In this chapter we'll focus more on how to operate the JBoss AS from JBoss Developer Studio.
JBoss Developer Studio ships with JBoss EAP v.4.2 bundled. When you followed the default installation of JBoss Developer Studio, you should already have a JBoss 4.2 server installed and defined. To run JBoss AS 4.2 you need JDK 1.5, JDK 6 is not formally supported yet, although you may be able to start the server with it.
This section covers the basics of working with the JBoss server supported directly by JBDS via bundled AS plug-in. To read more about AS plug-in, read Server Manager guide.
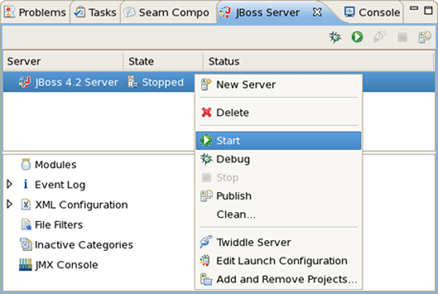
Starting JBoss server is quite simple. JBoss Developer Studio allows you to control its behaviour with the help of a special toolbar: where you could start it in a regular or debug mode, stop it or restart it.
To launch the server click the green-with-white-arrow icon on the JBoss Server View or right click server name in this view and select Start. If this view is not open, select Window > Show View > Other > Server > JBoss Server View
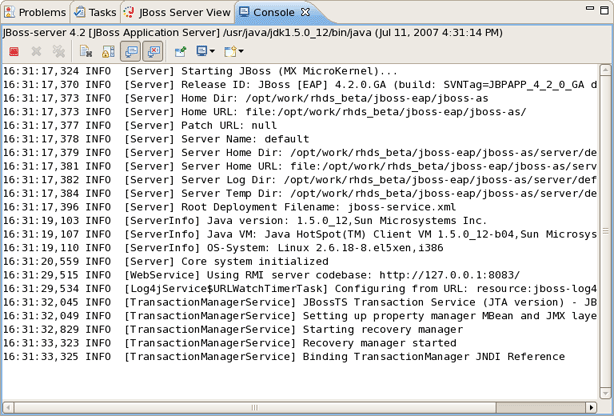
While launching, server output is written to the Console view:
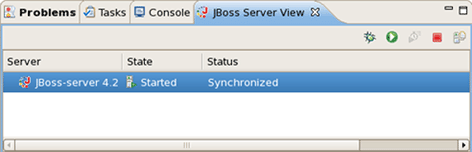
When the server is started you should see Started right to its name in JBoss Server View (column "Status").
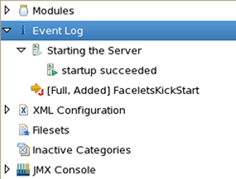
To see event log after the server is started, expand Event Log branch beneath JBoss Server View:
To stop the server, click the Stop icon in JBoss Server View or right click the server name and press Stop.
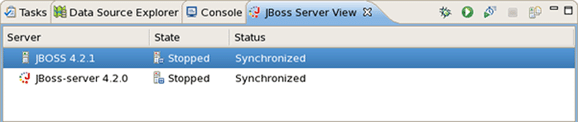
When the server is stopped you will see Stopped next to its name in the Status column.
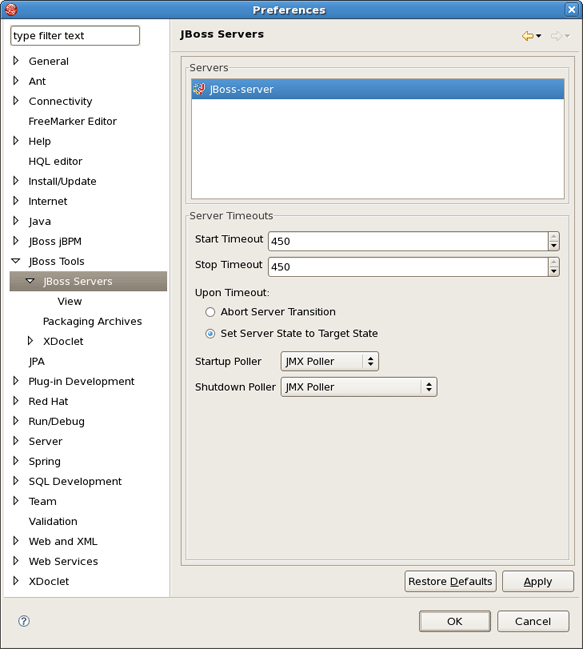
You can control how JBoss Developer Studio interacts with servlet containers in Preferences. Select Window > Preferences > JBoss Tools > JBoss Servers and switch to the desired server:
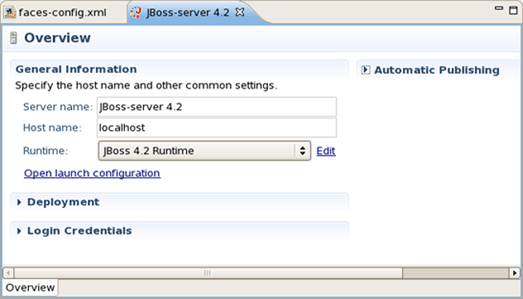
Also you can double click the server name in JBoss Server View and open an overview of the server. Here you can specify some common settings: host name, server name, runtime and so on.
Although JBoss Developer Studio works closely with JBoss EAP 4.2 we do not ultimately tie you to any particular server for deployment. There are some servers that Studio supports directly (via the bundled Eclipse WTP plug-ins). In this section we discuss how to manage self-installed JBoss AS. Suppose you want to deploy the application to JBoss 4.2.1 server. First of all you need to install it.
Download the binary package of JBoss 4.2.1 and save it on your computer: http://labs.jboss.com/jbossas/downloads
It does not matter where on your system you install JBoss server.
Note:
The installation of JBoss server into a directory that has a name containing spaces provokes problems in some situations with Sun-based VMs. Try to avoid using installation folders that have spaces in their names.
There is no requirement for root access to run JBoss Server on UNIX/Linux systems because none of the default ports are within the 0-1023 privileged port range.
After you have the binary archive you want to install, use the JDK jar tool (or any other ZIP extraction tool) to extract the jboss-4.2.1.zip archive contents into a location of your choice. The jboss-4.2.1.tgz archive is a gzipped tar file that requires a gnutar compatible tar which can handle the long pathnames in the archive. The extraction process will create a jboss-4.2.1 directory.
Now we should add just installed server into server manager in JBoss Developer Studio.
Open the JBoss Server View by selecting Window > Show View > Other > Server > JBoss Server View. You will see JBoss Server view.
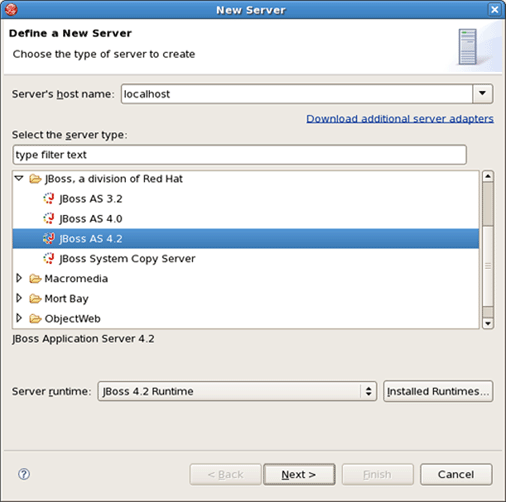
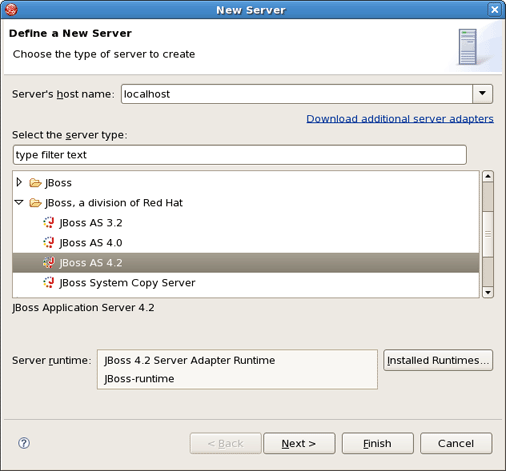
Right click anywhere in this view and select New Server.
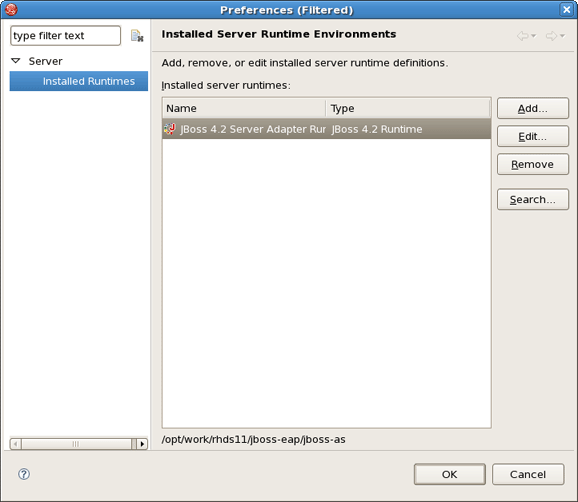
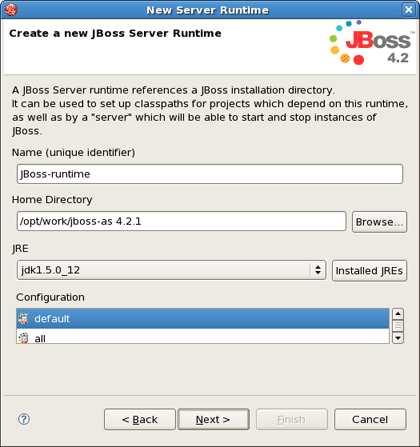
Select JBoss, a division of Red Hat > JBoss v4.2 and click the Installed Runtimes button to select a new installed runtime.
Click Add button to add a new jboss runtime.
Select JBoss, a division of Red Hat > JBoss v4.2 and press Next.
In the next step make JBoss Developer Studio to know where you have installed the server and define JRE.
Note:
When adding a new server you will need to specify what JRE to use. It is important to set this value to a full JDK, not JRE. Again, you need a full JDK to run Web applications, JRE will not be enough.
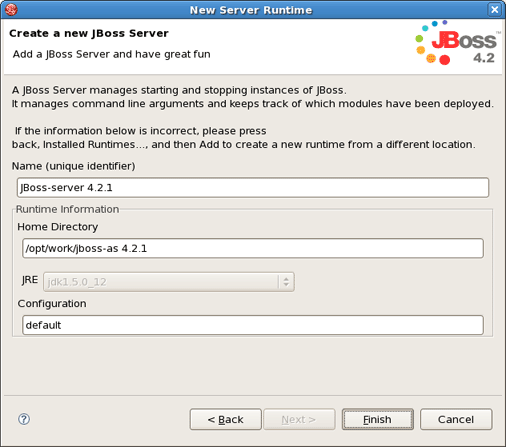
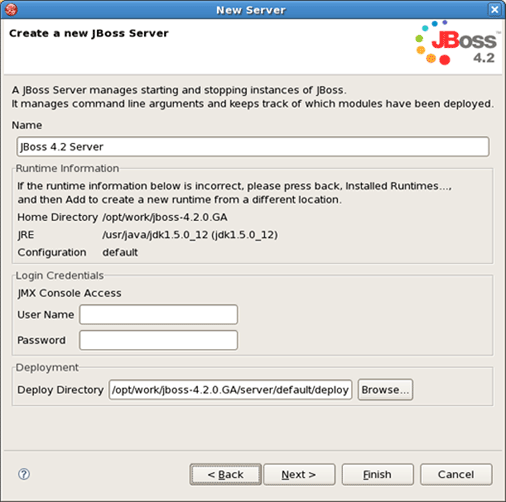
In the following window leave all settings default or give your name to a new jboss server and press Finish.
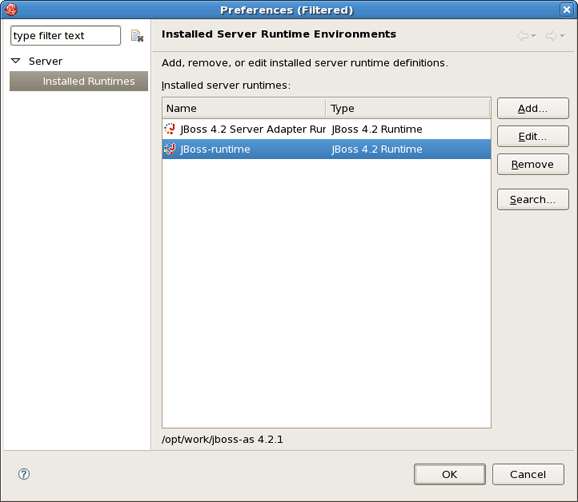
A new runtime will now appear in the Preferences > Server > Installed Runtimes dialog.
Click OK. Then select a new added runtime in Server runtime drop down list and click Next button twice.
In the next dialog verify a JBoss runtime information and if something is unfair go back and correct it.
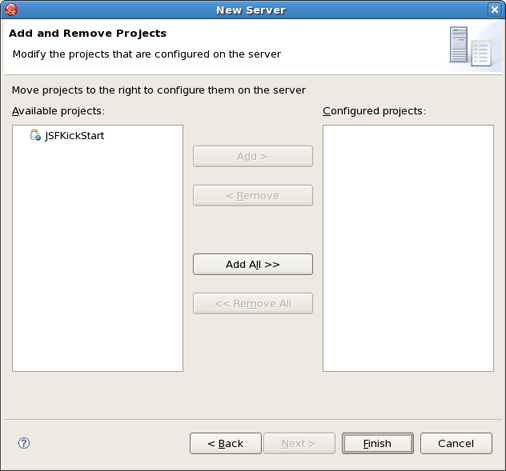
In the last wizard's dialog modify the projects that are configured on the server and click Finish.
A new JBoss server should now appear in JBoss Server View.
Now, we are ready to create the first web application.