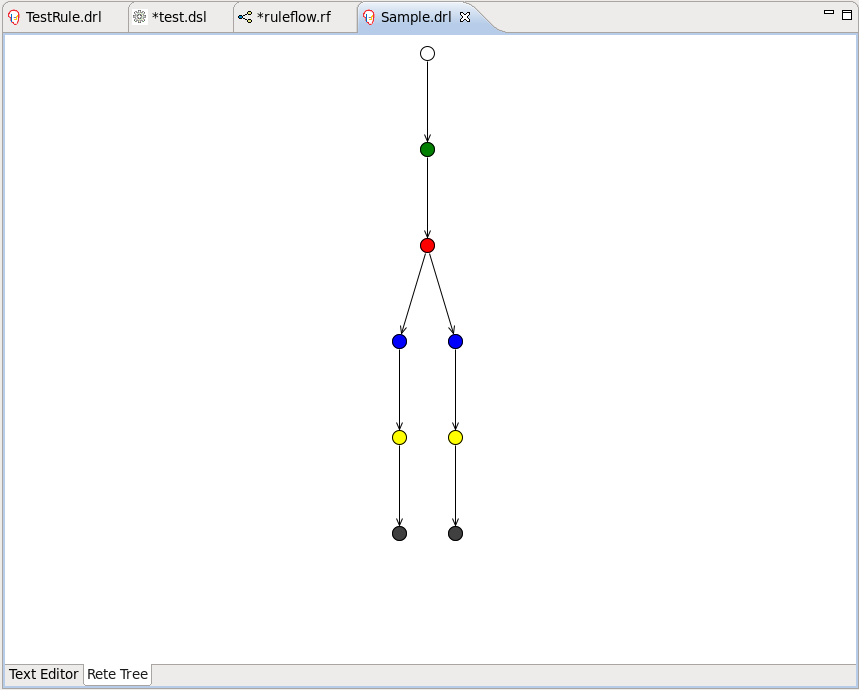
The Rete Tree view shows you the current Rete Network for your .drl file. Just click on the Rete Tree tab at the bottom of the Rule editor.
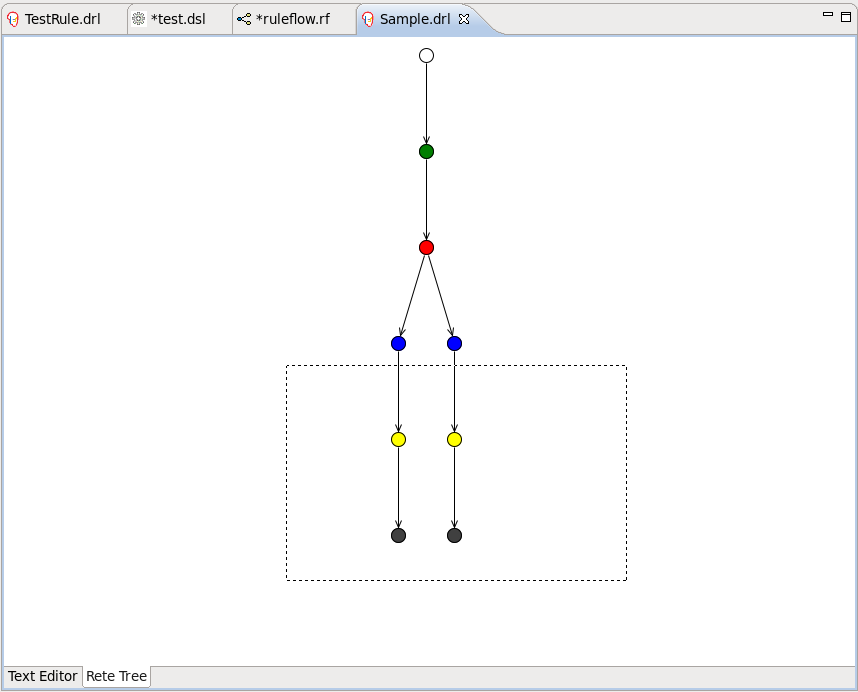
Afterwards you can generate the current Rete Network visualization. You can push and pull the nodes to arrange your optimal network overview.
If you have a large number of nodes, select some of them with a frame. Then you can pull groups of them.
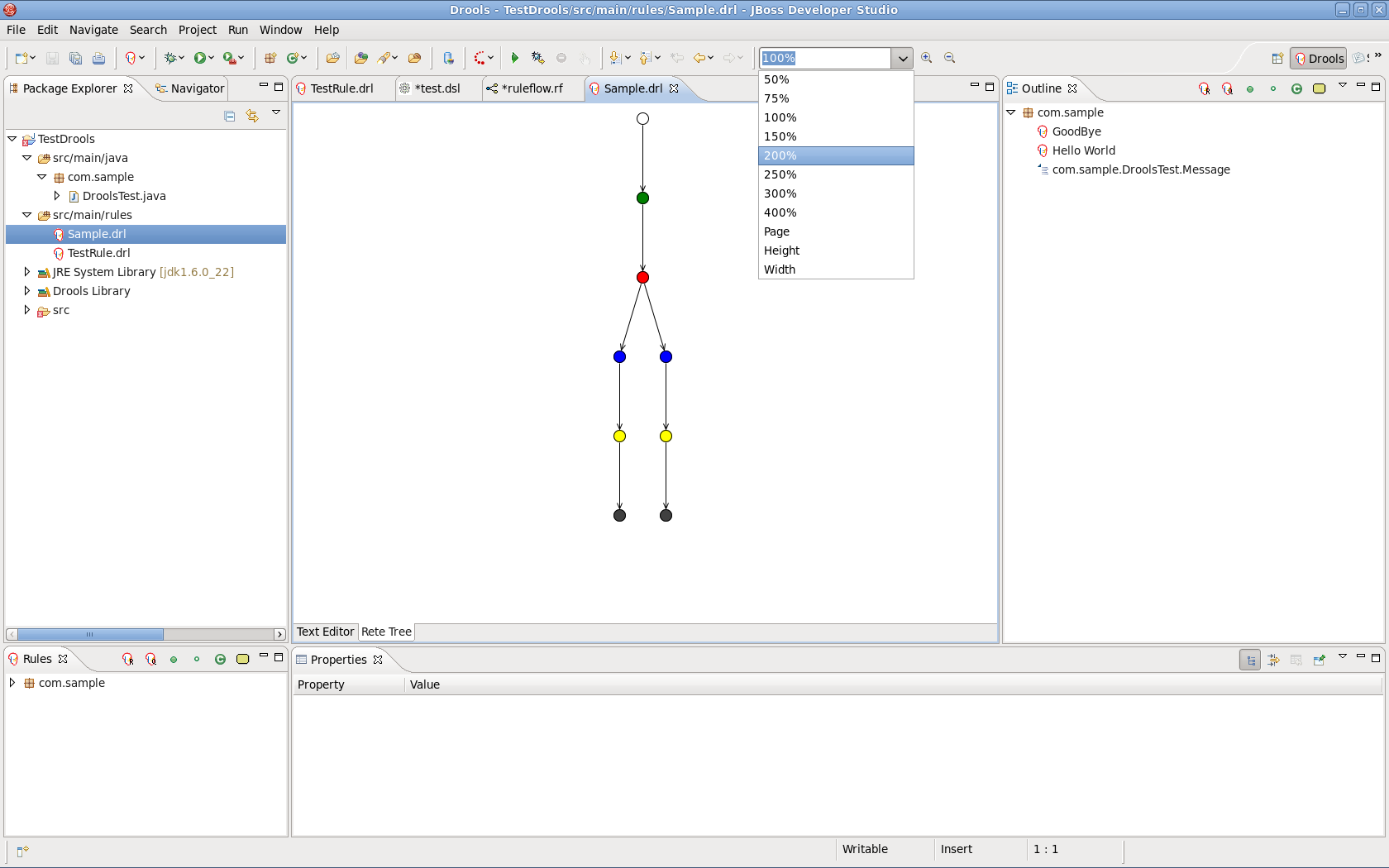
You can zoom in and out the Rete tree in case not all nodes are shown in the current view. For this use the combobox or and icons on the toolbar.
Note:
The Rete Tree view works only in Drools Rule Projects, where the Drools Builder is set in the project properties.
We hope, this guide helped you to get started with the JBoss BPMN Convert module. For additional information you are welcome on JBoss forum.