JBoss.orgCommunity Documentation
Version: 3.0.0.beta1
Copyright © 2007, 2008 JBoss, a division of Red Hat Inc.
April 2008
- 1. Introduction
- 2. Creating a New Seam Project via the New Seam Project wizard
- 3. Directory Structure of the Generated Project
- 4. Seam Menus and Actions
- 5. Seam Wizards
- 6. Seam Generate Entities
- 7. Seam Editors Features
- 8. Seam Views
- 9. Seam Preferences
- 10. Generate a CRUD Database Application
- 11. The CRUD Application Walkthrough
- 12. Using TestNG project
This introduction will help you to understand what is Seam.
Seam is a fully featured application framework on top of Java EE 5. It is also one of the most popular enterprise Java framework today. Seam deeply integrates many other standard-based or open source frameworks (e.g., JSF, EJB3, JMS, Web Services, jBPM, JBoss Rules, Ajax4jsf, RichFaces, Facelets, Spring, iText, Quartz, TestNG, etc.), and provides a single programming model for developers to "drive" those underlying frameworks via simple annotated POJOs (Plain Old Java Objects). It makes life easier for developers to tackle complex enterprise applications with many component frameworks.
Here, we are going to explain how to install Seam plugin into Eclipse.
Seam is a one module of JBoss Tools project. Since Seam has a dependence on other JBoss Tools modules we recommend you to install a bundle of all JBoss Tools plug-ins. Installation instruction you can find on JBoss Wiki in InstallingJBossTools section.
The Seam Framework - Next generation enterprise Java development.
All latest release versions of JBoss Developer Studio/JBoss Tools documentation you can find here.
The latest documentation builds are available here.
In this chapter we provide you with the necessary steps to start working with Seam Framework.
At first, we suggest setting the specific Seam perspective that combines a number of different views and editors needed for work with resources concerned. For that select Window > Open Perspective > Other > Seam or you can also access it through the button in the right top corner.
The best way to get started with Seam is to organise a simple Seam Project and experiment with it by creating variations.
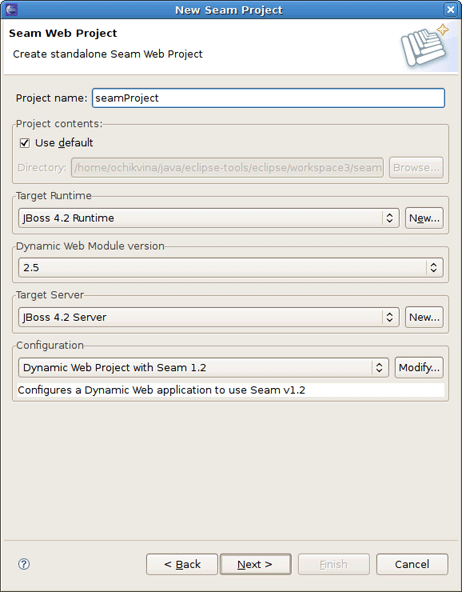
Thus, you should select File > New > Seam Web Project to run the New Seam Project wizard. The wizard form allows you to create runtime and server instances in order to get started creating, running, and debugging J2EE (only) applications.
Seam Web Project wizard has an option for selecting the actual Server (not just WTP runtime) that will be used for the project. This allows the wizard to identify correctly where the required datasource and driver libraries need to go.
Let's get through the wizard step-by-step. First, you should enter a name and a location directory for your new project.
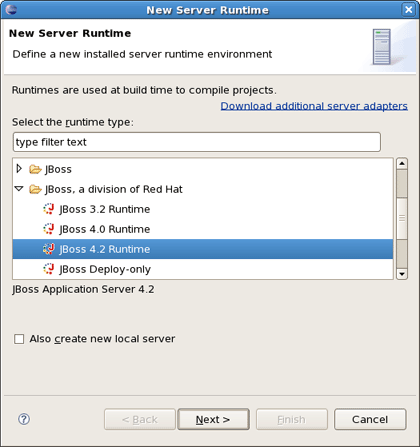
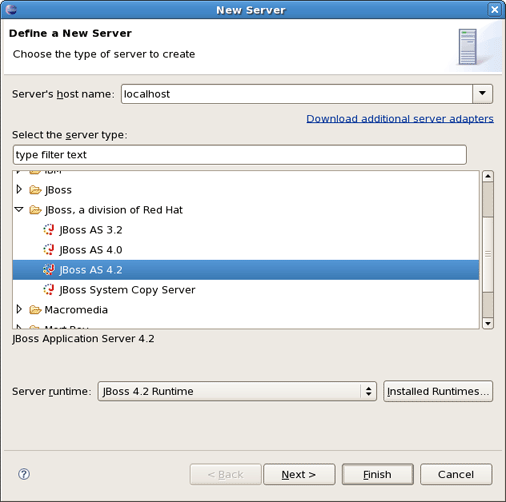
Clicking on New... button in the <proeprty>Target Runtime</proeprty> section will bring you to another dialog. Here, you can specify a new installed Runtime environment or the other type of runtime appropriate for configuring your project. Let's create a JBoss 4.2 Runtime. For that after choosing it click on Next button.
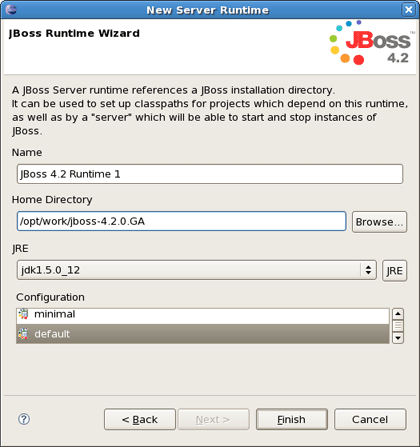
All what you need here is to name runtime, type the path to its install directory or locate it by using Browse button, select a Java Runtime Environment, and select which configuration you want.
Clicking on Finish returns you to the previous dialog. The next step is to define an installed server that you can do by clicking on New... button in the Target Server section. In appeared Server Dialog it's possible to select a server version.
If the chosen server has already got an installed runtime, there appears a combo box with all declared runtimes under the servers view. Here, you can indicate a server runtime that you need. Use Installed Runtimes... button to see or edit which runtimes are installed. If there is no any declared runtime for chosen server, click on Next to specify it on the next preferences page.
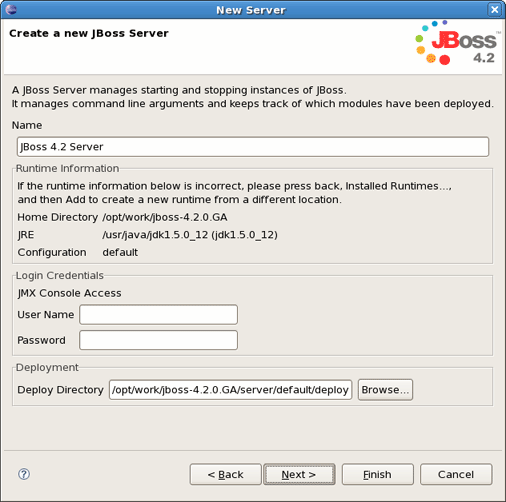
Next dialog allows you to verify the information for chosen server, set login credentials to authorize an access to the server and specify a directory for deploying. Leave everything as it is and click on Next .
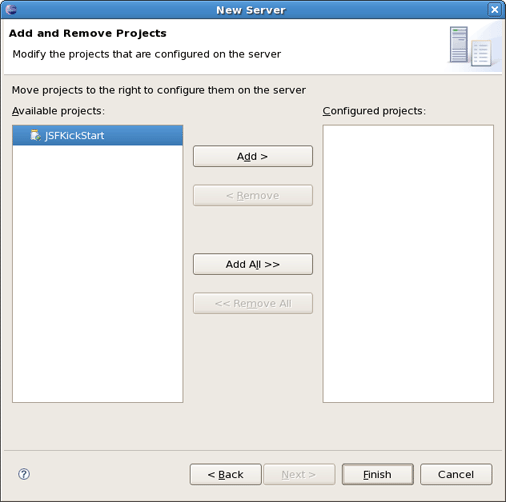
On the last wizard step you can modify your project to configure it on server.
Once you have the Target Server defined click on Finish button to return to the first page of the New Seam Project wizard.
Tip:
We suggest that you look through our AS manager guide to find out more about runtimes and servers.
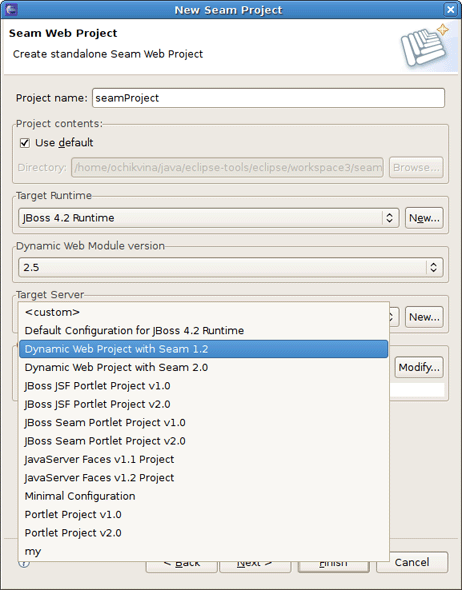
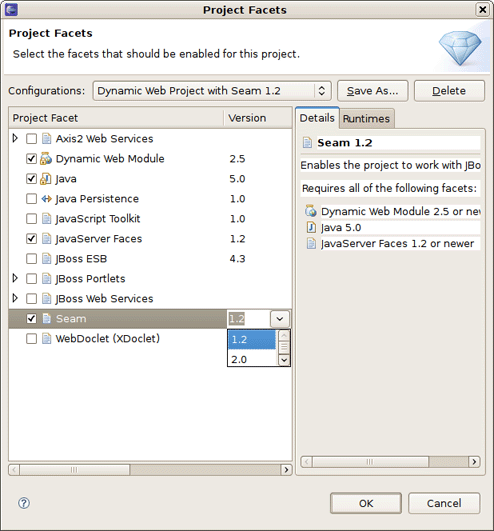
The last section on this wizard step is Configuration. Here, you can select one of the pre-defined project configurations either associated with Seam 1.2 or with Seam 2.0. Furthermore, you can create your own configuration by pressing the Modify... button. It will open the dialog which allows to configure your own set of facets for adding extra functionality to your project.
Pass to the next section to find out more details on this dialog.
The Project Facets wizard allows you to enable or disable specific facets which define necessary characteristics for the project. In time you switch to this wizard form, all critical facets are already checked for the chosen Configuration.
Notice that this page of the wizard also allows you to set the necessary version for any facet.
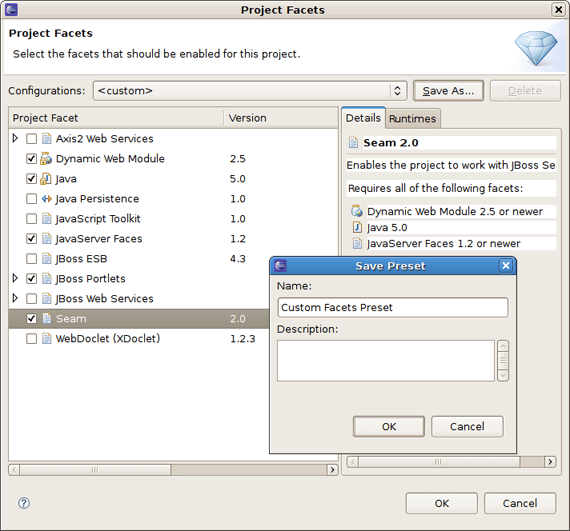
Moreover, here you can specify your own preset of selected facets by checking needed ones in project facets window and clicking on Save button.
To see all available Server runtimes click on Runtimes tab on the left. You can create a new one using the New button. If more than one runtimes are checked here, the Make Primary button won't be dimmed yet. So you can make use of it to mark primary runtime.
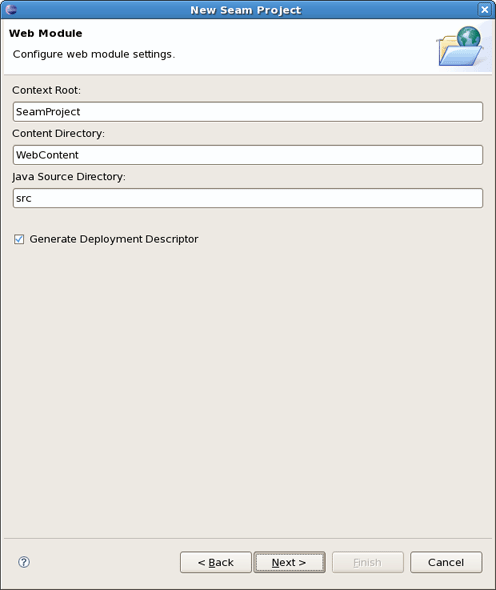
Next button will bring you to the Web Module wizard form.
As we deal with a Dynamic Web Application we should first specify the top level directory of our application for deploying it to a server afterwards. You know, this kind of application contains both Web and Java code resources. Thus, it's also important to indicate the content directory as well as Java source directory. The wizard will put all those values itself. So you can leave everything as it is.
Choose Next to switch to the next wizard form.
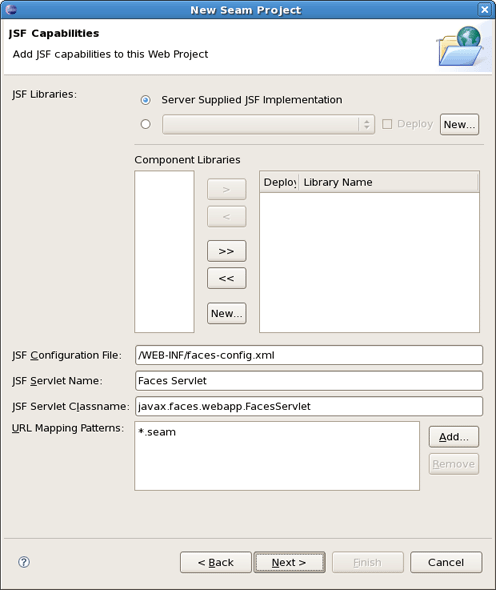
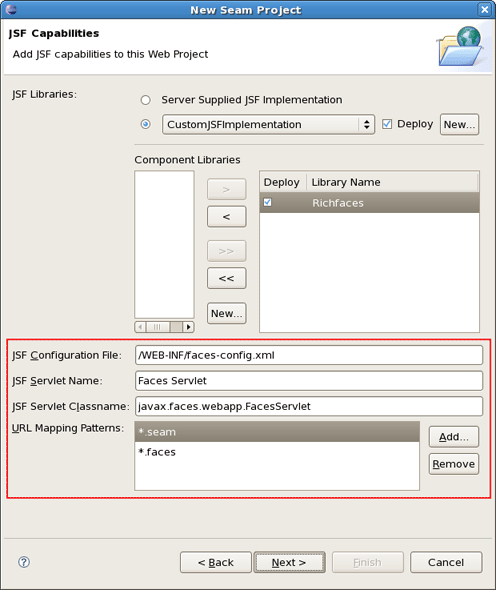
This wizard helps you to add JSF capabilities into your project for representing appropriate behaviours associated with JSF.
Checking Server Supplied JSF Implementation means that you will have a default JSF implementation given by server.
In case when you want to use your custom JSF implementation check a lower radio button. You are able to create a library of jars by clicking on New button.
Here, it's necessary to type a Library Name, select a Version Supported and add proper Library jars. Then click on Finish to complete the choice.
In the Component Libraries section of the wizard you can also add Component Libraries (e.g. Richfaces). Just click on New button. Appeared dialog will ask you to type the Library name, supported version and add necessary jar's. Press Finish to complete the choice.
The last wizard options allows to edit a path for JSF Configuration File, a name for JSF Servlet, JSF Servlet Classname and change URL Mapping Patterns.
Finally, as we are arranging the Seam Web project, the last step we should do is to adjust project configurations associated with the Seam.
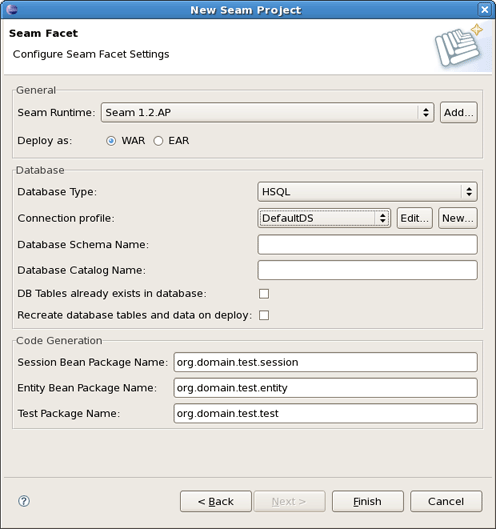
The last wizard step is related to Seam facet and allows you to do the following:
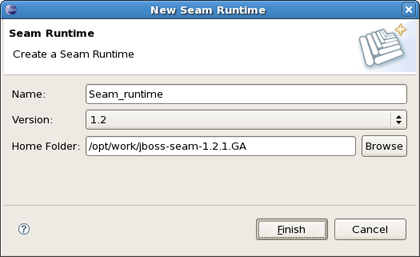
Create Seam runtime and define Seam home folder.
For that click on Add button in the General section. Notice that in this wizard presented below you can create a Seam runtime only for that version which was selected in the Project Facets wizard (version 1.2 in our case).
Select EAR or WAR deployment by checking a necessary radio button.
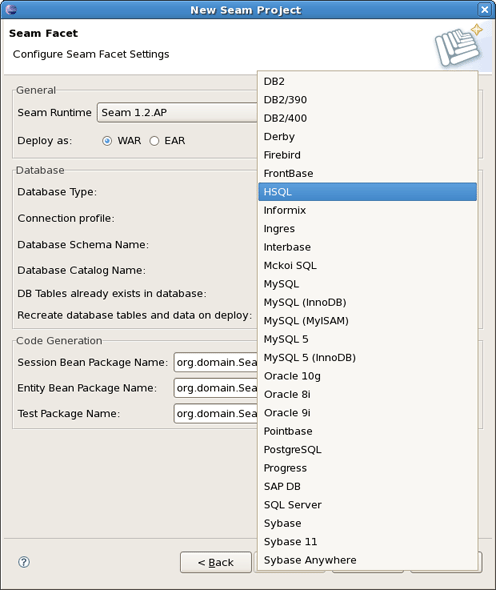
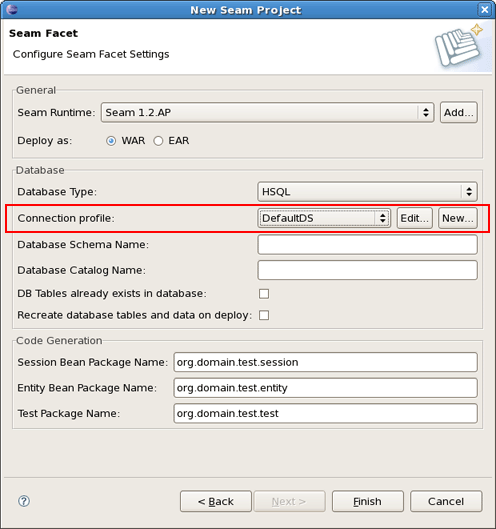
Select a Database Type
and then specify a Connection profile appropriate for your database.
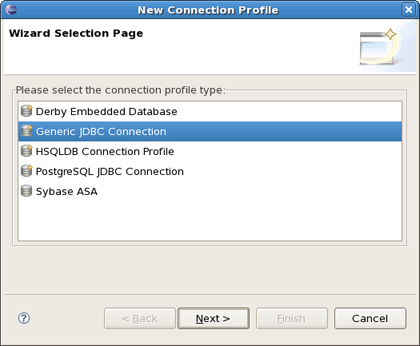
You can edit chosen profile by using Edit button or organise a new one by clicking on New button and selecting necessary for you type of connection profile.
On the other dialog you'll be asked to enter its name and description. And then you should select a proper driver and adjust connection details. Press Next to preview all the adjusted settings and complete the creation of the new profile.
The next block of settings in the Seam Facet wizard are describing a Database and a connection to it.
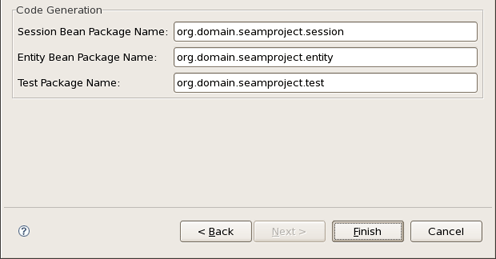
In the Code Generation section the wizard have already put the names for your Session Bean, Entity Bean and Test packages. Of course, you can change them into the others which you like.
Click on Finish to generate a project.
In this chapter we describe where the Seam wizard puts the generated files for both EAR and WAR deployments.
The Seam Project wizard generates projects like Eclipse WTP style in order to utilize Eclipse WTP features and to have a correct classpath. To be more precise it generates one project per artifact.
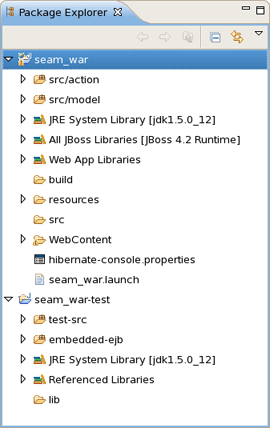
The project layout for WAR projects is:
A WAR project can only use Seam JavaBean and JPA Entity bean components; it cannot use EJB3 Session beans etc.
WAR projects are generated to enable Seam 1.2.1 war hotdeploy feature. Classes put into src/action will be deployed to WEB-INF/dev from which Seam 1.2.1 automatically will perform hotdeploy of new components.
Note:
Because of Eclipse WTP limits the hot deployed classes also existed in WEB-INF/classes, but since Seam gives WEB-INF/dev precedence it will work.
Furthermore the Seam Project wizard generates a test project that is setup to run TestNG directly against the proper libraries and server runtime libraries. When the TestNG plugin is installed you can just run your tests via Run As > TestNG Test.
In order to deploy WAR project on server, right-click on the project and select Run As > Run on Server. Studio will deploy WAR project into one web application on server to deploy folder.
The project layout for EAR projects is:
An EAR project can use the whole range of Seam components, including EJB3 Session beans.
In order to deploy EAR project on server, right-click on the project with -ear postfix and select Run As > Run on Server. Studio will take care about all modules and deploy EAR project into one enterprise application on server to deploy folder. EAR application keeps ejb and war modules of the EAR project.
If you need to rename one of the Seam Project artifacts (<project_name>, <project_name>-test, <project_name>-test or <project_name>-ejb) or any entire folder like <project_name>/WebContent, <project_name>/ejbModule, <project_name>-test/test-src, or project name in packages org.domain.<project_name>.session, org.domain.<project_name>.entity, you can do this by brining the context menu and navigating Refactor > Rename... or just pressing Shift + Alt + R under the chosen resource.
Use Refactor > Move... (or Shift + Alt + V ), if you need to move <project_name>/WebContent folder, <project_name>/ejbModule folder or <project_name>/test-src folder in the other place within the Project structure.
In this chapter we provide a description of Seam actions that are available from
Menu bar
Toolbar
Context menus in views
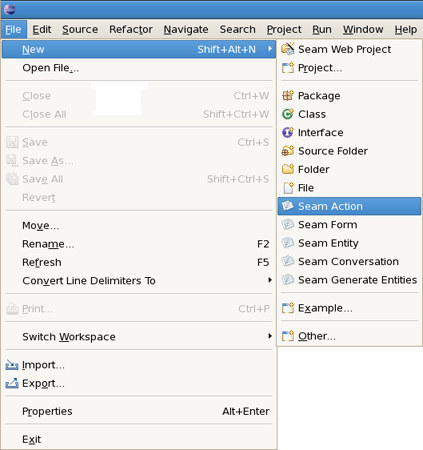
In a Seam perspective, by default there are the following actions in File > New submenu
Table 4.1. Seam Actions in the New Submenu
|
Name |
Function |
|---|---|
|
Seam Web Project |
Runs New Seam Project wizard for creating a new Seam project |
|
Seam Action |
Runs New Seam Action wizard for creating a new Seam action |
|
Seam Form |
Runs New Seam Form wizard for creating a new Seam form |
|
Seam Entity |
Runs New Seam Entity wizard for creating a new Seam entity |
|
Seam Conversation |
Runs New Seam Conversation wizard for creating a new Seam conversation |
|
Seam Generate Entities |
Runs Generate Seam Entities wizard |
In the next sections we are going to describe Seam actions which can help you to easily navigate through the source code.
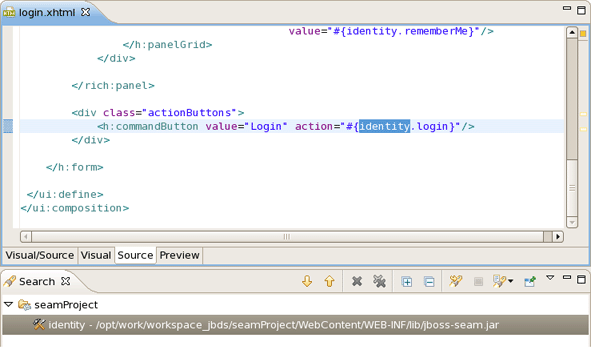
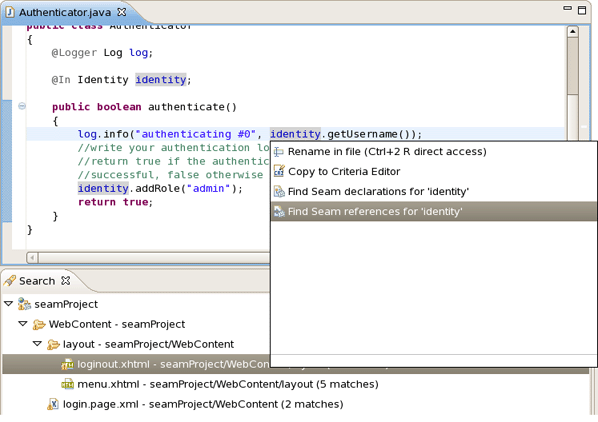
To find EL expretions both in .java and .xhtml files use Find Seam References/Declarations actions. For that, in the main menu bar click on Search > Find Seam References or Find Seam Declarations.
Look at the description of the actions in the table below.
Table 4.2. Find Seam References/Declarations actions
|
Name |
Function |
Keyboard Shortcut |
|---|---|---|
|
Find Seam References Find Seam Declarations |
Find all references and declarations to the selected element. It's available for EL expressions in both .java and .xhtml files. Differs from normal Eclipse Find References/Declarations by showing an EL or Seam references in the Search View. |
Ctrl+G Ctrl+Shift+G also Ctrl + 1 for .java files |
On the screenshot example below you could see that the search results are listed in the Search view.
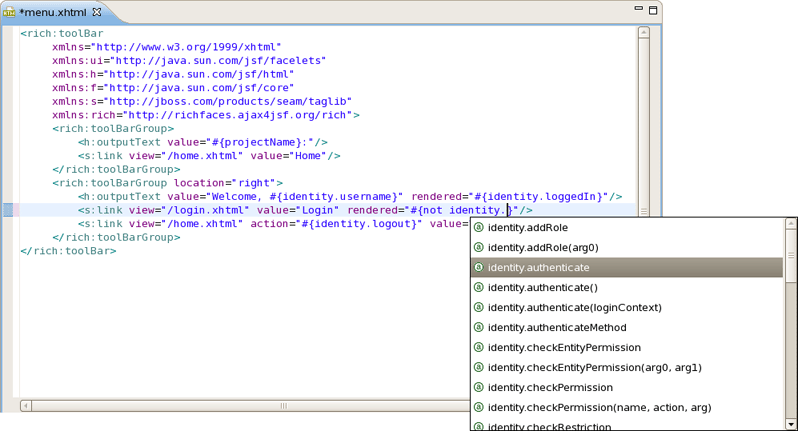
You can also use Ctrl + 1 in .java files to activate the actions:
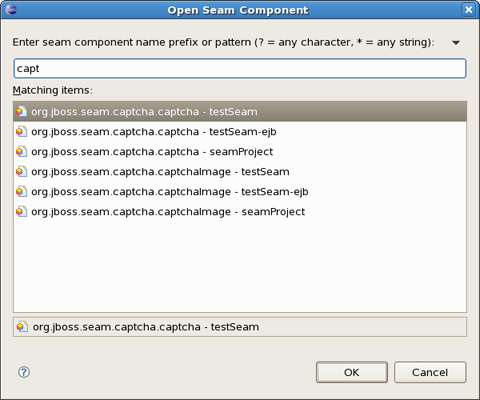
To open Seam Components click on Navigate > Open Seam Component in the main menu bar. This dialog is also available from toolbar icon.
In the table below read a description about the dialog.
Table 4.3. Open Seam Components Dialog
|
Name |
Function |
Keyboard Shortcut |
|---|---|---|
|
Open Seam Components |
Brings up the Open Seam Component dialog to open a component in the editor. The Open Seam Component selection dialog shows all Seam components existing in the workspace. You can search the components via their short, imported or full name. |
Ctrl+Shift+Z |
Enter a name in the text field and see the results as it shown on screenshot:
This chapter introduces you with Seam Components.
All the Seam component generations options known from Seam-gen are available as wizards (with sensible auto-defaulting) for creating various common Seam components:
Seam Action
Seam Form
Seam Entity
Seam Conversation
Go to File > New and select the component wizard.
The wizards create multiple resources and place it in the appropriate folders depending on your project structure (WAR or EAR).
Let's create a WAR project using the New Seam Project wizard.
After the project is created you need deploy it on server.
In this and following sections you can see example creating Seam Components.
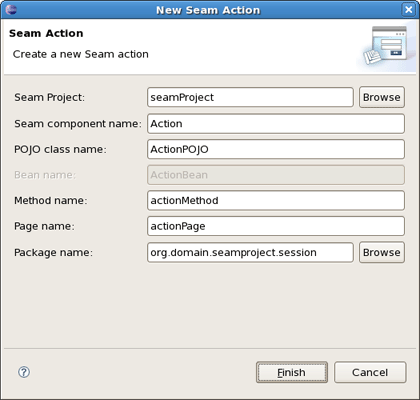
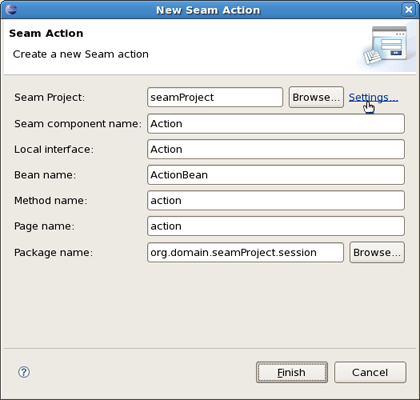
To create a New Seam Action you should select a necessary project, type a name for Seam component, POJO class, Method, Page and select a Package using Browse button.
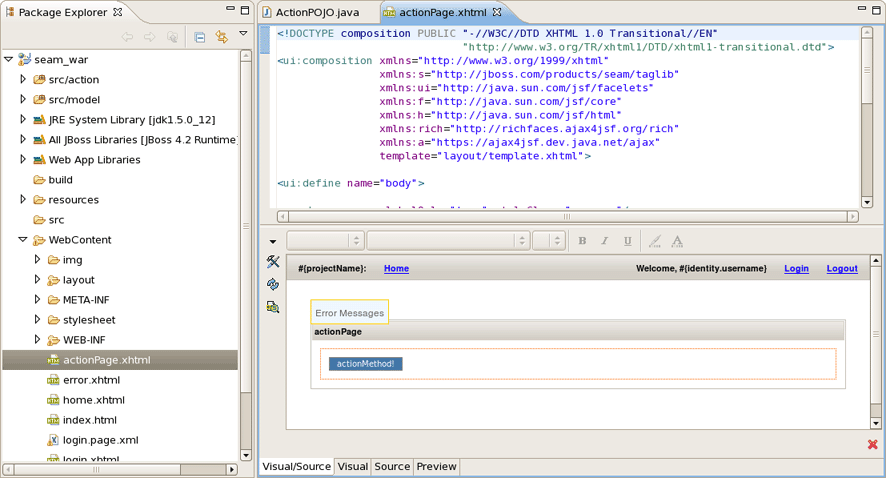
You can see the action page in WebContent folder. Click on it to open in JBoss Tools HTML Editor.
Note:
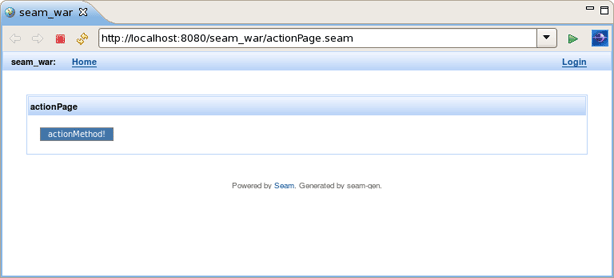
You don't need to restart the server to see how the action component works. Just use context menu Run As > Run On Server.
Action component was hot-deployed. Forms and Conversations will work the same way.
Click on actionMethod in the internal browser and add a form in your project using the New Seam Form wizard File > New > Seam Form.
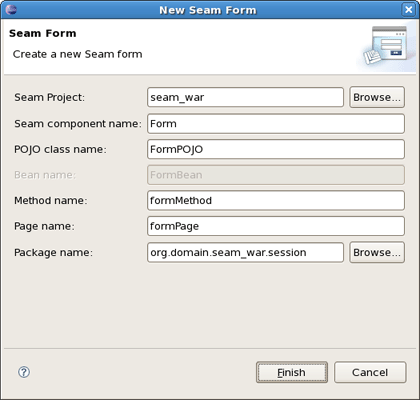
Select a necessary project, type a name for Seam component, POJO class, Method, Page and select a Package using Browse button.
The Form Page was created in WebContent folder.
Deploy the form on server. Right click on Form Page, select Run As > Run On Server.
Form component was hot-deployed.
Enter some value in the text field (e.g. value1) and click on formMethod.
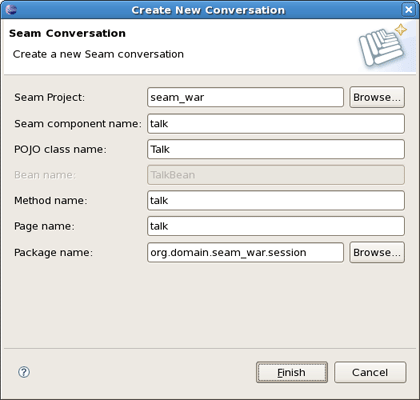
Add a conversation using the New Seam Conversation wizard File > New > Seam Form.
You should select a necessary project, type a name for Seam component, POJO class, Method, Page and select a Package using Browse button.
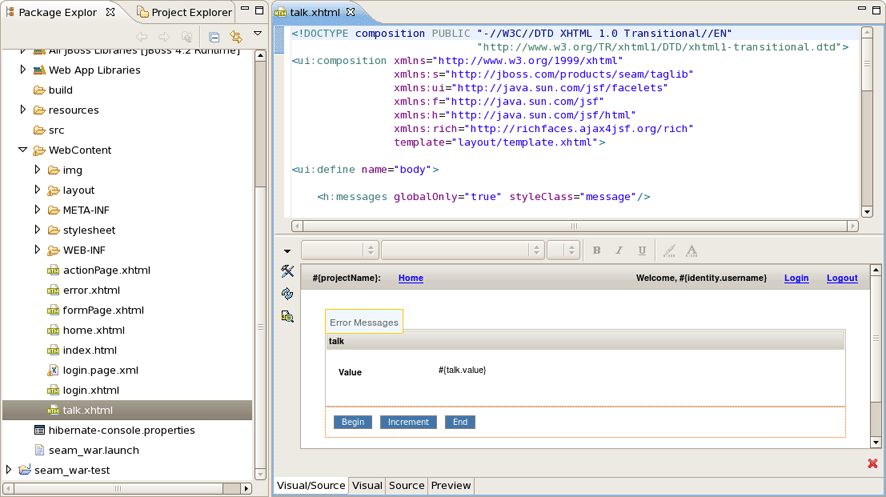
Conversation page was created in WebContent folder.
Right click on Conversation page, select Run As > Run On Server.
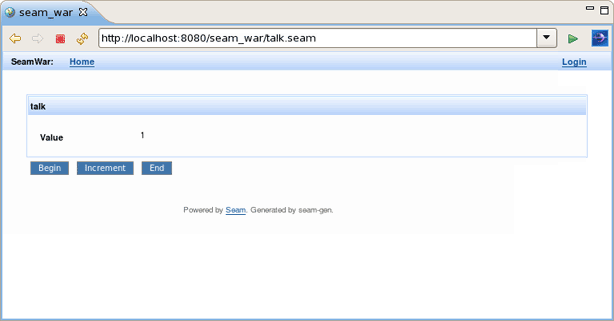
Conversation component was hot-deployed.
Click on Begin and Increment buttons to check the conversation functionality.
Entities cannot be hot-deployed, so we need to stop the server.
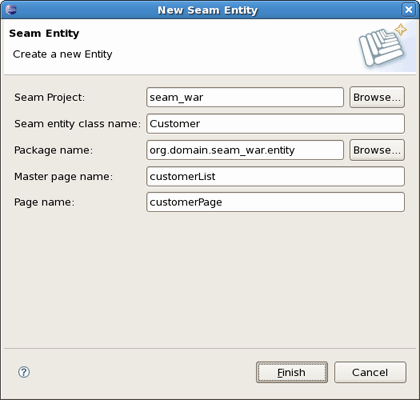
Create an Entity using the New Entity wizard File > New > Seam Entity.
You should select a necessary project, type a name for Entity class, select a Package using Browse button, type a name for Master Page and Page.
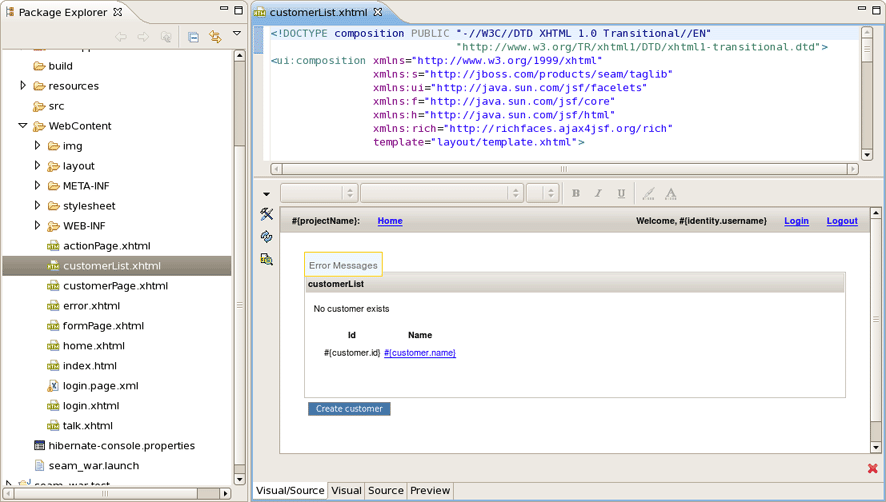
The Master Page and the Entity were created in WebContent folder.
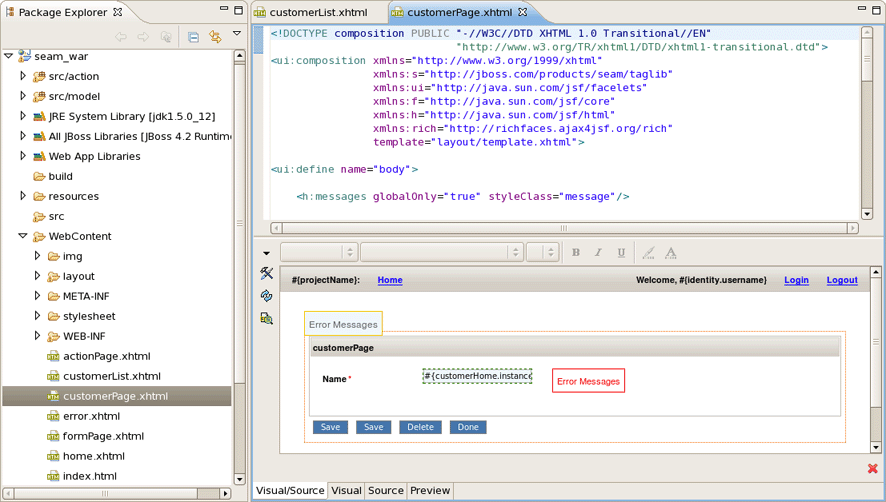
The Entity page is:
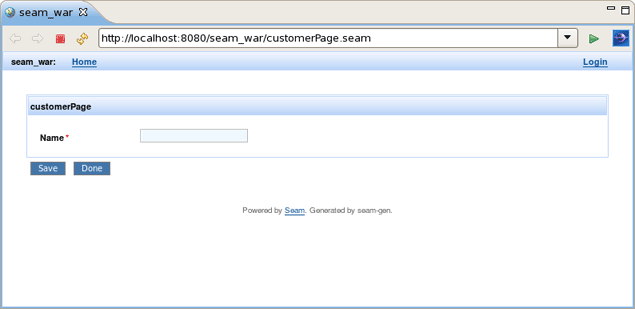
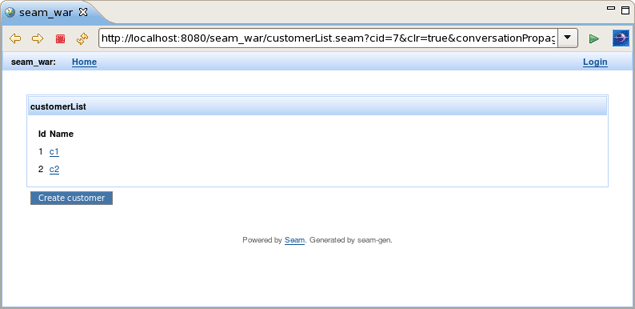
Run the Entity page on server. This is what you get:
Let's create two customers c1 and c2. Enter the name in the text field and press the Save button. Customer should be successfully created. Press Done. Do the same for c2 customer. The result should be:
The main purpose of this chapter is to tell you about Seam Generate Entities.
Generate Entities is available directly from within Eclipse using Hibernate Tools plugin for the standard seam-gen generation.
Generate Entities generates a set of CRUD Seam components and web pages based on existing tables in a database or on existing entities in your application.
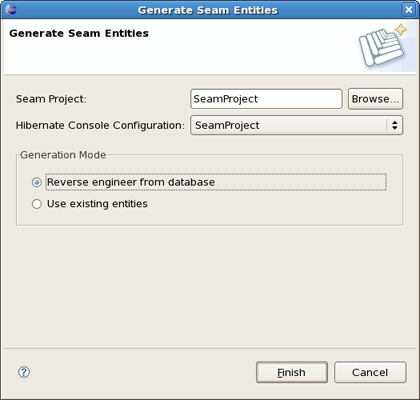
In the Generate Seam Entities wizard there are two generation modes: Reverse Engineer from database and Use existing entities.
The Reverse Engineer from database mode can be described in four steps:
The wizard gets in database, extracts the tables and their connections
On basis of this metainfomation the Entity classes are generated into org.domain.project.entity package
For the entities from step 2 the classes EntityList and EntityHome are generated into org.domain.project.session package
The xhtml pages are generated.
Checking the Use existing entities mode the wizard executes only 3 and 4 steps. It generates missing classes and xhtml pages.
Read the Generate a CRUD Database Application chapter in order to see how the Generate Seam Entities wizard can be used.
In this chapter you know what Seam Editors Features are and how to work with them.
Content Assist (ctrl + space) is available when using expression language in:
JSP
XHTML
XML
JAVA
The Seam components are available in content assist.
Note:
To get Code Assist available for an externally generated and imported project, don't forget to enable Seam features and configure Seam Settings in Project Preferences.
OpenOn let's you easily navigate through your project without using the Package Explorer or Project Explorer. After pressing ctrl + left click (or just F3) you will see a corresponding method or class.
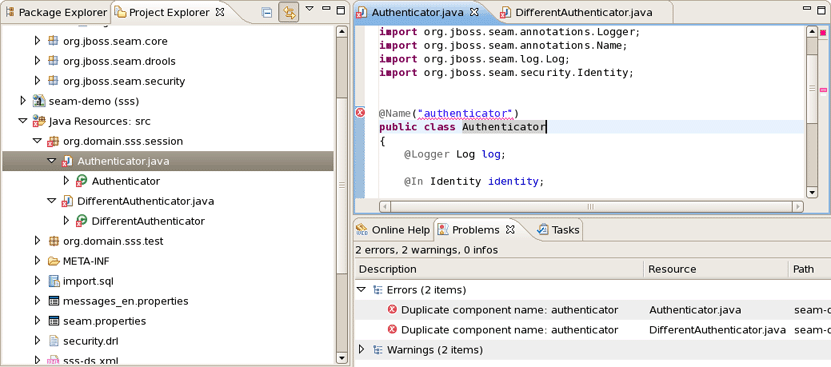
Validation of various possible problematic definitions is implemented for Seam applications.
If an issue is found it will be showed in the standard Problems View.
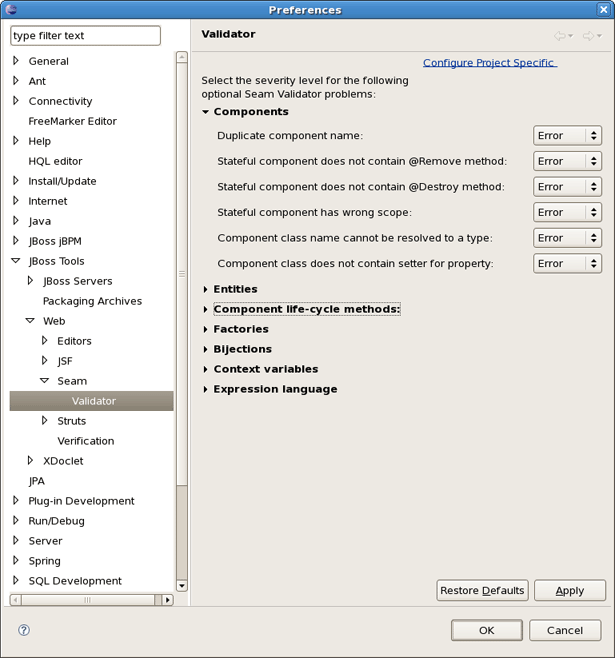
In the preferences page for Seam Validator you can see and modify the validator behavior. Go to Window > Preferences > JBoss Tools > Web > Seam > Validator and select the severity level for the optional Seam Validator problem.
On WTP projects validation are enabled by default and thus executed automatically, but on normal Java projects you will have to go and add the Validation builder to your project . It is available in the properties of your project under Validation. The validations can be run manually by clicking Validate via the context menu on your project which will execute all the active WTP validations.
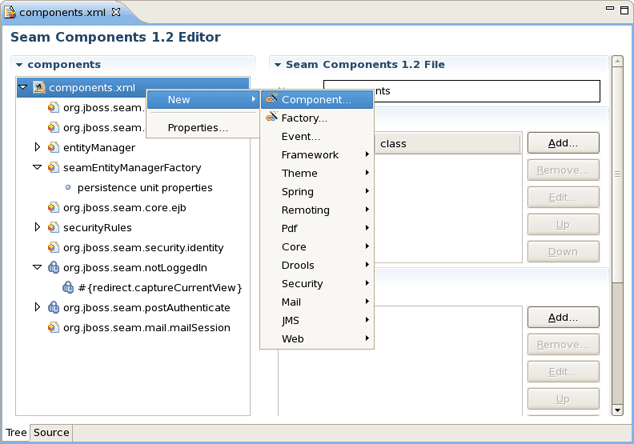
When editing components.xml a structured tree editor is available in addition to pure source editing. It has a graphical view (Tree tab) and source (Source tab).
Note:
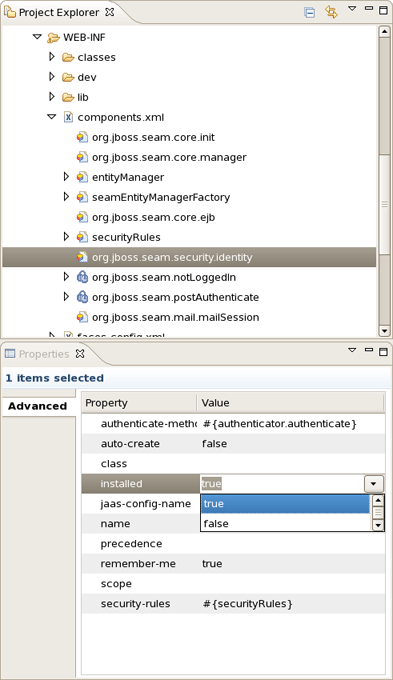
You can view and edit components.xml and other xml files directly in the Project Explorer and Properties sheet without opening the components.xml editor.
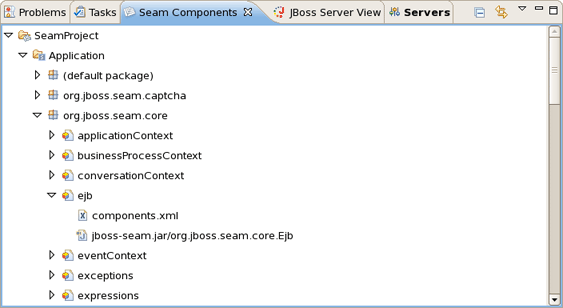
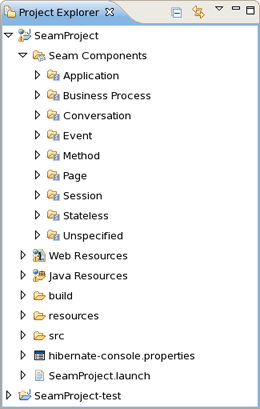
This chapter introduces you with Seam Components View.
The Seam Components View is available from Seam perspective. It provides a list of seam components found in a project.
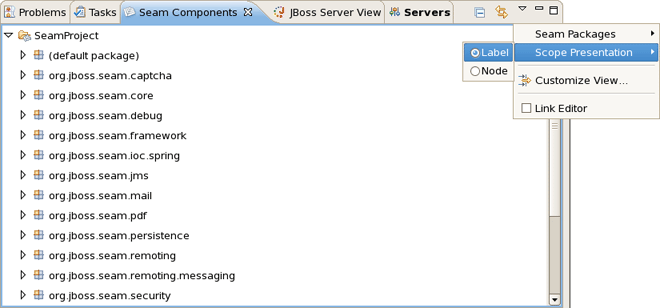
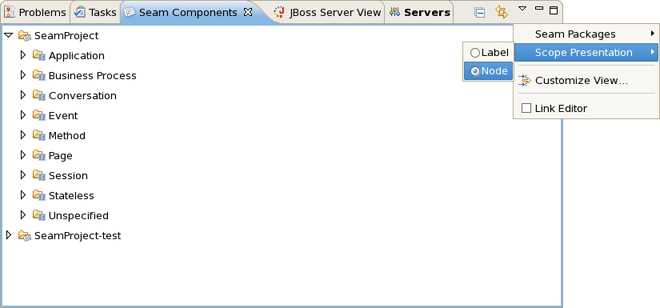
The Seam Components View can show a components default scope in two ways:
as labels on each component (click on the triangular symbol at the top of the Seam Components View page and select Scope Presentation > Label)
as a node per scope where the components are grouped under a node representing its default scope.
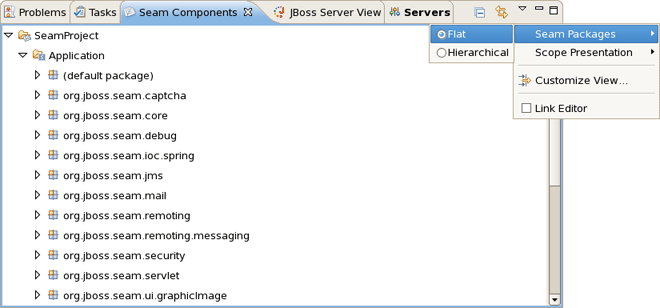
The Seam Packages can be presented in two ways:
Flat
Hierarchical
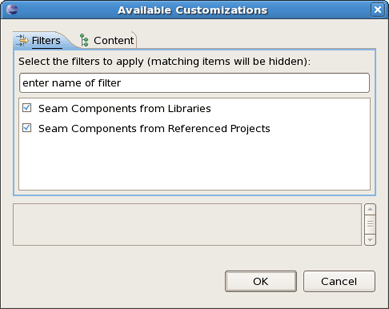
The Seam Component View can be filtered by choosing Customize View.
Select the Seam Components from Libraries under the Filters tab. This will make the view ignore components defined in jars. This will hide the many built-in Seam components and leave only those that are actually defined in the project or have been actively configured via components.xml. Therefore, deselecting the filter will show you all available components.
Selecting the Seam Components from Referenced Projects will hide the components that dependent on other project.
In this chapter you get to know how Seam preferences can be modified during the development process.
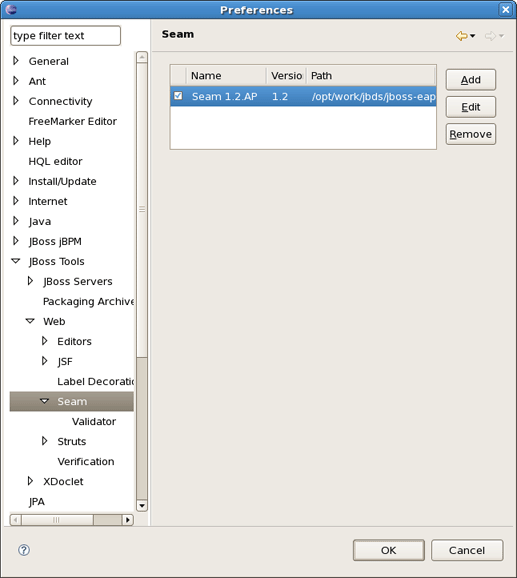
Seam preferences can be set using the Seam preference page. Click on Window > Preferences > JBoss Tools > Web > Seam.
On this page you can manage the Seam Runtime. Use the appropriate buttons to Add more runtimes or to Remove those that are not needed.
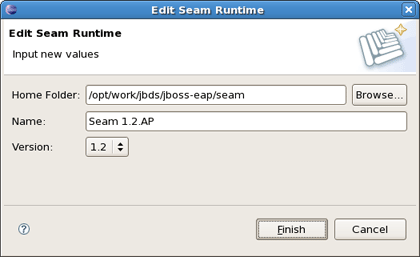
Clicking on Edit button you get the form where you can change the path of Seam runtime home folder, modify name and version. Press Finish to apply the changes.
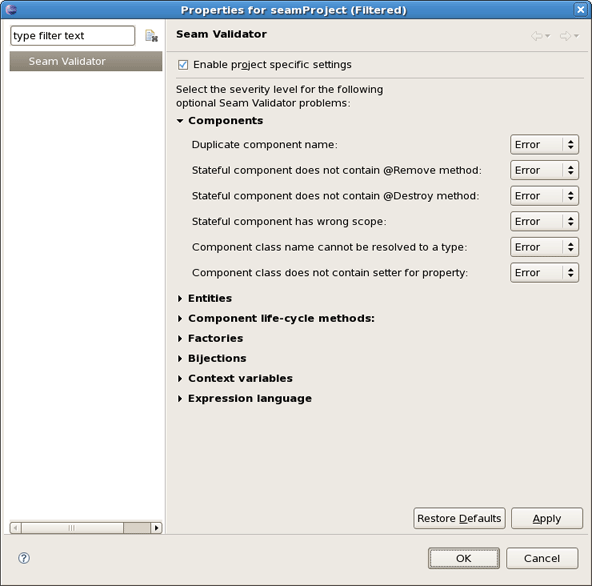
Seam preference page includes a subsection Validator. See Window > Preferences > JBoss Tools > Web > Seam > Validator.
On this page you can choose a severity level for the various Seam validator problems. For example, if you want to ignore the case when component name is duplicated expand the Components node and select Ignore next to Duplicate component name. After that you won't see the error.
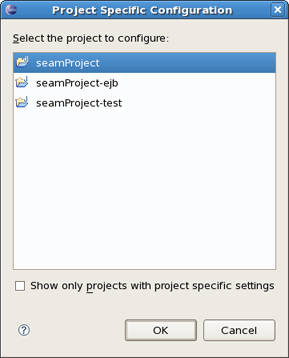
In the upper right corner of the page there is a Configure Project Specific link. Clicking on it you get the form where you can choose a project for specific setting. Project specific configuration allows you to have different validator settings for each project. Check the Show only projects with project specific settings if you want to see the projects that have been already set. Click on Ok.
You get the validator properties page for chosen project. Check the Enable project specific settings to be able to change the settings.
Note:
You can open the same page by right clicking on the needed project in Package Explorer, then Properties > Seam Validator.
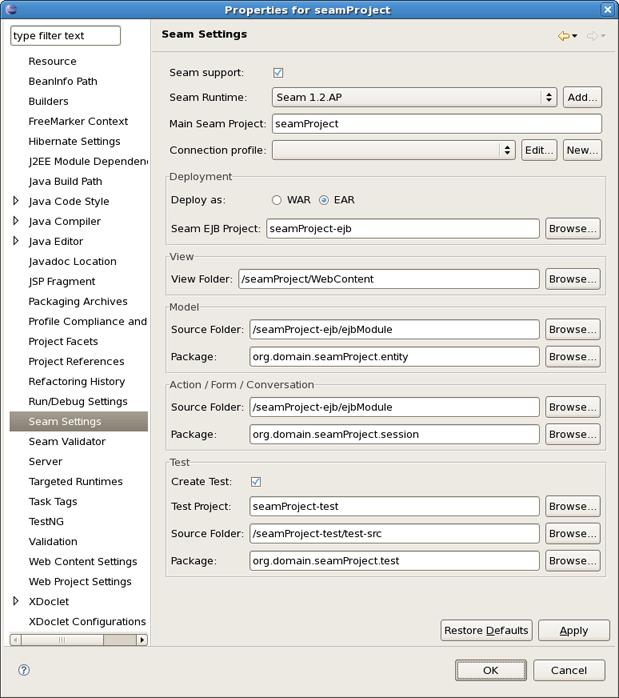
Once Seam project is created you can modify its settings. Right click on Seam project in Project Explorer and select Properties > Seam Settings.
This project properties page allows you to have a flexible project layout. It means that you are not restricted with a specific project structure. You can use the Seam wizards (New Action, Form, Entity, etc.) on Maven, command line seam-gen or your own project structure.
Moreover you are not required to use the Seam New Project wizard to benefit from Seam artifact wizards. You can just enable Seam on your existing project and configure the folders as you want.
Tip:
The wizard doesn't allow the renaming of the artifacts listed in the Seam Settings. It's possible to do in the Package Explorer. See Renaming the Projects and Folders.
In Seam Wizards (New Action, Form, Entity, Conversation, Generate Entities) you can get a quick access to project settings using the Settings link in the upper right corner of each wizard.
CRUD is an acronym for the four basic types of SQL commands: Create , Read , Update , Delete . Most applications have some kind of CRUD functionality, and we can assume that every programmer had to deal with CRUD at some point. A CRUD application is one that uses forms to get data into and out of a database.
In the next section we will create Seam Web application, connect it to the HSQL database and add CRUD support.
First, you should download a database and start it by running ./runDBServer.sh or runDBServer.bat from the database directory.
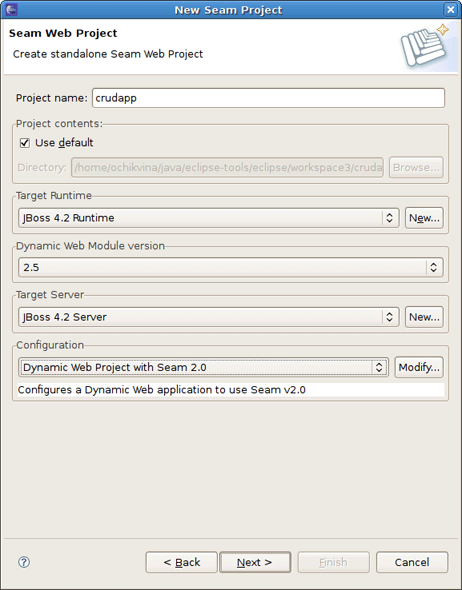
Create a new Seam Web Project using New Seam Project wizard or main menu File > New > Seam Web Project.
Name your project as crudapp, specify Target Runtime, Server and Seam Runtime configuration. Then press Next and follow the next wizard steps keeping default settings.
Tip:
Please have a look here how to create Target Runtime and Seam Runtime in order to get started creating, running, and debugging J2EE applications.
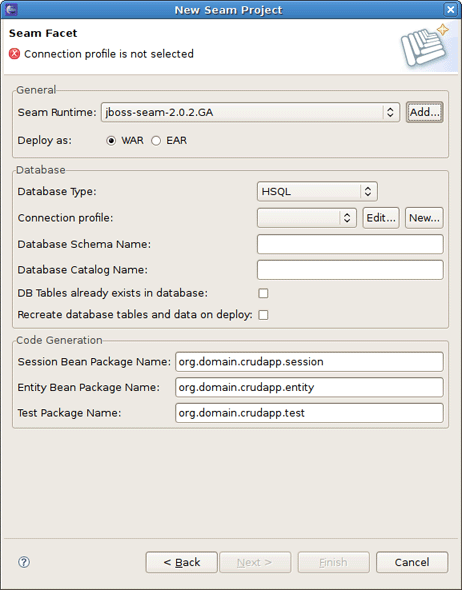
On Seam Facet page click New... next to the Connection profile section to create a new Connection profile.
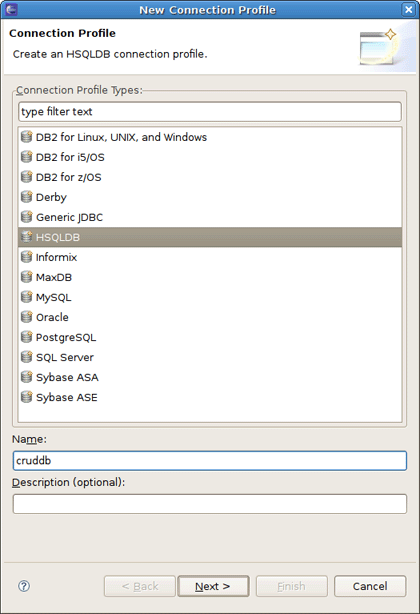
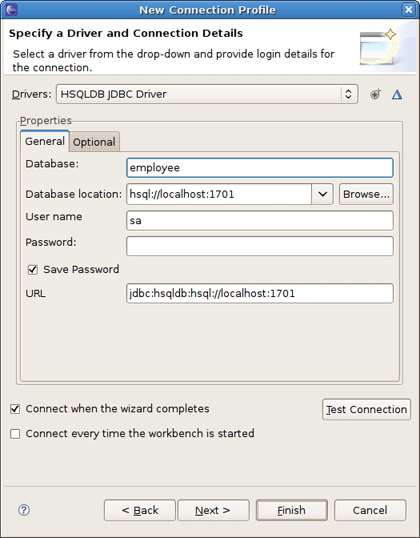
On New Connection Profile dialog select the HSQLDB connection profile type, name it cruddb and click Next.
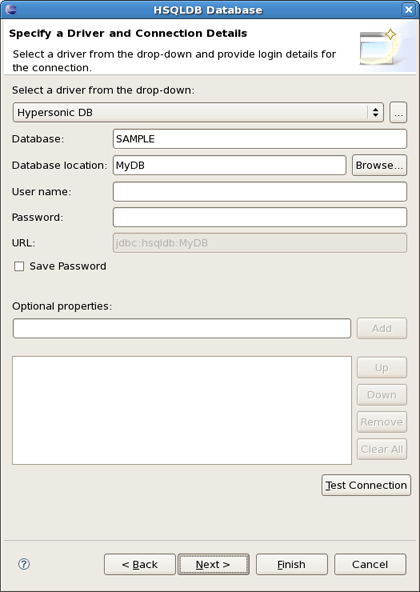
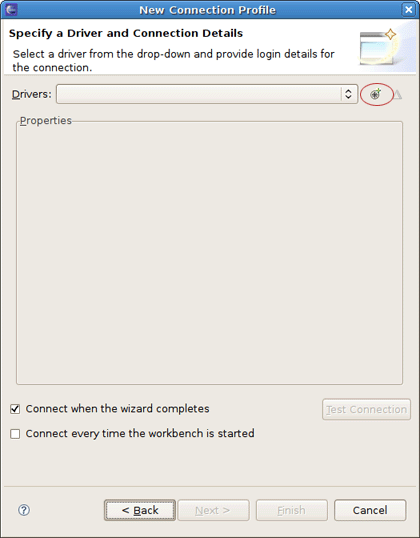
On the next page click the round icon next to the Drivers field to select a database driver.
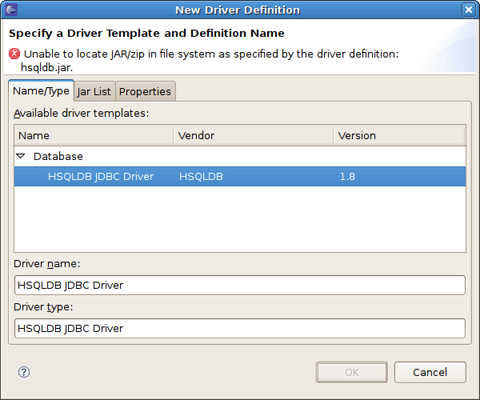
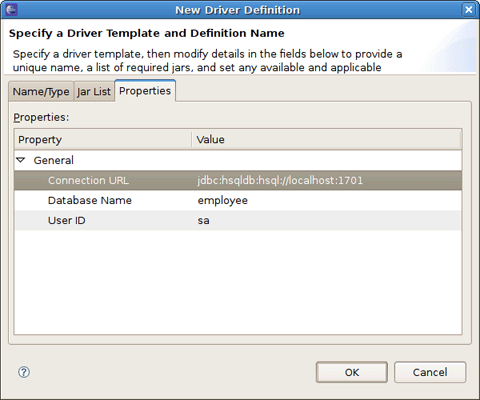
Now you should see the New Driver Definition dialog. On the first tab select the HSQLDB JBDC Driver. Underneath in the Driver name field you can change its name if you need.
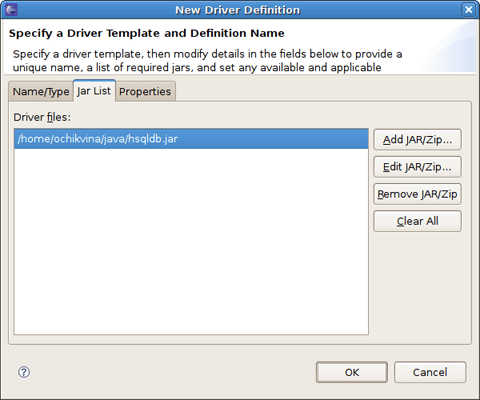
You may notice the note on the previous figure. It prompts that you should specify the driver of the type you pointed. Set the location of the driver by switching to the next tab and press Add JAR/Zip button.
On the Properties tab set the Connection URL, Database Name and User ID and click OK.
After clicking OK to submit the newly created driver you can observe and if you need edit all specified connection details.
Now click Test Connection to be sure that connection can be established.
Validate JDBC Connection profile settings and press Finish or Back if something is wrong.
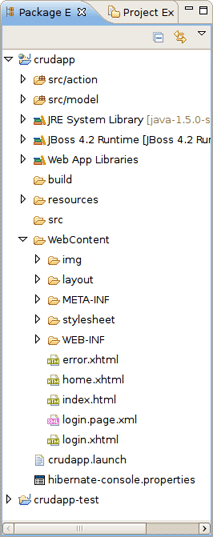
After clicking Finish two projects crudapp and crudapp-test will be created.
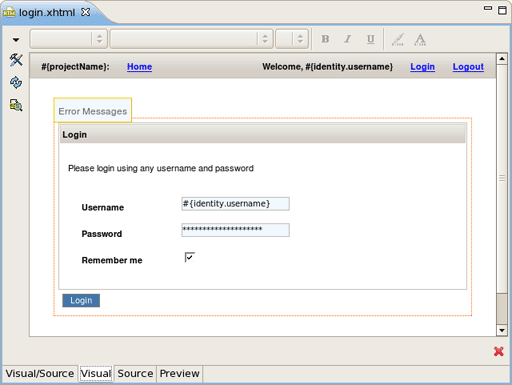
Have a look at the created projects. You can expand WEB_CONTENT folder and open home.xhtml or login.xhtml with JBoss Visual Editor.
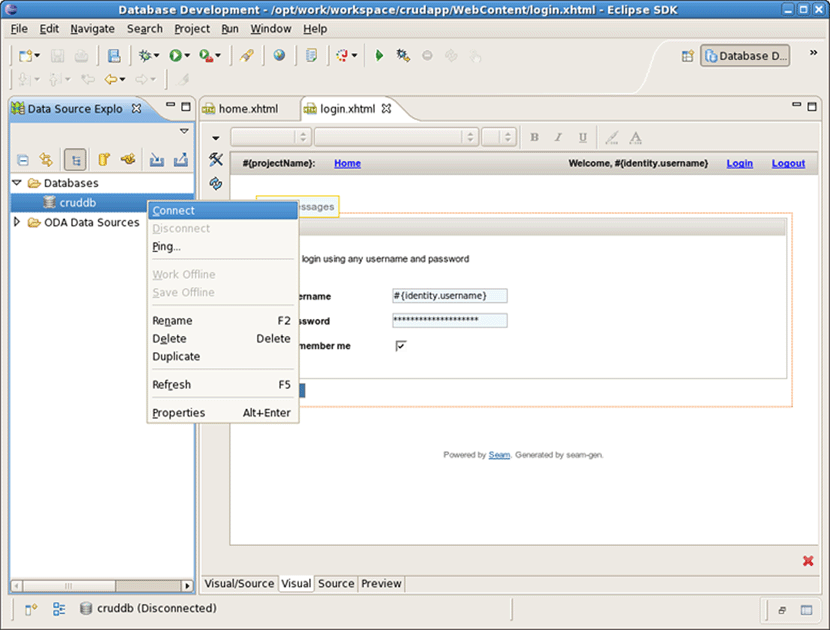
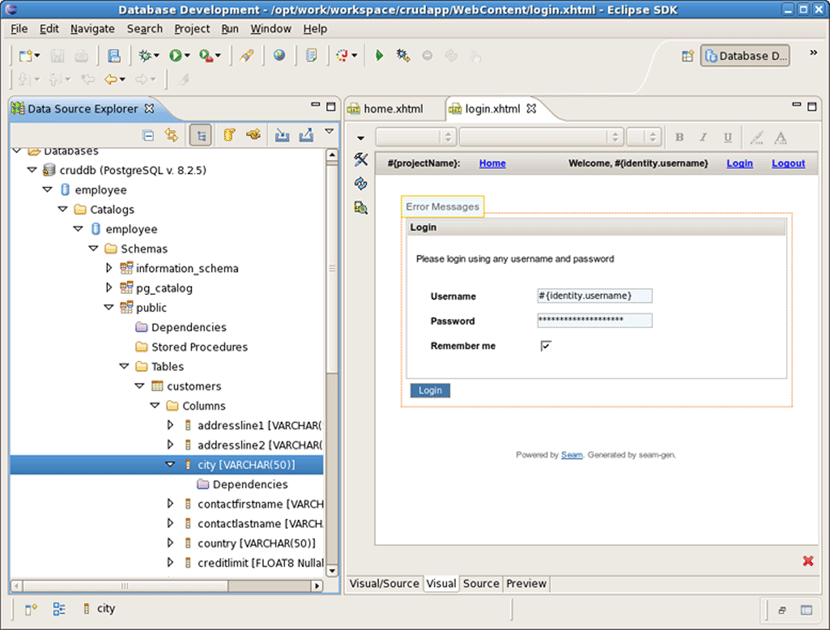
Switch to Database Development perspective with Window->Open Perspective->Other... and connect to the cruddb database.
Expand cruddb nodes to view its Schemas , Tables , Columns etc.
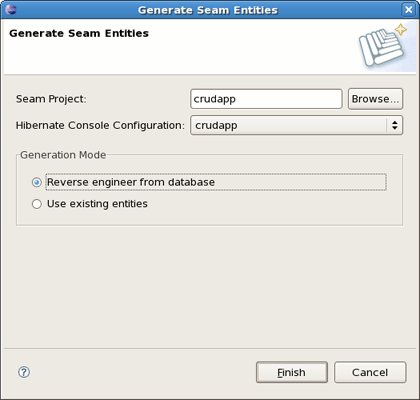
Switch back to the Seam perspective. From the toolbar select New->Seam Generate Entities to create a set of CRUD Seam components and web pages based on existing tables in the database. In the Generate Seam Entities dialog keep everything by default and press Finish .
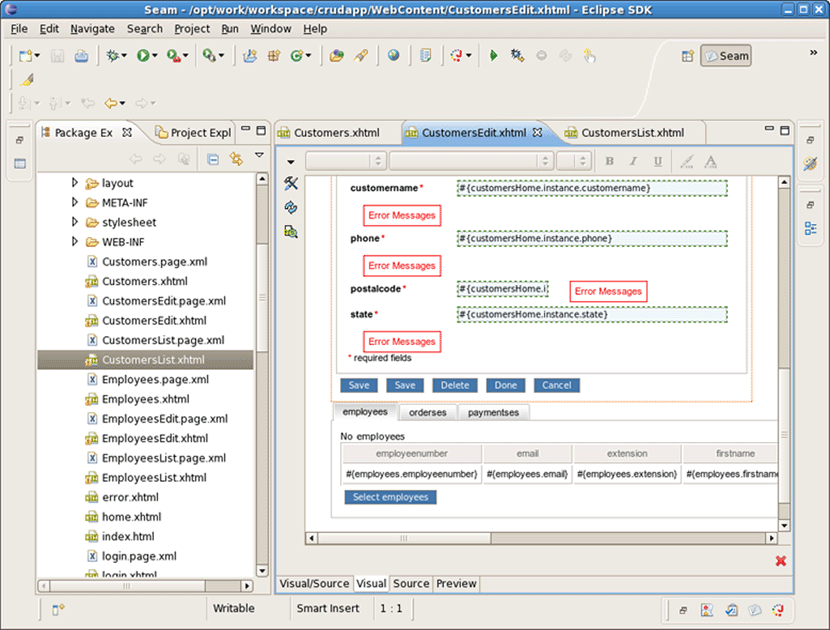
Under WebContent folder you can find a lot of generated xhtml files:
And under src folder java classes are created.
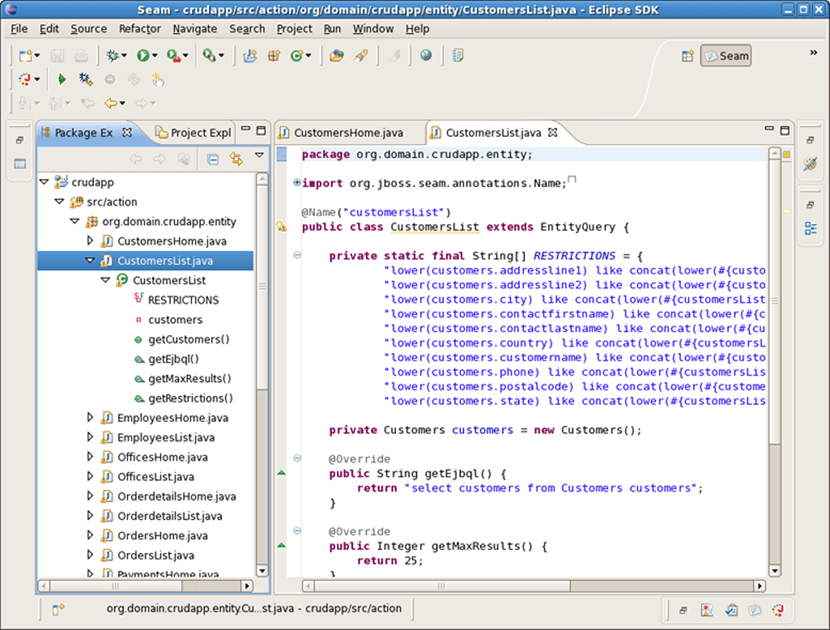
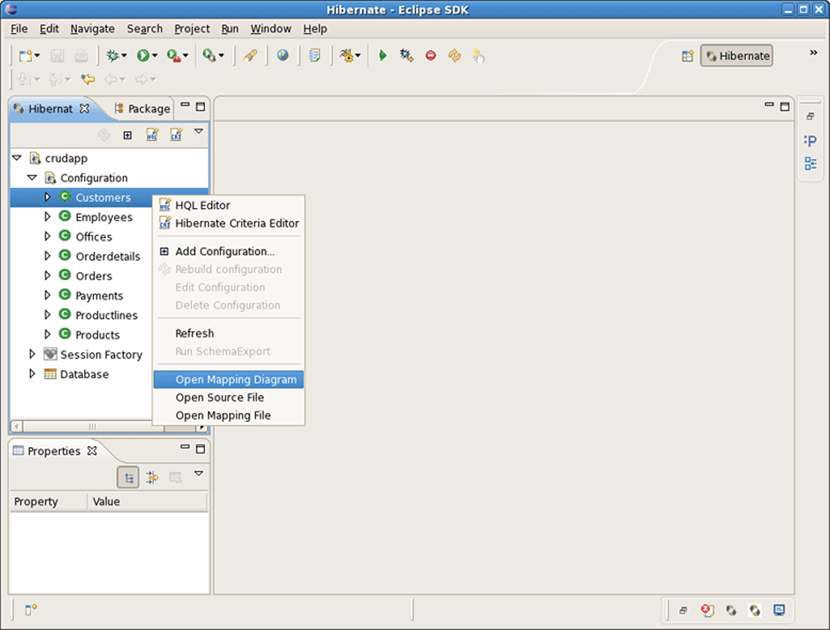
Switch to Hibernate perspective with Window->Open Perspective->Other... . On Hibernate Configurations view expand the crudapp configuration. Right click on Customers and select Open Mapping Diagram from the popup menu.
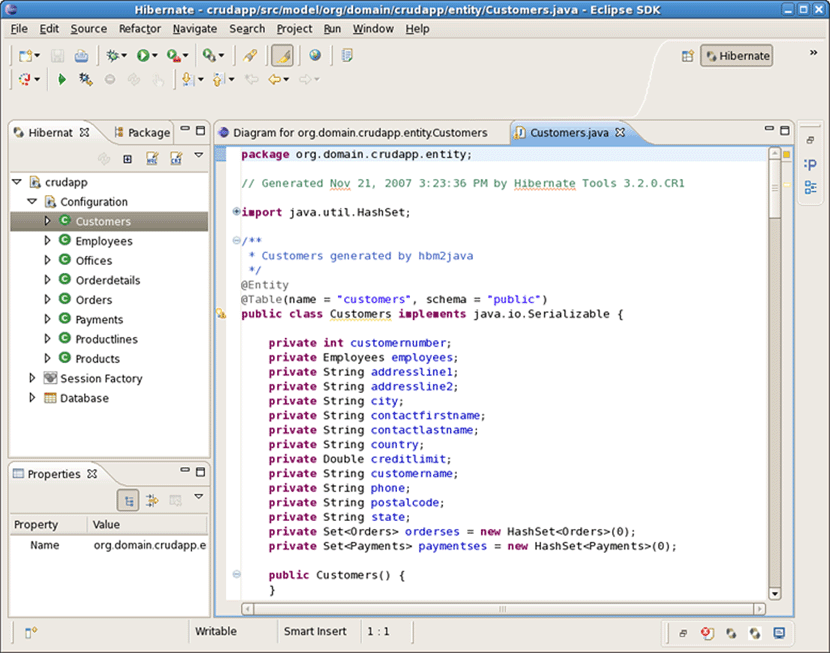
Observe that Mapping Diagram is opened in the editor. Here you can see the relations between models and database tables. Select Customers entity model, right click and select Open Source File .
This will open the Customers.java file in the java editor.
After that you are ready to deploy your application to J2EE application server. This is described in the next chapter.
After you familiarized oneself with example of creating the CRUD Database Application with Seam, you can read this charter.
To run your CRUD Application you should do the following steps:
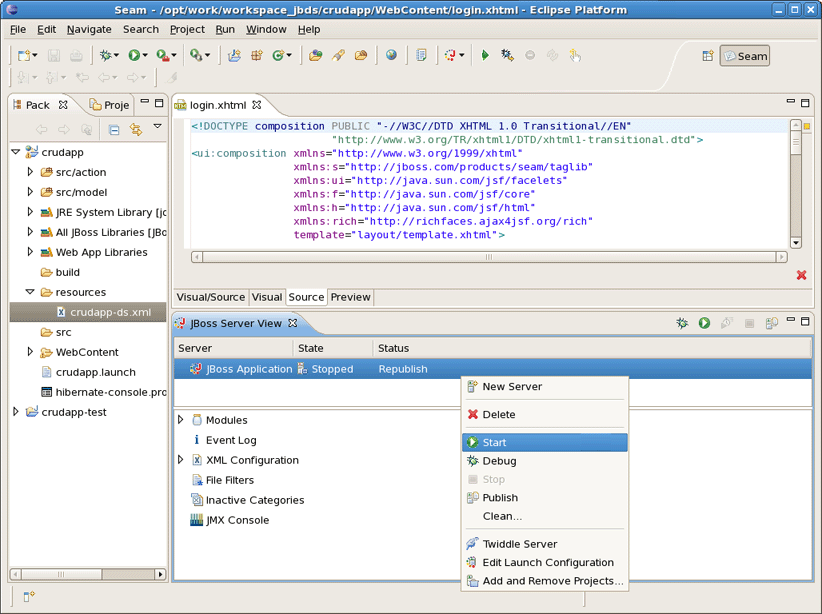
Start JBoss Application Server if it was not started before.
On JBossServer View right click on the JBoss Application Server and select Start
Run a project on the Server.
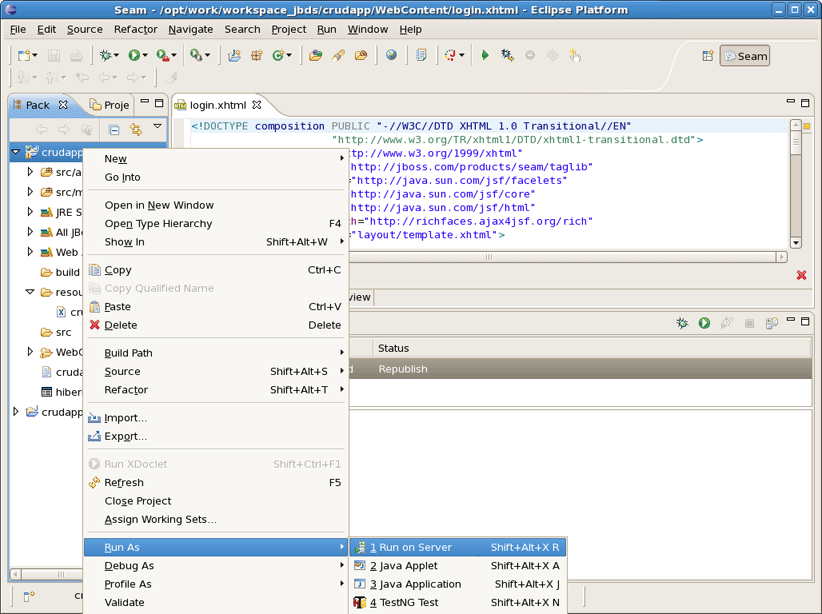
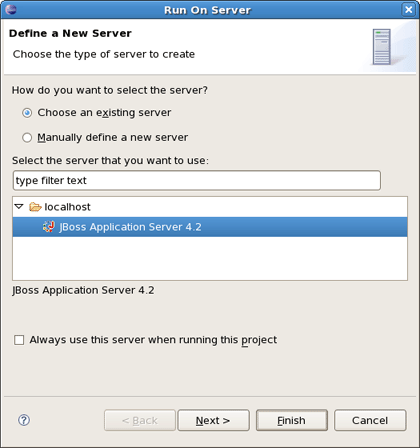
On Package Explorer View right click on the crudapp project, select Run As > Run on Server.
Select a Server and click Finish
Home page of the crudapp project should appear in Web Browser.
After that you can use CRUD application with "employee" database.
You can use internal JBDS Web Browser or your external Web Browser with the same link (http://localhost:8080/crudapp/home.seam).
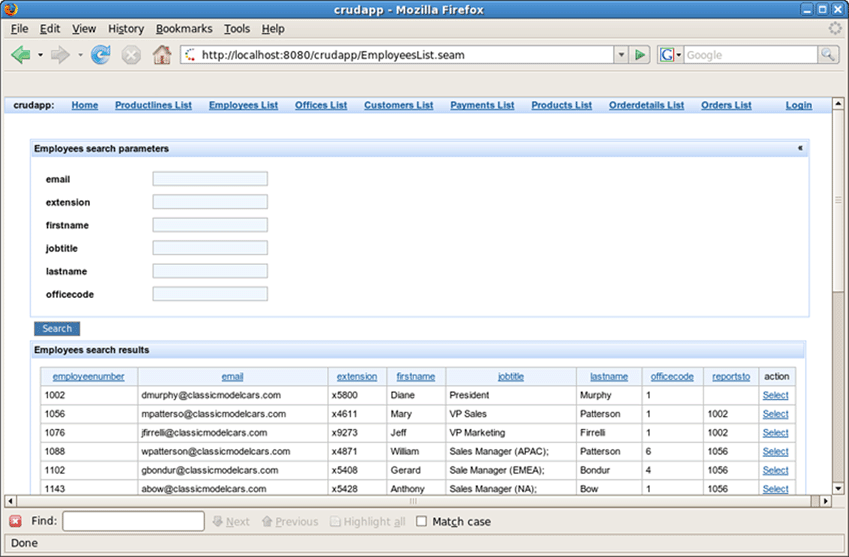
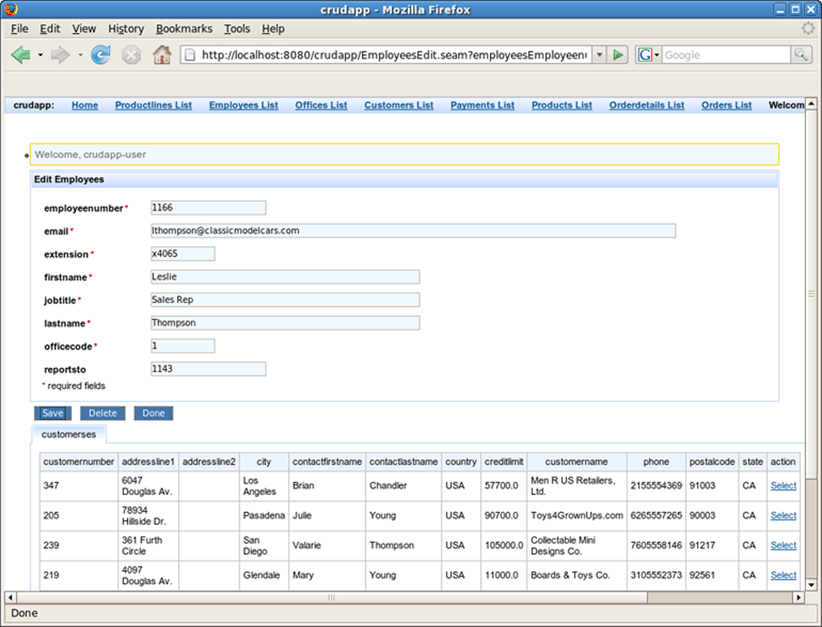
Click on the Employees List link and observe that data from employee database is displayed.
Use Employees search parameters fields to filter the selected list.
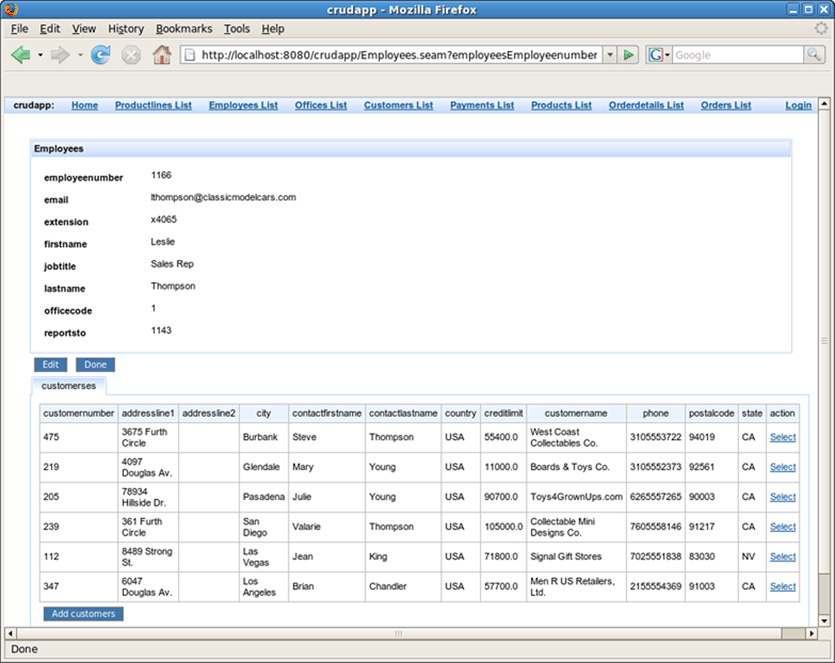
Press Select opposite one of employees.
Press Edit to edit employee fields.
Enter Login and Password to login. (Use "crudapp-user"/"secret" for example)
Fill in firstname and press Update.
Database will be updated.
With the help this chapter you will get to know with TestNG.
TestNG ("Testing, the Next Generation") is a Java unit testing framework that aims to overcome many limitations of JUnit. TestNG introduces some new functionalities that make it more powerful and easier to use, such as:
JDK 5 Annotations (JDK 1.4 is also supported with JavaDoc annotations)
Flexible test configuration
Support for data-driven testing (with @DataProvider)
Support for parameters
Allows distribution of tests on slave machines
Powerful execution model (no more TestSuite)
Supported by a variety of tools and plug-ins (Eclipse, IDEA, Maven, etc...)
Embeds BeanShell for further flexibility
Default JDK functions for runtime and logging (no dependencies)
Dependent methods for application server testing
More information can be found on home page: www.testng.org
Next-Generation Testing with TestNG (An Interview with Cedric Beust)
TestNG: The next generation of unit testing
Test Categorization Techniques with TestNG
Create a new Seam Web Project with EAR deployment using the New Seam Project wizard.
After a project is created you will have the generated Seam-test project that is setup to run TestNG directly against the proper libraries and server runtime libraries.
Add Seam Action to your project via File > New > Seam Action.
Fill out the wizard fields. New Seam Action wizard will create resources and place them in the appropriate folders dependent on EAR project structure.
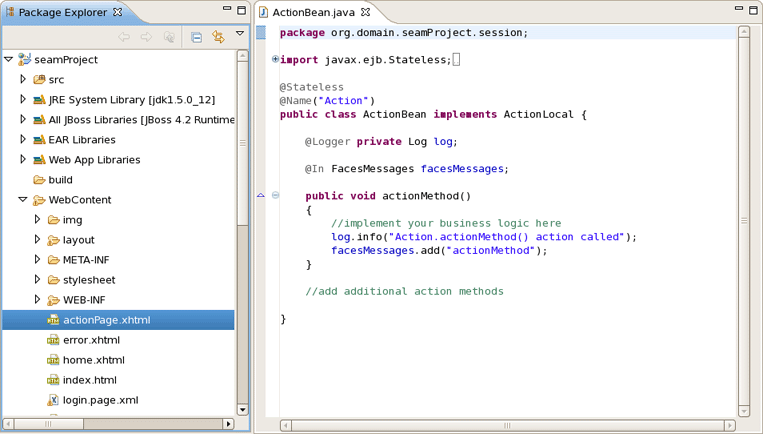
When Action is created you will see actionPage.xhtml in Package Explorer view. ActionBean.java will be automatically opened in Java Editor.
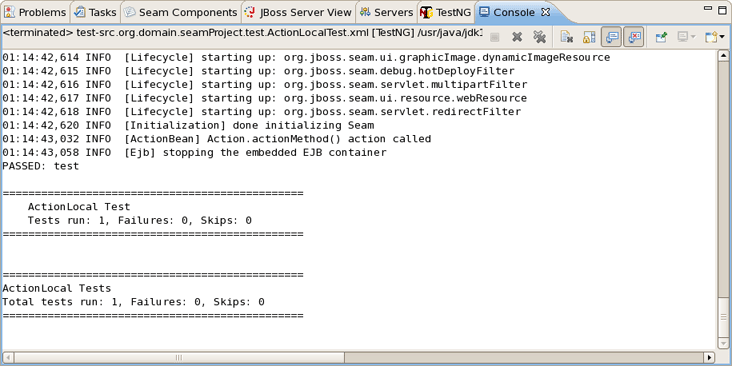
Select ActionLocalTest.xml in Seam-test project and run the test with right click Run As > TestNG Suite.
The test process will start and its output will be written in Console View.
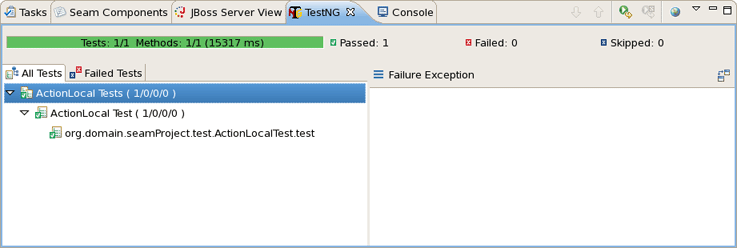
After running TestNG you will have the test results in test-output folder in Seam-test project (press F5 to refresh the Package Explorer view). Open index.html file with Web Browser or simply use the TestNG view.
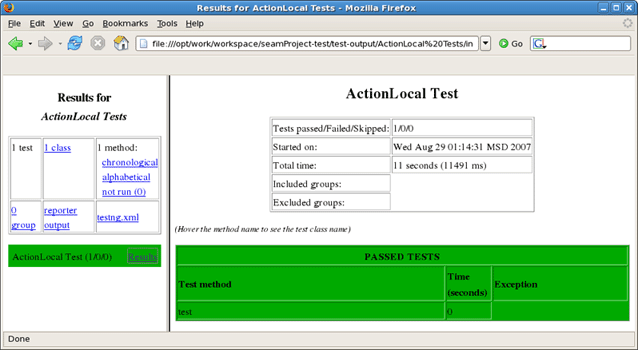
The below view shows a successful run of the test.
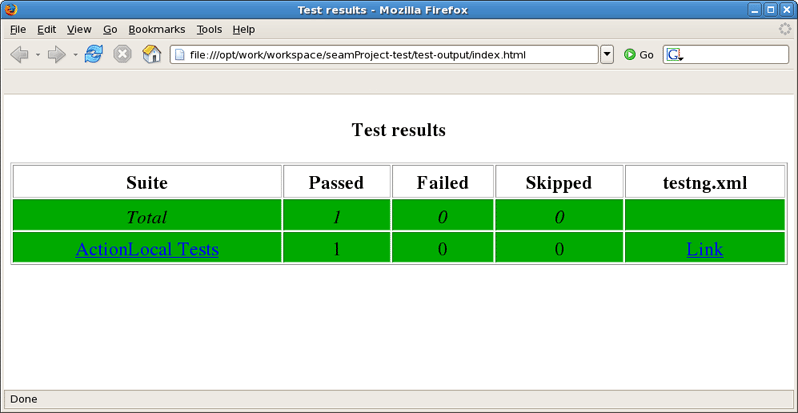
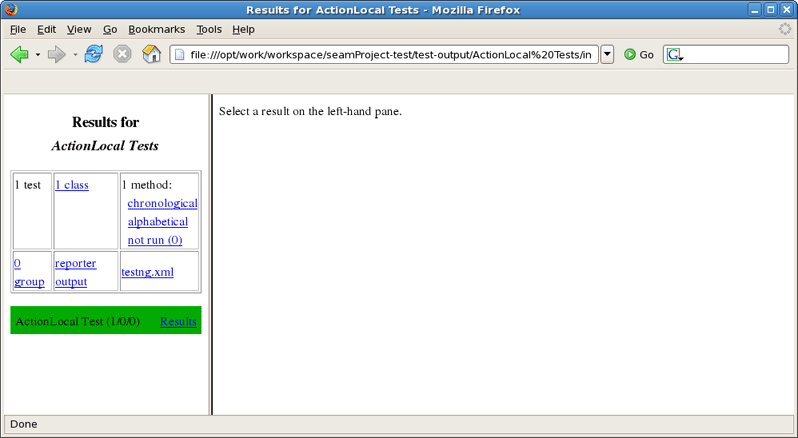
You can see the test results in Web Browser.
After clicking on ActionLocal Tests link you will see the Results for ActionLocal Tests.
Select a result on the left-hand pane and its details will be displayed on the right-hand one.
Thus with Seam tooling you can easily take advantage of TestNG framework. As you can see, it generates its own TestNG project as a separate module within which you can easily monitor the tests execution and their output.
In conclusion, the main goal of this document is to get you know with a full featureset that JBoss Tools provides to support Seam development. Thus if you have some questions, comments or suggestions on the topic, please fell free to ask in the JBoss Tools Forum. You can also influence on how you want to see JBoss Tools docs in future leaving your vote on our page here.
A set of movies on Seam tooling is available here.